|
Listoghil
Listoghil () is the large central monument in the Carrowmore group of prehistoric tombs in County Sligo in Ireland. It was numbered as ''Carrowmore 51'' by George Petrie in 1837 and this designation is still used. Although the district of Cuil Irra is steeped in legend, Listoghil has never been satisfactorily connected with the ancient legends in the way that say Newgrange has. It is the only cairn in Carrowmore. Antiquarians in the 19th century made references to another cairn nearby at Leacharail, but the site of this has never been located. Etymology According to Petrie (Letter to Larcom, Aug. 1837), the name may mean 'Ryefort' (it appears as Lios a' tSeagail, seagail meaning rye in Irish, in early maps). However ''lios'' in Irish refers generally to a court or enclosed area, so it may be that the name originally referred to the area enclosed by the dolmens, on which Listoghil stands, rather than the cairn itself. Location Listoghil stands 59m above sea level at the geograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
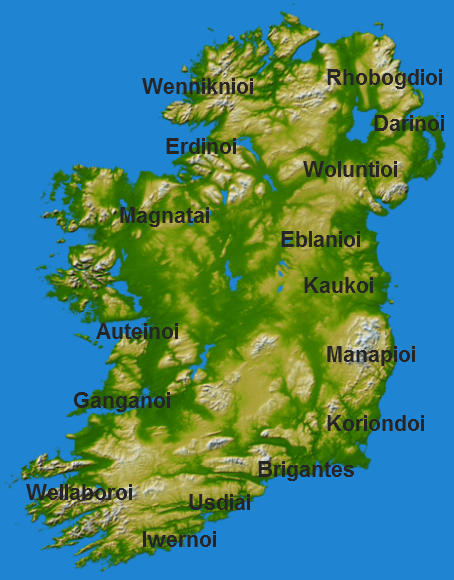
Carrowmore
Carrowmore ( ga, An Cheathrú Mhór, 'the great quarter') is a large group of megalithic monuments on the Coolera Peninsula to the west of Sligo, Ireland. They were built in the 4th millennium BC, during the Neolithic (New Stone Age). There are thirty surviving tombs, making Carrowmore one of the largest clusters of megalithic tombs in Ireland, and one of the 'big four' along with Carrowkeel, Loughcrew and Brú na Bóinne. Carrowmore is the heart of an ancient ritual landscape which is dominated by the mountain of Knocknarea to the west. It is a protected National Monument. Location Placed on a small plateau at an altitude of between 36.5 and 59 metres above sea level Carrowmore is the focal point of a prehistoric ritual landscape which is dominated by the mountain of Knocknarea to the west with the great cairn of Miosgán Médhbh on top. To the east, in Carns townland, two large cairns overlook Lough Gill, and along the eastern boundary of the peninsula the Ballygawley M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knocknarea
Knocknarea (; ) is a large prominent hill west of Sligo town in County Sligo, Ireland, with a height of . Knocknarea is visually striking as it has steep limestone cliffs and stands on the Cúil Irra peninsula overlooking the Atlantic coast. At the summit is one of Ireland's largest cairns, known as Queen Maeve's Cairn, which is believed to contain a Neolithic passage tomb. In recent years there has been concern that the ancient cairn, a protected National Monument, is being damaged by climbers. There are also remains of several smaller tombs on the summit. Knocknarea overlooks the Carrowmore tombs and is thought to have been part of an ancient ritual landscape. Name Knocknarea is an anglicization of an Irish name. "Knock" means hill, but the etymology of the rest of the name is disputed. The Placenames Database of Ireland gives the Irish name as ''Cnoc na Riabh'' (meaning "hill of the stripes"). However, P.W. Joyce preferred the interpretation ''Cnoc na Riaghadh'' ("hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Public Works
The Office of Public Works (OPW) ( ga, Oifig na nOibreacha Poiblí) (legally the Commissioners of Public Works in Ireland) is a major Irish Government agency, which manages most of the Irish State's property portfolio, including hundreds of owned and rented Government offices and police properties, oversees National Monuments and directly manages some heritage properties, and is the lead State engineering agency, with a special focus on flood risk management. It lies within the remit of the Minister for Public Expenditure and Reform, with functions largely delegated to a Minister of State at the Department of Public Expenditure and Reform with special responsibility for the Office. The OPW has a central role in driving the Government's property asset management reform process, both in respect of its own portfolio and that of the wider public service. The agency was initially known as Board of Works, a title inherited from a preceding body, and this term is still sometimes en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In County Sligo
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Of Tara
The Hill of Tara ( ga, Teamhair or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial and burial site near Skryne in County Meath, Ireland. Tradition identifies the hill as the inauguration place and seat of the High Kings of Ireland; it also appears in Irish mythology. Tara consists of numerous monuments and earthworks—dating from the Neolithic to the Iron Age—including a passage tomb (the "Mound of the Hostages"), burial mounds, round enclosures, a standing stone (believed to be the '' Lia Fáil'' or "Stone of Destiny"), and a ceremonial avenue. There is also a church and graveyard on the hill. Tara forms part of a larger ancient landscape and Tara itself is a protected national monument under the care of the Office of Public Works, an agency of the Irish Government. Name The name ''Tara'' is an anglicization of the Irish name or ('hill of Tara'). It is also known as ('Tara of the kings'), and formerly also ('the grey ridge'). The Old Irish form is . It is believed this co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mound Of The Hostages
The Mound of the Hostages () is an ancient passage tomb located in the Tara-Skryne Valley in County Meath, Leinster, Ireland. The mound is a Neolithic structure, built between 3350 and 2800 BCE.http://spartanideas.msu.edu/2015/01/27/reuse-of-cemeteries-in-prehistoric-ireland/ Michigan State University - Reuse of Cemeteries in Prehistoric Ireland It is circular in form, roughly fifteen metres in diameter and three metres high. It is built in the same style as the Newgrange tomb. The structure is dome-shaped with an inset for the entrance and a small doorway, set almost one metre into the side of the monument. The doorway is framed with undecorated standing stones. As is common in passage tombs, this alignment allows for the rising sun to shine down the passageway at only two times of the year, illuminating the chamber within. At this mound, the passage is illuminated on the mornings of Samhain and Imbolc, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-quarter Day
The Wheel of the Year is an annual cycle of seasonal festivals, observed by many modern pagans, consisting of the year's chief solar events (solstices and equinoxes) and the midpoints between them. While names for each festival vary among diverse pagan traditions, syncretic treatments often refer to the four solar events as " quarter days", with the four midpoint events as "cross-quarter days". Differing sects of modern paganism also vary regarding the precise timing of each celebration, based on distinctions such as lunar phase and geographic hemisphere. Observing the cycle of the seasons has been important to many people, both ancient and modern. Contemporary Pagan festivals that rely on the Wheel are based to varying degrees on folk traditions, regardless of actual historical pagan practices. Among Wiccans, each festival is also referred to as a sabbat (), based on Gerald Gardner's view that the term was passed down from the Middle Ages, when the terminology for Jewish Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record (often paper) of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills. Periods in a calendar (such as years and months) are usually, though not necessarily, synchronized with the cycle of the sun or the moon. The most common type of pre-modern calendar was the lunisolar calendar, a lunar calendar that occasionally adds one intercalary month to remain synchronized with the solar year over the long term. Etymology The term ''calendar'' is taken from , the term for the first day of the month in the Roman calendar, related to the verb 'to call out', referring to the "calling" of the new moon when it was fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx and Scottish Gaelic. Gaelic language and culture originated in Ireland, extending to Dál Riata in western Scotland. In antiquity, the Gaels traded with the Roman Empire and also raided Roman Britain. In the Middle Ages, Gaelic culture became dominant throughout the rest of Scotland and the Isle of Man. There was also some Gaelic settlement in Wales, as well as cultural influence through Celtic Christianity. In the Viking Age, small numbers of Vikings raided and settled in Gaelic lands, becoming the Norse-Gaels. In the 9th century, Dál Riata and Pictland merged to form the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba. Meanwhile, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King often claiming lordship over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seasonal
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical cultures whose number of seasons varies. The Northern Hemisphere experiences most direct sunlight during May, June, and July, as the hemisphere faces the Sun. The same is true of the Southern Hemisphere in November, December, and January. It is Earth's axial tilt that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the summer months, which increases the solar flux. However, due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremated
Cremation is a method of final disposition of a dead body through burning. Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India and Nepal, cremation on an open-air pyre is an ancient tradition. Starting in the 19th century, cremation was introduced or reintroduced into other parts of the world. In modern times, cremation is commonly carried out with a closed furnace (cremator), at a crematorium. Cremation leaves behind an average of 2.4 kg (5.3 lbs) of remains known as "ashes" or "cremains". This is not all ash but includes unburnt fragments of bone mineral, which are commonly ground into powder. They do not constitute a health risk and may be buried, interred in a memorial site, retained by relatives or scattered in various ways. History Ancient Cremation dates from at least 17,000 years ago in the archaeological record, with the Mungo Lady, the remains of a partly cremated body found at L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



_MET_DP-13486-011.jpg)