|
Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), in Ayrarat province, and later the capital of Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia in 929–961. Currently, the mayor of Kars is Türker Öksüz. The city had an Armenian ethnic majority until it was conquered by Turkish nationalist forces in late 1920. Etymology The city's name may be derived from the Armenian word հարս (''hars''), meaning "bride". Another hypothesis has it that the name derives from the Georgian word "the gate. History Medieval period Little is known of the early history of Kars beyond the fact that, during medieval times, it had its own dynasty of Armenian rulers and was the capital of a region known as Vanand. Medieval Armenian historians referred to the city by a variety of names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kars Province
Kars Province ( tr, Kars ili; ku, Parêzgeha Qersê; hy, Կարսի նահանգ) is a province of Turkey, located in the northeastern part of the country. It shares part of its closed border with Armenia. The provincial capital is the city of Kars. The provinces of Ardahan and Iğdır were until the 1990s part of Kars Province. History In ancient times, Kars ( hy, Կարս) was part of the province of Ararat in the Kingdom of Armenia. The first known people were the followers of Vanand (Վանանդ), for whom Kars was their main settlement and fortress. In 928, Kars became the capital of Bagratid Armenia. In 968, the capital of Armenia was moved to Ani, but Kars remained the capital of the feudal principality of Vanand. The Seljuks quickly relinquished direct control over Kars and it became a small emirate whose territory corresponded closely to that of Vanand, and which bordered the similarly created but larger Shaddadid emirate centered at Ani. The Kars emirate was a vass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
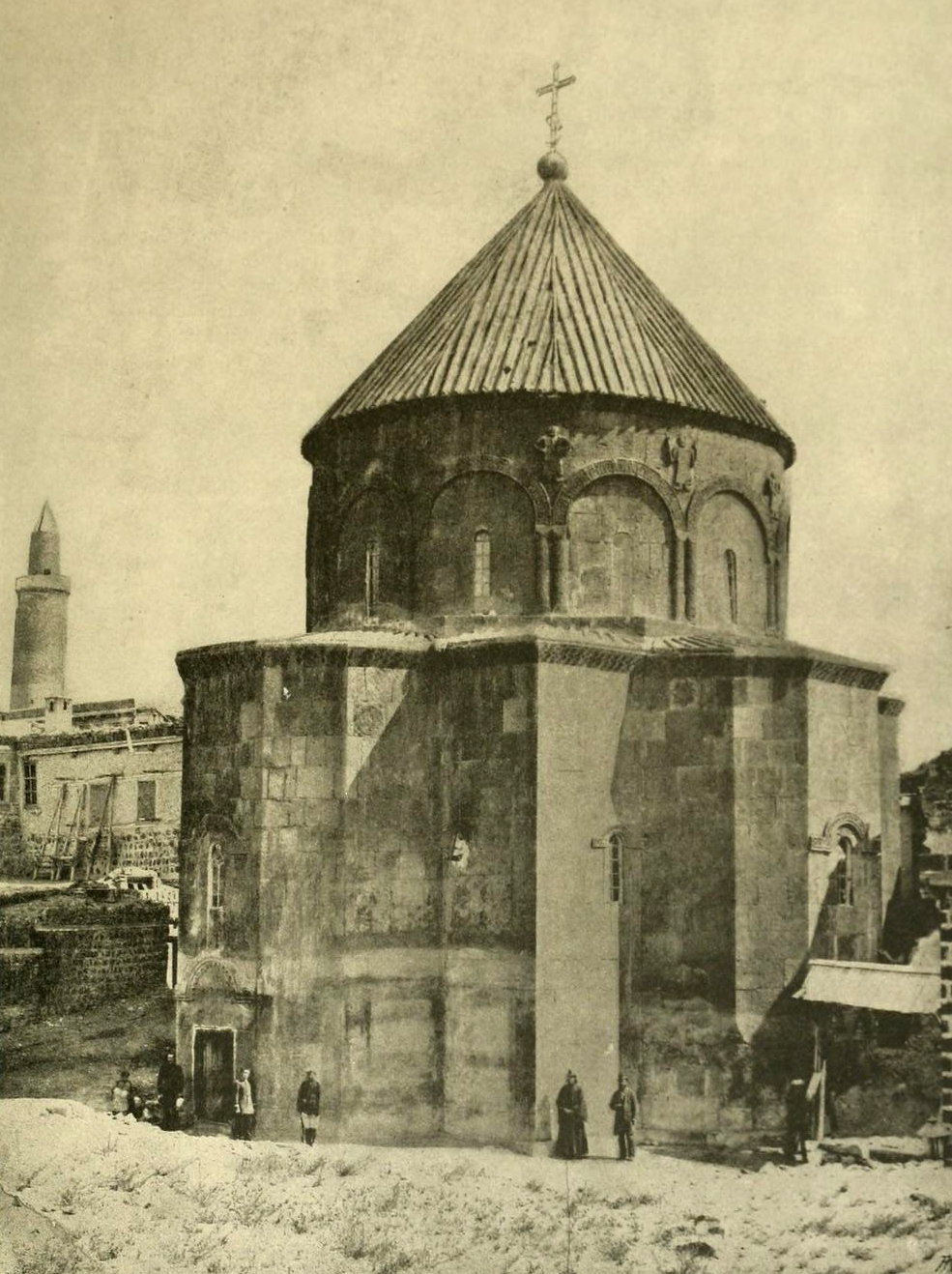
Cathedral Of Kars
The Cathedral of Kars, also known as the Holy Apostles Church ( hy, Կարսի Սուրբ Առաքելոց եկեղեցի, ; tr, Aziz Havariler Kilisesi or "Church of the Twelve Apostles" ''12 Havariler Kilisesi'') is a former Armenian Apostolic church in Kars, eastern Turkey. Built in the mid-10th century by the Armenian Bagratid King Abas I (r. 928–953), it was converted into a mosque in 1579. In the 19th and early 20th century it was converted into a Russian Orthodox and later Armenian cathedral. In 1993 it was again converted into a mosque and is called Kümbet Mosque ( tr, Kümbet Camii, literally "domed mosque"). It currently comprises part of a larger Islamic complex that includes the Evliya Mosque, the biggest mosque in Kars. Overview The cathedral is located at the base of the Kars Citadel. Historians Stepanos Asoghik, Samuel of Ani, and Mxitar of Ayrivank called the church a cathedral. In 19th century Armenian sources it began to be known as the Church of Holy Apo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Of Kars
The Castle of Kars ( tr, Kars Kalesi, arm, Կարսի բերդ) is a former fortification located in Kars, Turkey. It is also known under the name Iç Kale ("Central/Inner Castle", "Citadel"). It was first built during the rule of the Armenian Bagratid dynasty and then rebuilt in 1153 by Firuz Akay Commissioned by Sultan Melik Izzeddin Saltuk II. The outer walls surrounding the city were built in the 12th century. The castle, which was destroyed by Timur in 1386, was rebuilt again in 1579 by Lala Mustafa Pasha, who came to Kars ordered by the Ottoman Sultan Murat III. It is said in the Ottoman sources that the castle was rebuilt with the help of one hundred thousand soldiers and workers. In 1606, the castle was destroyed by the Iranian Shah Abbas I, and in 1616 and in 1636 it was restored twice and new elements were added to it. The castle was badly damaged after the occupation of the Russians after the Ottoman-Russian War of 1877-1878, and partially changed after 40 yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagratid Kingdom Of Armenia
The Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia, also known as Bagratid Armenia ( xcl, Բագրատունեաց Հայաստան, or , , 'kingdom of the Bagratunis'), was an independent Armenian state established by Ashot I Bagratuni of the Bagratuni dynasty in the early 880s following nearly two centuries of foreign domination of Greater Armenia under Arab Umayyad and Abbasid rule. With each of the two contemporary powers in the region—the Abbasids and Byzantines—too preoccupied to concentrate their forces in subjugating the region, and with the dissipation of several of the Armenian '' nakharar'' noble families, Ashot succeeded in asserting himself as the leading figure of a movement to dislodge the Arabs from Armenia. Ashot's prestige rose as both Byzantine and Arab leaders—eager to maintain a buffer state near their frontiers—courted him. The Abbasid Caliphate recognized Ashot as "prince of princes" in 862 and, later on, as king (in 884 or 885). The establishment of the Bagratu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagratid Armenia
The Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia, also known as Bagratid Armenia ( xcl, Բագրատունեաց Հայաստան, or , , 'kingdom of the Bagratunis'), was an independent Armenian state established by Ashot I Bagratuni of the Bagratuni dynasty in the early 880s following nearly two centuries of foreign domination of Greater Armenia under Arab Umayyad and Abbasid rule. With each of the two contemporary powers in the region—the Abbasids and Byzantines—too preoccupied to concentrate their forces in subjugating the region, and with the dissipation of several of the Armenian '' nakharar'' noble families, Ashot succeeded in asserting himself as the leading figure of a movement to dislodge the Arabs from Armenia. Ashot's prestige rose as both Byzantine and Arab leaders—eager to maintain a buffer state near their frontiers—courted him. The Abbasid Caliphate recognized Ashot as "prince of princes" in 862 and, later on, as king (in 884 or 885). The establishment of the Bagratuni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Anatolia Region
The Eastern Anatolia Region ('' tr, Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi'') is a geographical region of Turkey. The most populous province in the region is Van Province. Other populous provinces are Malatya, Erzurum and Elazığ. It is bordered by the Black Sea Region and Georgia in the north, the Central Anatolia Region in the west, the Mediterranean Region in the southeast, the Southeastern Anatolia Region and Iraq in the south, and Iran, Azerbaijan and Armenia in the east. The region encompasses most of Western Armenia () and had a large population of indigenous Armenians until the Armenian genocide. The Anatolia peninsula never encompassed what is now called "Eastern Anatolia", which has been seen as an attempt by Turkey to erase the Armenian history of the region. It has the highest average altitude, largest geographical area, and lowest population density of the seven Turkish regions. Substitution for the name Armenia Beginning in 1880, the name Armenia was forbidden to be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taşköprü (Kars)
Taşköprü, or the Stone Bridge, is a stone three-arch bridge over the Kars River (a tributary of the Aras River) river, northwest of Kars city center and directly south of Kars castle. The bridge was built in 1579 of ashlar basalt blocks as part of a program of works in Kars by Lala Mustafa Pasha, who became Sultan Murad III's grand vizier Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ... the following year. This bridge was subsequently destroyed by a flood, and it was rebuilt in 1719 (some records say 1725) by Karahanoğlu Haci Ebubekir Bey. It was restored by the 18th Region of the Highways Directorate in 2013. References Sources {{Bridges in Turkey Deck arch bridges Ottoman bridges in Turkey Buildings and structures in Kars Province Stone bridges in Turkey Tou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Turkey
Turkey is divided into 81 provinces ( tr, il). Each province is divided into a number of districts (). Each provincial government is seated in the central district (). For non- metropolitan municipality designated provinces, the central district bears the name of the province (e.g. the city/district of Rize is the central district of Rize Province). Each province is administered by an appointed governor () from the Ministry of the Interior. List of provinces Below is a list of the 81 provinces of Turkey, sorted according to their license plate codes. Initially, the order of the codes matched the alphabetical order of the province names. After Zonguldak (code 67), the ordering is not alphabetical, but in the order of the creation of provinces, as these provinces were created more recently and thus their plate numbers were assigned after the initial set of codes had been assigned. Codes The province's ISO code suffix number, the first two digits of the vehicle regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayrarat
Ayrarat () was the central province of the kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), ancient kingdom Armenia, located in the plain of the upper Aras (river), Aras River. Most of the historical capitals of Armenia were located in this province, including Armavir (ancient city), Armavir, Yervandashat (ancient city), Yervandashat, Artaxata, Artashat, Vagharshapat, Dvin (ancient city), Dvin, Bagaran (ancient city), Bagaran, Shirakavan (ancient city), Shirakavan, Kars and Ani (the current capital of Armenia, Yerevan, is also located on the territory of historical Ayrarat). It is believed that the name ''Ayrarat'' is the Armenian language, Armenian equivalent of the toponym ''Urartu'' ( hy, Արարատ, Mount_Ararat, Ararat). It seems to have corresponded geographically with the territory of the Etiuni tribal confederation, mentioned in Urartian sources.Armen Petrosyan (2007). "Towards the Origins of the Armenian People: The Problem of Identification of the Proto-Armenians: A Critical Review (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neolithic sites like Göbekli Tepe, and was inhabited by ancient civilisations including the Hattians, Hittites, Anatolian peoples, Mycenaea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanand
Vanand () is the area of historic Armenia that roughly corresponds to the Kars Province of present-day Turkey. Named after the Armenian family of Vanandi, it was a principality of the Kingdom of Armenia and a later province of the Democratic Republic of Armenia. Its historic capital was the city of Kars. The region fell to numerous invaders including the Assyrians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Arabs, Mongols, Persians, and the Ottoman Turks. After the 1877-1878 Russo-Turkish War, the Russian Empire acquired the region at the Congress of Berlin. The area still retained a substantial Armenian population, but after World War I, most of it was decimated during the Turkish-Armenian War in 1920. This region was passed to Turkish control by the Treaty of Alexandropol and the Treaty of Kars. See also * Armavir region Princes of Vanand * Until 451: Aravand Vanandi * 451: Tathul Vanandi * 480: Vren Vanandi See also *List of regions of old Armenia This is a list of regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Turkey
The geographical regions of Turkey comprise seven regions ( tr, bölge) which were originally defined at the country's First Geography Congress in 1941.Ali Yiğit, "Geçmişten Günümüze Türkiye'yi Bölgelere Ayıran Çalışmalar ve Yapılması Gerekenler", ''Ankara Üniversitesi Türkiye Coğrafyası Araştırma ve Uygulama Merkezi, IV. Ulural Coğrafya Sempozyumu, "Avrupa Birliği Sürecindeki Türkiye'de Bölgesel Farklılıklar"''pp. 34–35. These seven regions are subdivided into twenty one sections ( tr, bölüm), which are further split into numerous areas ( tr, yöre) as defined by microclimate and bounded by local geographic formations. "Regions" as defined in this context are merely for geographic, demographic, and economic purposes, and do not refer to an administrative division. Regions and subregions * Aegean Region **Aegean Section *** Edremit Area *** Bakirçay Area *** Gediz Area *** Izmir Area ***Küçük Menderes Area ***Büyük Menderes Area *** M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |