|
Lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually treated separately from "conventional" lipases. Unlike esterases, which function in water, lipases "are activated only when adsorbed to an oil–water interface". Lipases perform essential roles in digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, organisms. Structure and catalytic mechanism Classically, lipases catalyse the hydrolysis of triglycerides: :triglyceride + H2O → fatty acid + diacylglycerol :diacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + monacylglycerol :monacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + glycerol Lipases are serine hydrolases, i.e. they function by transesterification generating an acyl serine intermediate. Most lipases act at a specific position on the glycerol backbone of a lipi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipase PLRP2
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually treated separately from "conventional" lipases. Unlike esterases, which function in water, lipases "are activated only when adsorbed to an oil–water interface". Lipases perform essential roles in digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, organisms. Structure and catalytic mechanism Classically, lipases catalyse the hydrolysis of triglycerides: :triglyceride + H2O → fatty acid + diacylglycerol :diacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + monacylglycerol :monacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + glycerol Lipases are serine hydrolases, i.e. they function by transesterification generating an acyl serine intermediate. Most lipases act at a specific position on the glycerol backbone of a lipid subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Pancreatic Lipase
Triglyceride lipases () are a family of lipolytic enzymes that hydrolyse ester linkages of triglycerides. Lipases are widely distributed in animals, plants and prokaryotes. At least three tissue-specific isozymes exist in higher vertebrates, pancreatic, hepatic and gastric/lingual. These lipases are closely related to each other and to lipoprotein lipase (), which hydrolyses triglycerides of chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). The most conserved region in all these proteins is centred on a serine residue which has been shown to participate, with a histidine and an aspartic acid residue, in a charge relay system. Such a region is also present in lipases of prokaryotic origin and in lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase () (LCAT), which catalyzes fatty acid transfer between phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Human pancreatic lipase ''Pancreatic lipase'', also known as ''pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase'' or ''steapsin'', is an enzyme secreted from the pancr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosomal Lipase
Lysosomal lipase is a form of lipase which functions intracellularly, in the lysosomes. Biochemical Significance The primary function of lysosomal lipase is to hydrolyze lipids such as triglycerides and cholesterol. These fats are transported and degraded into free fatty acids. Lysosomal lipases function optimally at an acidic pH which are complementary with the environment found in the lysosomal lumen. These enzymes were believed to only hydrolyze the lipids found in organelle membranes and extracellular lipids. However, recent studies suggest that lysosomal lipases also play a significant role in the degradation of cytosolic lipids, a characteristic that was previously limited to neutral lipases. The ability of the lysosome to degrade a diverse set of cargo is attributed to the lysosomal lipase and other soluble hydrolases. These enzymes include sulphatases, phosphatases, peptidases, glycosidases, and nucleases. The biochemical role of these enzymes are observed in various path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine Hydrolase
Serine hydrolases are one of the largest known enzyme classes comprising approximately ~200 enzymes or 1% of the genes in the human proteome. A defining characteristic of these enzymes is the presence of a particular serine at the active site, which is used for the hydrolysis of substrates. The hydrolysis of the ester or peptide bond proceeds in two steps. First, the acyl part of the substrate (the acid part of an ester or the part of a peptide ending in a carboxyl group) is transferred to the serine, making a new ester or amide bond and releasing the other part of the substrate (the alcohol of an ester or the part of the peptide ending in an amino group) is released. Later, in a slower step, the bond between the serine and the acyl group is hydrolyzed by water or hydroxide ion, regenerating free enzyme. Unlike other, non-catalytic, serines, the reactive serine of these hydrolases is typically activated by a proton relay involving a catalytic triad consisting of the serine, an acidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. Mechanical digestion takes place in the mouth through mastication and in the small intestine through segmentation contractions. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use. In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An acid- base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence (primary structure). As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
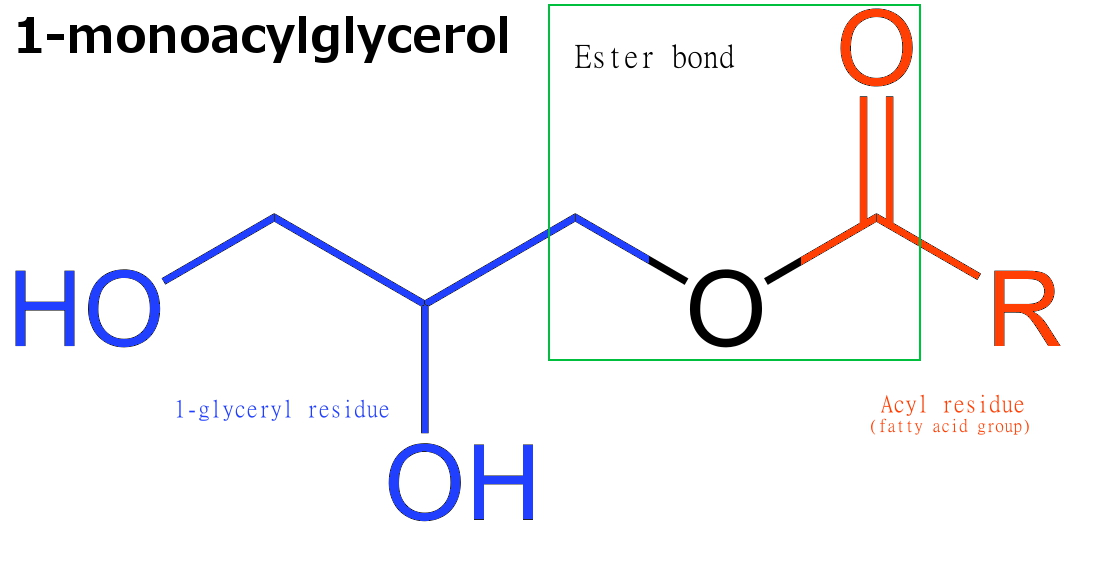
Monoglyceride
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol. Synthesis Monoglycerides are produced both biologically and industrially. They are naturally present at very low levels (0.1-0.2%) in some seed oils such as olive oil, rapeseed oil and cottonseed oil. They are biosynthesized by the enzymatic hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase and the enzymatic hydrolysis of diglycerides by diacylglycerol lipase; or as an intermediate in the alkanoylation of glycerol to form fats. Several monoglycerides are pharmacologically active (e.g. 2-oleoylglycerol, 2-arachidonoylglycerol). Industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha/beta Hydrolase Fold
The alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily is a superfamily of hydrolytic enzymes of widely differing phylogenetic origin and catalytic function that share a common fold. The core of each enzyme is an alpha/beta-sheet (rather than a barrel), containing 8 beta strands connected by 6 alpha helices. The enzymes are believed to have diverged from a common ancestor, retaining little obvious sequence similarity, but preserving the arrangement of the catalytic residues. All have a catalytic triad, the elements of which are borne on loops, which are the best-conserved structural features of the fold. The alpha/beta hydrolase fold includes proteases, lipases, peroxidases, esterases, epoxide hydrolases and dehalogenases. Database The ESTHER database provides a large collection of information about this superfamily of proteins. Subfamilies * 3-oxoadipate enol-lactonase Human proteins containing this domain ABHD10; ABHD11; ABHD12; ABHD12B; ABHD13; ABHD2; ABHD3; ABHD4; ABHD5; ABHD6; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphingomyelinase
Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.12, also known as neutral sphingomyelinase, sphingomyelinase, or SMase; systematic name sphingomyelin cholinephosphohydrolase) is a hydrolase enzyme that is involved in sphingolipid metabolism reactions. SMase is a member of the DNase I superfamily of enzymes and is responsible for breaking sphingomyelin (SM) down into phosphocholine and ceramide. The activation of SMase has been suggested as a major route for the production of ceramide in response to cellular stresses. Sphingomyelinase family Five types of SMase have been identified. These are classified according to their cation dependence and pH optima of action and are: * Lysosomal acid SMase * Secreted zinc-dependent acid SMase * Magnesium-dependent neutral SMase * Magnesium-independent neutral SMase * Alkaline SMase Of these, the lysosomal acidic SMase and the magnesium-dependent neutral SMase are considered major candidates for the production of ceramide in the cellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
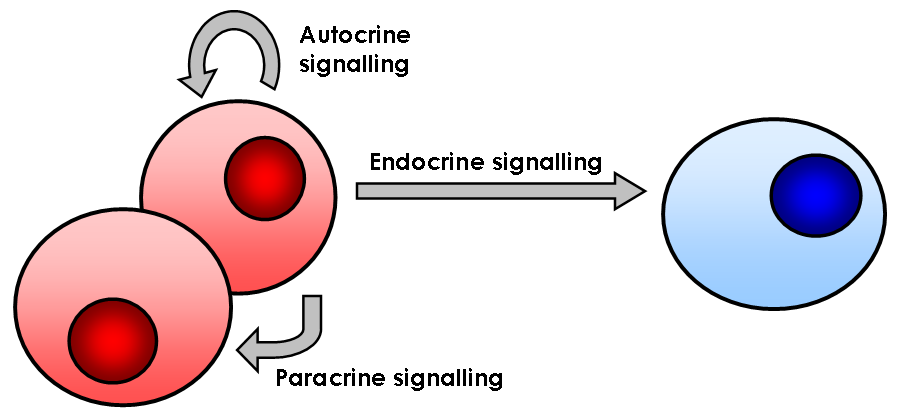
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |