|
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus '' Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver. Infections in humans are caused by more than 20 species of ''Leishmania''. Risk factors include poverty, malnutrition, deforestation, and urbanization. All three types can be diagnosed by seeing the parasites under microscopy. Additionally, visceral disease can be diagnosed by blood tests. Leishmaniasis can be par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
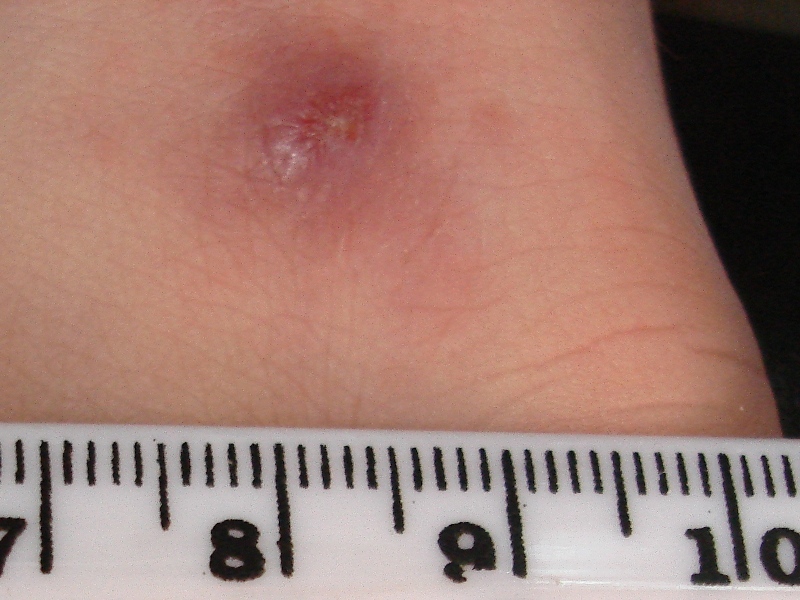
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sand fly. There are about thirty species of '' Leishmania'' that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis. This disease is considered to be a zoonosis (an infectious disease that is naturally transmissible from animals to humans), with the exception of ''Leishmania tropica'' — which is often an anthroponotic disease (an infectious disease that is naturally transmissible from humans to vertebrate animals). Signs and symptoms Post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis Post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL) is a recurrence of kala-azar that may appear on the skin of affected individuals months and up to 20 years after being partially treated, untreated or even in those considered adequately treated. In Sudan, they can be demonstrated in up to 60% of treated cases. They manifest as hypopigmented sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visceral Leishmaniasis
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), also known as kala-azar ( Hindi: kālā āzār, "black sickness") or "black fever", is the most severe form of leishmaniasis and, without proper diagnosis and treatment, is associated with high fatality. Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by protozoan parasites of the genus '' Leishmania''. The parasite migrates to the internal organs such as the liver, spleen (hence "visceral"), and bone marrow, and, if left untreated, will almost always result in the death of the host. Signs and symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, anemia, and substantial swelling of the liver and spleen. Of particular concern, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), is the emerging problem of HIV/VL co-infection. VL is the second-largest parasitic killer in the world (after malaria), responsible for an estimated 20,000 to 30,000 deaths each year worldwide. Upendranath Brahmachari synthesised urea stibamine (carbostibamide) in 1922 and determined that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miltefosine
Miltefosine, sold under the trade name Impavido among others, is a medication mainly used to treat leishmaniasis and free-living amoeba infections such as ''Naegleria fowleri'' and ''Balamuthia mandrillaris''. This includes the three forms of leishmaniasis: cutaneous, visceral and mucosal. It may be used with liposomal amphotericin B or paromomycin. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, headaches, and decreased kidney function. More severe side effects may include Stevens–Johnson syndrome or low blood platelets. Use during pregnancy appears to cause harm to the baby and use during breastfeeding is not recommended. How it works is not entirely clear. Miltefosine was first made in the early 1980s and studied as a treatment for cancer. A few years later it was found to be useful for leishmaniasis and was approved for this use in 2002 in India. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Leishmaniasis
Canine leishmaniasis (LEESH-ma-NIGH-ah-sis) is a zoonotic disease (see human leishmaniasis) caused by ''Leishmania'' parasites transmitted by the bite of an infected phlebotomine sandfly. Canine leishmaniasis was first identified in Europe in 1903, and in 1940, 40% of all dogs in Rome were determined to be positive for leishmaniasis. Traditionally thought of as a disease only found near the Mediterranean basin, 2008 research claims new findings are evidence that canine leishmaniasis is currently expanding in continental climate areas of northwestern Italy, far from the recognized disease-endemic areas along the Mediterranean coasts. Cases of leishmaniasis began appearing in North America in 2000, and, as of 2008, ''Leishmania''-positive foxhounds have been reported in 22 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces.Rosypal, Alexa. (2005Characterization of Canine Leishmaniasis in the United States: Pathogenesis, Immunological Responses, and Transmission of an American Isolate of ''Leishman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglected Tropical Disease
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms ( helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases ( HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly. Some treatments for NTDs are relatively inexpensive. For example, the treatment for schistosomiasis is US$0.20 per child per year. Nevertheless, in 2010 it was estimated that control of neglected diseases would require funding of between US$2 billion and $3 billion over the subsequent five to seven years. Some p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmania
''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus '' Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus ''Lutzomyia'' in the New World. At least 93 sandfly species are proven or probable vectors worldwide.WHO (2010) Annual report. Geneva Their primary hosts are vertebrates; ''Leishmania'' commonly infects hyraxes, canids, rodents, and humans. History Members of an ancient genus of the ''Leishmania'' parasite, '' Paleoleishmania'', have been detected in fossilized sand flies dating back to the early Cretaceous period. The first written reference to the conspicuous symptoms of cutaneous leishmaniasis surfaced in the Paleotropics within oriental texts dating back to the 7th century BC (allegedly transcribed from sources several hundred years older, between 1500 and 2000 BC). Due to its broad and persistent prevalence throughout antiquity as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutzomyia
''Lutzomyia'' is a genus of phlebotomine sand flies consisting of nearly 400 species, at least 33 of which have medical importance as vectors of human disease. Species of the genus ''Lutzomyia'' are found only in the New World, distributed in southern areas of the Nearctic and throughout the Neotropical realm. ''Lutzomyia'' is one of the two genera of the subfamily Phlebotominae to transmit the Leishmania parasite, with the other being ''Phlebotomus'', found only in the Old World. ''Lutzomyia'' sand flies also serve as vectors for the bacterial Carrion's disease and a number of arboviruses. Evolution The genus, named after Adolfo Lutz, is known from the extinct Burdigalian (20-15 mya) species ''Lutzomyia adiketis'' found as a fossil in Dominican amber on the island of Hispaniola. It is thought that species in the genus ''Lutzomyia'' all originated in the lowland forests to the east of the Andes mountain range, and that their radiation throughout the Neotropics was sparked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paromomycin
Paromomycin is an antimicrobial used to treat a number of parasitic infections including amebiasis, giardiasis, leishmaniasis, and tapeworm infection. It is a first-line treatment for amebiasis or giardiasis during pregnancy. Otherwise it is generally a second line treatment option. It is taken by mouth, applied to the skin, or by injection into a muscle. Common side effects when taken by mouth include loss of appetite, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. When applied to the skin side effects include itchiness, redness, and blisters. When given by injection there may be fever, liver problems, or hearing loss. Use during breastfeeding appears to be safe. Paromomycin is in the aminoglycoside family of medications and causes microbe death by stopping the creation of bacterial proteins. Paromomycin was discovered in the 1950s from a type of streptomyces and came into medical use in 1960. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Paromomycin is avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
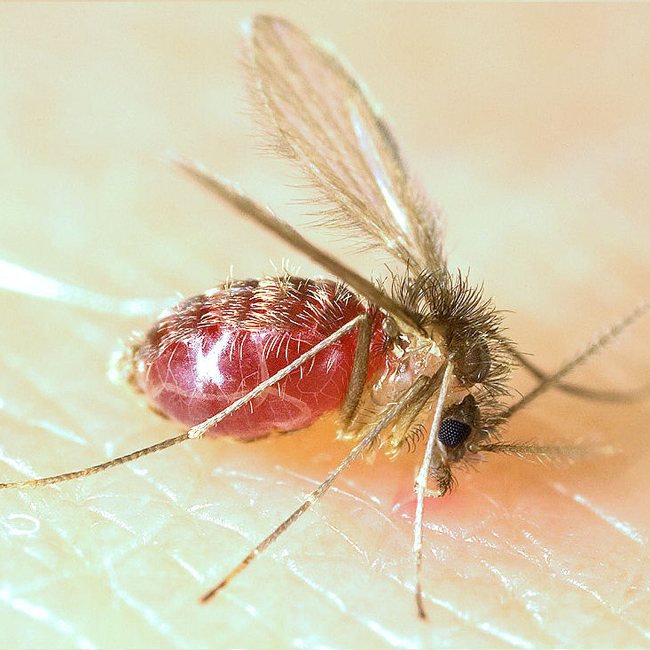
Phlebotominae
The Phlebotominae are a subfamily of the family Psychodidae. In several countries, their common name is sandfly; but that name is also applied to other flies. The Phlebotominae include many genera of blood-feeding (hematophagous) flies, including the primary vectors of leishmaniasis, bartonellosis and pappataci fever. In the New World, leishmaniasis is spread by sand flies in the genus ''Lutzomyia'', which commonly live in caves, where their main hosts are bats. In the Old World, sand flies in the genus ''Phlebotomus'' spread leishmaniasis. Phlebotomine females, and only females, suck blood from various mammals, reptiles and birds. Some species are selective, whereas others bite any suitable host they find. Some species can produce one clutch of eggs before their first blood meal; such females are said to practise autogenous or partly autogenous reproduction. Other species need a blood meal before they can produce any eggs at all; they are said to practise anautogenous repro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentamidine
Pentamidine is an antimicrobial medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, '' Balamuthia'' infections, babesiosis, and to prevent and treat pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in people with poor immune function. In African trypanosomiasis it is used for early disease before central nervous system involvement, as a second line option to suramin. It is an option for both visceral leishmaniasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis. Pentamidine can be given by injection into a vein or muscle or by inhalation. Common side effects of the injectable form include low blood sugar, pain at the site of injection, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and kidney problems. Common side effects of the inhaled form include wheezing, cough, and nausea. It is unclear if doses should be changed in those with kidney or liver problems. Pentamidine is not recommended in early pregnancy but may be used in later pregnancy. Its safety during breastfeeding is unclear. Pentamidine is in the aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
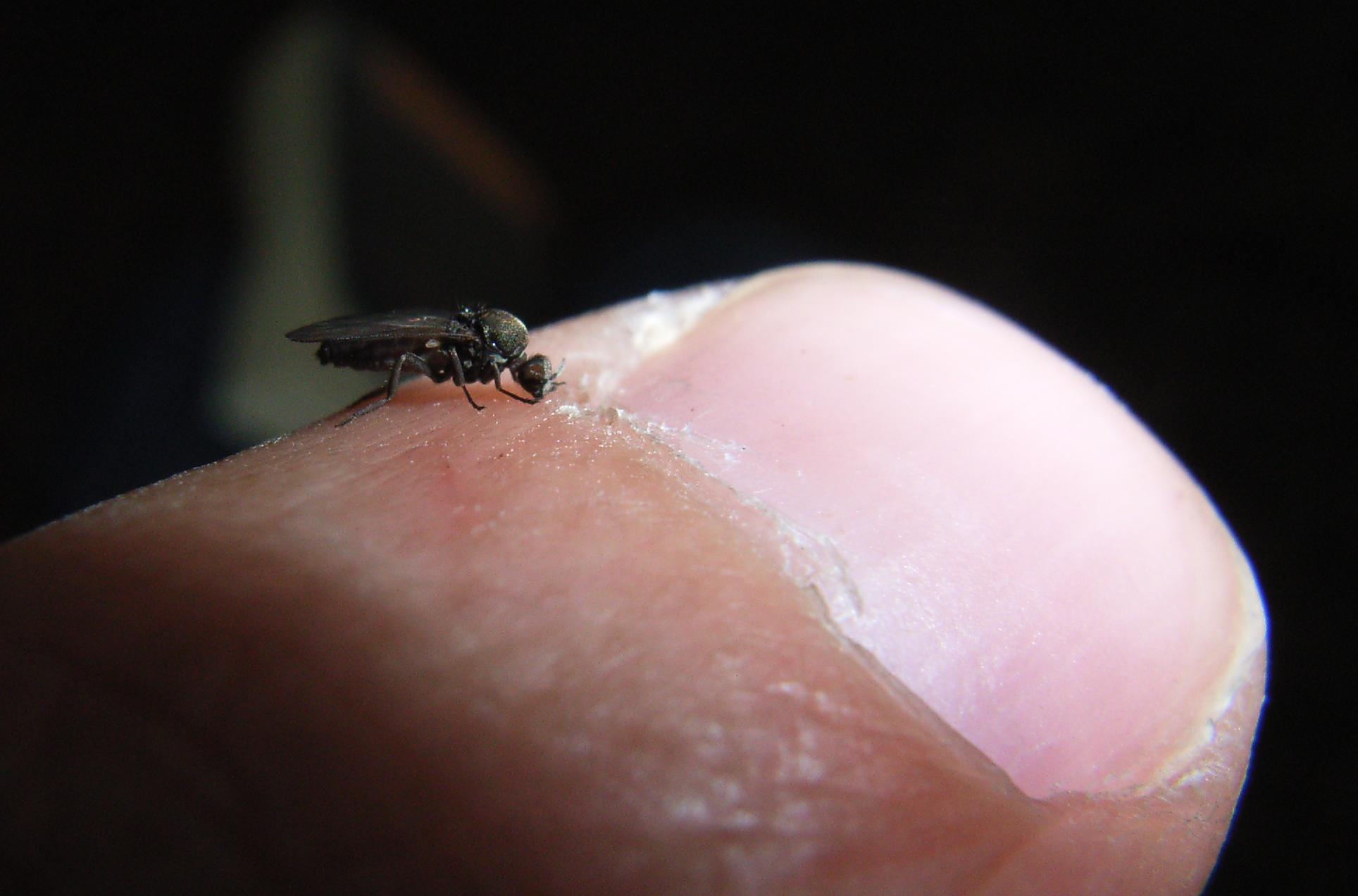
Sandflies
Sandfly (or sand fly) is a colloquial name for any species or genus of flying, biting, blood-sucking dipteran (fly) encountered in sandy areas. In the United States, ''sandfly'' may refer to certain horse flies that are also known as "greenheads" (family Tabanidae), or to members of the family Ceratopogonidae. The bites usually result in a small, intensely itchy bump or welt, the strength of which intensifies over a period of 5-7 days before dissipating. Moderate relief is achieved with varying success through the application of over the counter products such as Benadryl (ingested) or an analgesic cream such as After Bite (applied topically). Outside the United States, ''sandfly'' may refer to members of the subfamily Phlebotominae within the Psychodidae. Biting midges (Ceratopogonidae) are sometimes called sandflies or no-see-ums (no-see-em, noseeum). New Zealand sandflies are in the genus ''Austrosimulium'', a type of black fly. In the various sorts of sandfly only t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liposomal Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. For certain infections it is given with flucytosine. It is typically given intravenously (injection into a vein). Common side effects include a reaction with fever, chills, and headaches soon after the medication is given, as well as kidney problems. Allergic symptoms including anaphylaxis may occur. Other serious side effects include low blood potassium and myocarditis (inflammation of the heart). It appears to be relatively safe in pregnancy. There is a lipid formulation that has a lower risk of side effects. It is in the polyene class of medications and works in part by interfering with the cell membrane of the fungus. Amphotericin B was isolated from ''Streptomyces nodosus'' in 1955 at the Squibb For Medical Research Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |