|
KNOT
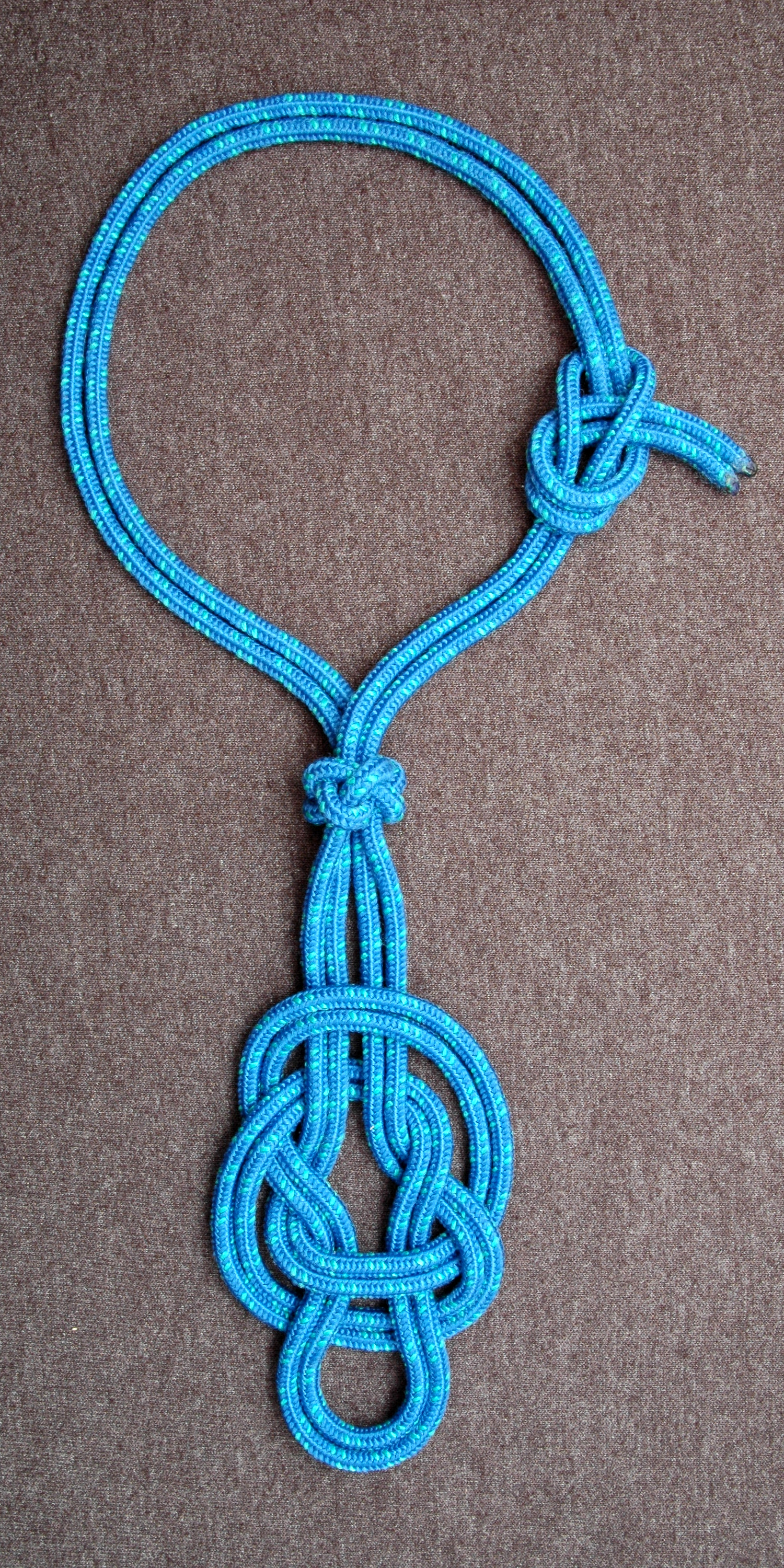
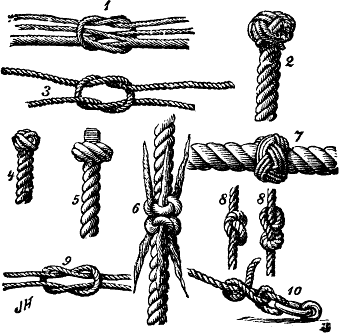
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ''bend'' fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a ''loop knot'' is any knot creating a loop; and ''splice'' denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory. History Knots and knotting have been used and studied throughout history. For example, Chinese knotting is a decorative handicraft art that began as a form of Chinese folk art in the Tang and Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD) in China, later popularized in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Theory
In the mathematical field of topology, knot theory is the study of mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be undone, the simplest knot being a ring (or "unknot"). In mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3 (in topology, a circle is not bound to the classical geometric concept, but to all of its homeomorphisms). Two mathematical knots are equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a deformation of \mathbb^3 upon itself (known as an ambient isotopy); these transformations correspond to manipulations of a knotted string that do not involve cutting it or passing through itself. Knots can be described in various ways. Using different description methods, there may be more than one description of the same knot. For example, a common method of describing a knot is a planar d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Theory
In the mathematical field of topology, knot theory is the study of mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be undone, the simplest knot being a ring (or "unknot"). In mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3 (in topology, a circle is not bound to the classical geometric concept, but to all of its homeomorphisms). Two mathematical knots are equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a deformation of \mathbb^3 upon itself (known as an ambient isotopy); these transformations correspond to manipulations of a knotted string that do not involve cutting it or passing through itself. Knots can be described in various ways. Using different description methods, there may be more than one description of the same knot. For example, a common method of describing a knot is a planar d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Loop Knots
This page explains commonly used terms related to knots. B Bend A bend is a knot used to join two lengths of rope. Bight A bight has two meanings in knotting. It can mean either any central part of a rope (between the standing end and the working end) or an arc in a rope that is at least as wide as a semicircle. "Any slack part of a rope between the two ends, particularly when curved or looped." In either case, a bight is a length of rope that does not cross itself. Knots that can be tied without use of the working end are called knots ''on the bight''. Binding knot Binding knots are knots that either constrict a single object or hold two objects snugly together. Whippings, seizings and lashings serve a similar purpose to binding knots, but contain too many wraps to be properly called a knot. In binding knots, the ends of rope are either joined together or tucked under the turns of the knot. Bitter end Another term for the working end. C Capsiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-sided Overhand Bend
The offset overhand bend (OOB, The Ashley Book of Knots, ABoK No. 1410) is a conceptually simple and easy to tie 'end-to-end joining knot' (ie bend). It is formed by holding two rope ends next to each other and tying an overhand knot in them as if they were a single line. Due to its common use in several fields, this List of bend knots, bend has become known by many names, such as thumb knot, openhand knot, one-sided overhand knot or flat overhand bend (FOB), though the terms "one-sided" and "flat" are considered incorrect. Geometry The term 'offset' refers to the knot core being displaced from the axis of tension. This geometry allows the knot to more easily translate around an edge - particularly a 90 degree edge. Uses Long used by Weaving, weavers to join the ends of yarn, the offset water knot is very old. It was one of the knots likely identified among the possessions of Ötzi the Iceman, who dates from 3300 BC. The knot is also tied in a slipped form by mechanical ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reef Knot
The reef knot, or square knot, is an ancient and simple binding knot used to secure a rope or line around an object. It is sometimes also referred to as a Hercules knot. The knot is formed by tying a left-handed overhand knot between two ends, instead of around one end, and then a right-handed overhand knot via the same procedure, or vice versa. A common mnemonic for this procedure is "right over left; left over right", which is often appended with the rhyming suffix "... makes a knot both tidy and tight". Two consecutive overhands tied as described above of the same handedness will make a granny knot. The working ends of the reef knot must emerge both at the top or both at the bottom, otherwise a thief knot results. The reef knot is not recommended for tying two ropes together, because of the potential instability of the knot when not stabilized; something that has resulted in many deaths (see Misuse as a bend). Naming The reef knot is at least 4,000 years old. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottle Sling
The bottle sling (also called a jug sling, a Hackamore knot, or a Scoutcraft knot) is a knot which can be used to create a handle for a glass or ceramic container with a slippery narrow neck, as long as the neck widens slightly near the top. While classed with binding knots, such as the reef knot and miller's knot, the bottle sling is able to perform a function for which most other binding knots are unsuited. The bottle sling's specific form allows it to grip a cylinder, assuming it has even a slight flare or collar, and lift it along its axis when the knot is loaded by all four strands. With appropriate size cord, most wine bottles can be reliably suspended with this knot. History The bottle sling was described in detail by the Greek physician Heraklas in his first century monograph on surgical knots and slings. It was included under the name ''diplous karkhesios brokhos'' ("double jug-sling noose"). Clearly familiar with the knot, Heraklas provided three distinct tying m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Knotting
Chinese knotting, also known as () and decorative knots in non-Chinese cultures, is a decorative handcraft art that began as a form of Chinese folk art in the Tang and Song dynasty (960–1279 CE) in China. This form of craft originated and was derived from the () culture which already existed in China since the ancient times. As a form of art, it is also called Chinese traditional decorative knots. Chinese knotting was later popularized in the Ming and spread to Japan and Korea. There are many different shapes of Chinese knots, the most common being butterflies, flowers, birds, dragons, fish, and even shoes. Culturally they were expected to ward off evil spirits similar to bagua mirrors or act as good-luck charms for Chinese marriages. Around the times of the Chinese new year festival, Chinese knot decorations can be seen hanging on walls, doors of homes and as shop decorations to add some festival feel. Usually, these decorations are red in colour, which is a colour associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bend Knots
This is a list of bends. A bend is a knot used to join two lengths of rope. They are used in a variety of situations, including climbing, sailing, and securing loads. Bend knots are classified based on their ability to be tightened or released, their resistance to slipping, and their strength. Some common types of bend knots include the double fisherman's knot, the double overhand knot, and the double figure-eight knot. Bend knots are important because they allow two ropes to be securely joined together, enabling the combined ropes to support weight or transmit force. It is important to choose the appropriate bend knot for the specific task at hand, as some bend knots may be stronger or more secure than others. The sheet bend is the classic bend. Misuse of reef knot as a bend The common reef knot (square knot) is sometimes mistakenly tied as a bend. When used as a bend rather than a binding knot, the reef knot will capsize under sufficient tension. For this reason, the reef k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskimo Bowline
The Eskimo bowline, Cossack knot (russian: Казачий узел), reverse bowline, or 'anti- bowline' is in a class of knots known as 'eye knots' or 'loop knots'. The eye is formed in the end of the rope to permit attachments/connections. It is quite common in Russia and is often used instead of the bowline (ABoK #1010). In the simple bowline, the collar component forms around the 'standing part'. In contrast, the collar component of an Eskimo bowline forms around the outgoing eye-leg. On the first of arctic explorer John Ross' expeditions (1818) the Inuit (Eskimos) presented him a sled that contained several of these knots, showing that it is a genuine Inuit knot. The knot is not mentioned in '' The Ashley Book of Knots'' but in its Russian equivalent, the book "Морские узлы" (Marine Knots) by Lev Skryagin (1930–2000). The slipped version is known as Kalmyk loop. The Eskimo bowline is about as strong as and even more secure than the bowline, especi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half Hitch
The half hitch is a simple overhand knot, where the working end of a line is brought over and under the standing part. Insecure on its own, it is a valuable component of a wide variety of useful and reliable hitches, bends, and knot A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ...s. Two successive half hitches tied around an object makes up the common clove hitch. Two successive half hitches tied around the standing part of a rope is known as two half-hitches or double half hitch. One instance where a half hitch stands on its own without additional embellishment is when added to a timber hitch to help stabilize a load in the direction of pull. A timber hitch is tied on the far end of the load to bind it securely and a half hitch made at the forward end to serve as a guid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cow Hitch
The cow hitch, also called the lark's head, is a hitch knot used to attach a rope to an object. The cow hitch comprises a pair of half-hitches tied in opposing directions, as compared to the clove hitch in which the half-hitches are tied in the same direction. It has several variations and is known under a variety of names. It can be tied either with the end of the rope or with a bight. History A simple and useful knotted structure, the cow hitch has been known since at least the first century when described by Greek physician Heraklas in a monograph on surgical knots and slings. Known under a variety of names, this knot has been used both on land and at sea. The common alternate name "lark's head" is attributed to Tom Bowling (pseudonym) in the 1866 work ''The Book of Knots'' which is presumed to have been adapted from a French manuscript; lark's head is a literal translation of the French name for the knot, ''tête d'alouette''.Ahsley, p. 11. Variations The underlying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
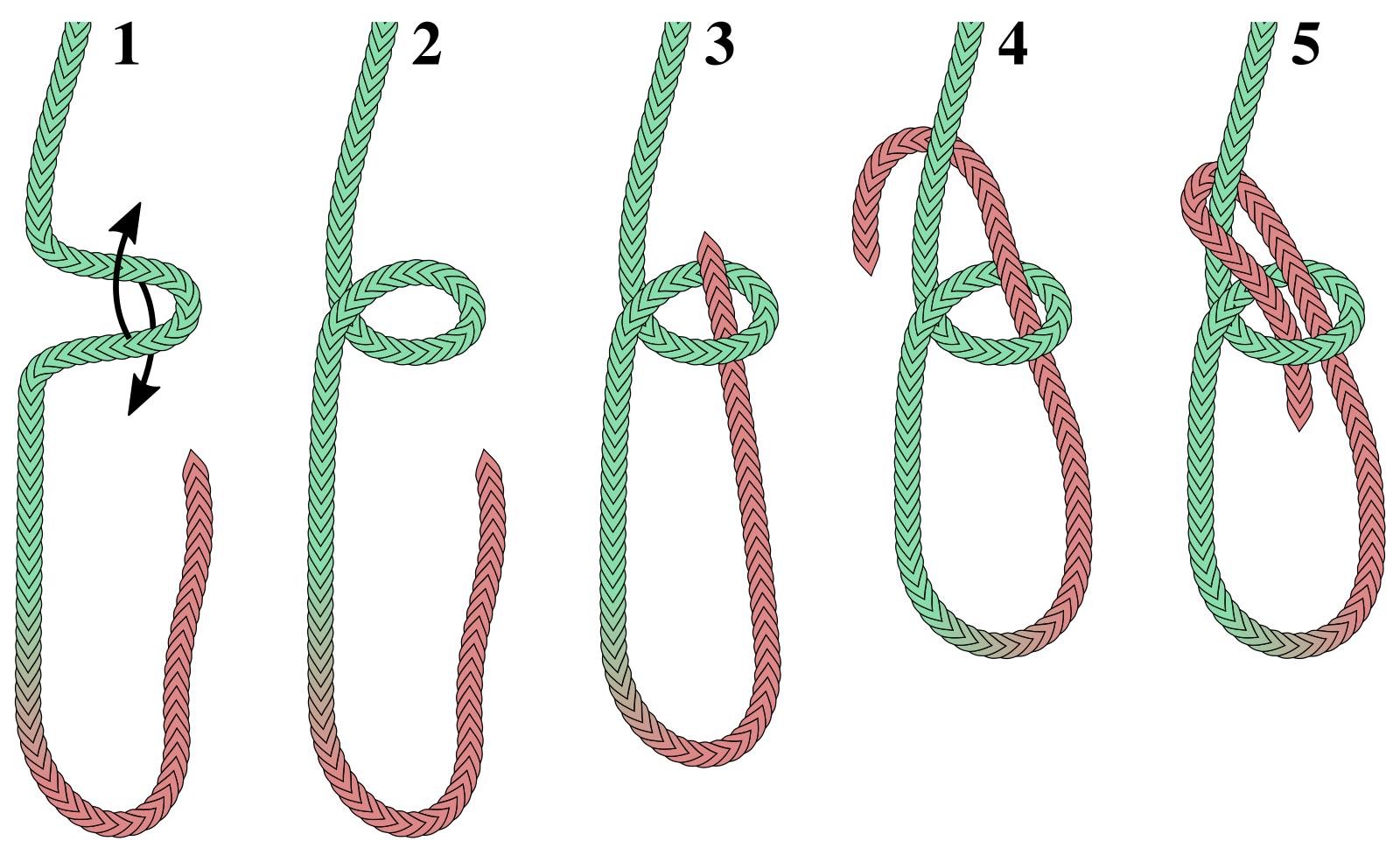
Bowline
The bowline ( or ) is an ancient and simple knot used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes referred to as ''King of the knots'' because of its importance. Along with the sheet bend and the clove hitch, the bowline is often considered one of the most essential knots. The common bowline shares some structural similarity with the sheet bend. Virtually all end-to-end joining knots (i.e., bends) have a corresponding loop knot. Although the bowline is generally considered a reliable knot, its main deficiencies are a tendency to work loose when not under load (or under cyclic loading), to slip when pulled sideways, and the bight portion of the knot to capsize in certain circumstances. To address these shortcomings, a number of more secure variations of the bowline have been developed for use in safety-critical applications, or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |