|
Lelantine Plain
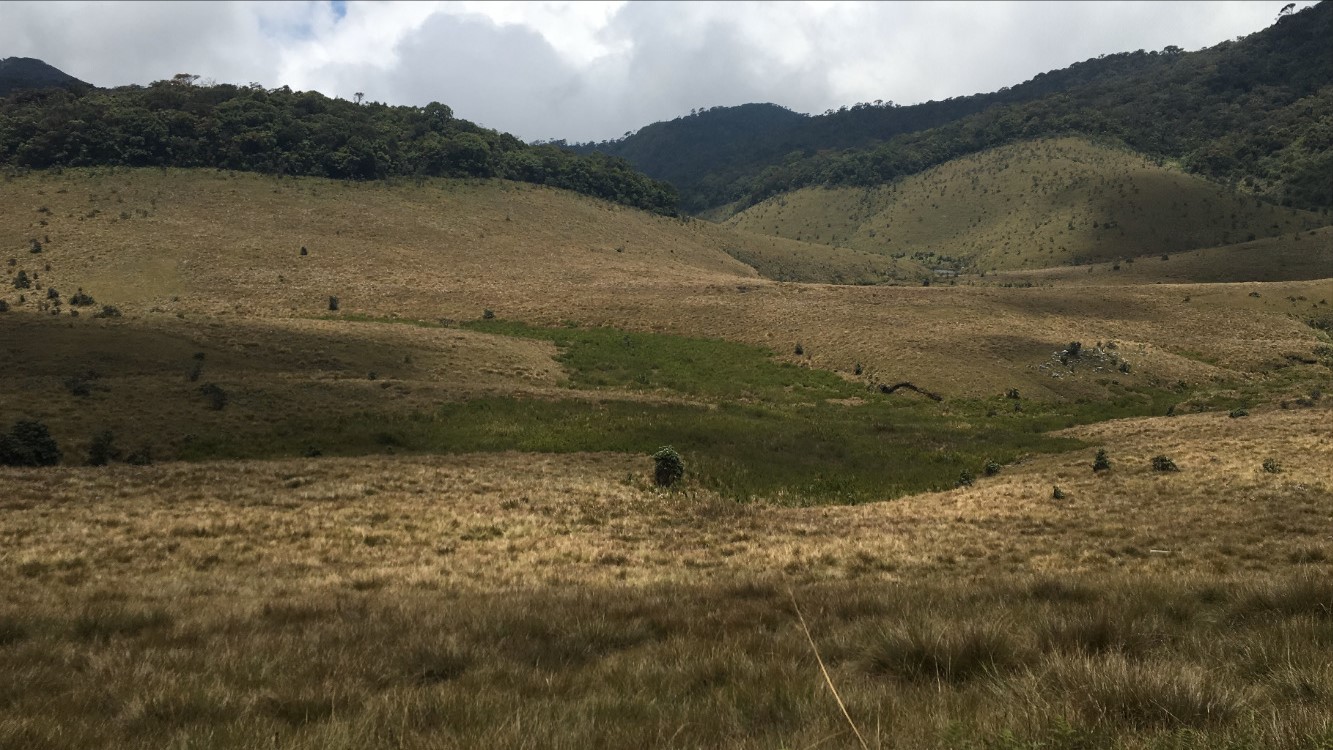
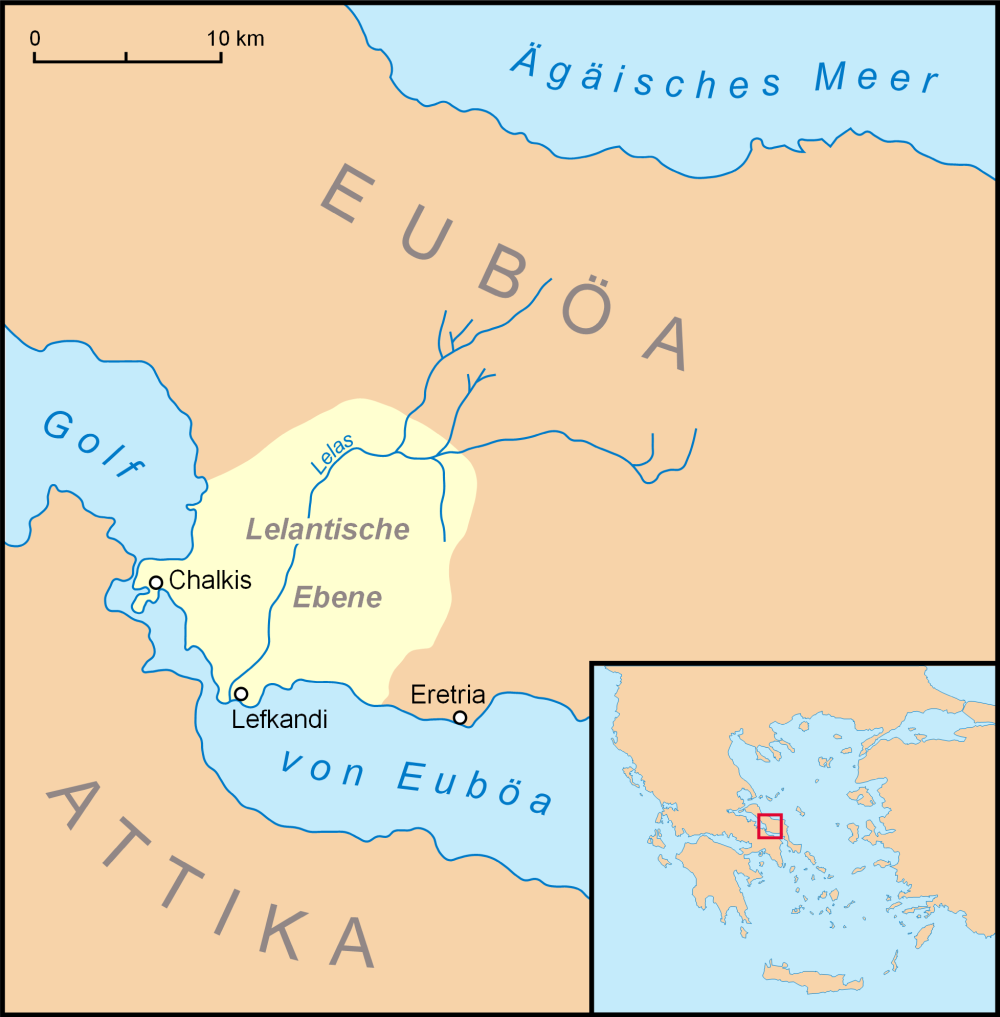
The Lelantine Plain (Ancient Greek: Ληλάντου πεδίον or Λήλαντον πεδίον; Modern Greek: Ληλάντιο πεδίο) is a fertile plain on the Greek island of Euboea, between Chalcis and Eretria. In the late eighth century BC a dispute over its possession was the cause of the Lelantine War The Lelantine War was a military conflict between the two ancient Greek city states Chalcis and Eretria in Euboea which took place in the early Archaic period, between c. 710 and 650 BC. The reason for war was, according to tradition, the struggl .... In the Middle Ages it was known as Lilanto; a Venetian document from 1439 describes a crisis caused by the powerful taking more than their share of the irrigation water: and so many plots have remained unirrigated, and if things continue like this, the place Lilanto, which is the life of this island, will turn into a desolation - a place which provides more utility to the Signoria than any other, through being the eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, , or , ''Kiní Neoellinikí Glóssa''), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the languages sometimes referred to as Standard Modern Greek. The end of the Medieval Greek period and the beginning of Modern Greek is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic features of the modern language arose centuries earlier, beginning around the fourth century AD. During most of the Modern Greek period, the language existed in a situation of diglossia, with regional spoken dialects existing side by side with learned, more archaic written forms, as with the vernacular and learned varieties ('' Dimotiki'' and ''Katharevousa'') that co-existed in Greece throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Varieties Varieties o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea
Evia (, ; el, Εύβοια ; grc, Εὔβοια ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (Μάκρις) and ''Doliche'' (Δολίχη) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'', ''Aonia'' and ''Abantis'' from the tribes inhabiting it. Its ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcis
Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from antiquity and is derived from the Greek χαλκός (copper, bronze), though there is no trace of any mines in the area. In the Late Middle Ages, it was known as Negropont(e), an Italian name that has also been applied to the entire island of Euboea. History Ancient Greece The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the Iliad, where it is mentioned in the same line as its rival Eretria. It is also documented that the ships set for the Trojan War gathered at Aulis, the south bank of the strait near the city. Chamber tombs at Trypa and Vromousa dated to the Mycenaean period were excavated by Papavasiliou in 1910. In the 8th and 7th centuries BC, colonists from Chalcis founded thirty townships on the peninsula of Chalcidice an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lelantine War
The Lelantine War was a military conflict between the two ancient Greek city states Chalcis and Eretria in Euboea which took place in the early Archaic period, between c. 710 and 650 BC. The reason for war was, according to tradition, the struggle for the fertile Lelantine Plain on the island of Euboea. Due to the economic importance of the two participating ''poleis'', the conflict spread considerably, with many further city states joining either side, resulting in much of Greece being at war. The historian Thucydides describes the Lelantine War as exceptional, the only war in Greece between the mythical Trojan War and the Persian Wars of the early 5th century BC in which allied cities rather than single ones were involved.Thucydides I. 15. Ancient authors normally refer to the ''War between Chalcidians and Eretrians'' (ancient Greek: '' ''). The war between Chalcis and Eretria was the one in which most cities belonging to the rest of Greece were divided up into alliances with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po and the Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta and the Sile). In 2020, around 258,685 people resided in greater Venice or the '' Comune di Venezia'', of whom around 55,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua and Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Veneti people who inhabited the region by the 10th century BC. The city was historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plains Of Greece
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands. In a valley, a plain is enclosed on two sides, but in other cases a plain may be delineated by a complete or partial ring of hills, by mountains, or by cliffs. Where a geological region contains more than one plain, they may be connected by a pass (sometimes termed a gap). Coastal plains mostly rise from sea level until they run into elevated features such as mountains or plateaus. Plains are one of the major landforms on earth, where they are present on all continents, and cover more than one-third of the world's land area. Plains can be formed from flowing lava; from deposition of sediment by water, ice, or wind; or formed by erosion by the agents from hills and mountains. Biomes on plains include grassland (temperate or subtropical), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Geography
;Pre-Hellenistic Classical Greece *Homer * Anaximander * Hecataeus of Miletus * Massaliote Periplus * Scylax of Caryanda (6th century BC) *Herodotus ;Hellenistic period * Pytheas (died c. 310 BC) *''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' (3rd or 4th century BC) *Megasthenes (died c. 290 BC) *Autolycus of Pitane (died c. 290 BC) *Dicaearchus (died c. 285 BC) *Deimakos (3rd century BC) *Timosthenes ( fl. 270s BC) * Eratosthenes (c. 276-194 BC) *Scymnus ( fl. 180s BC) *Hipparchus (c. 190-120 BC) *Agatharchides (2nd century BC) *Posidonius (c. 135-51 BC) *Pseudo-Scymnus (c. 90 BC) * Diodorus Siculus (c. 90-30 BC) *Alexander Polyhistor (1st century BC) ;Roman Empire period *''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' * Strabo (64 BC - 24 AD) *Pomponius Mela (fl. 40s AD) *Isidore of Charax (1st century AD) *Mucianus (1st century AD) *Pliny the Elder (23-79 AD), '' Natural History'' *Marinus of Tyre (c. 70–130)Hubert Cancik and Helmuth Schneider (ed.): "Marinus", '' Brill's New Pauly'', Brill, 2010: M. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
