|
Jicheng (Beijing)
Ji or Jicheng was an ancient city in northern China, which has become the longest continuously inhabited section of modern Beijing. Historical mention of Ji dates to the founding of the Zhou dynasty in about 1045BC. Archaeological finds in southwestern Beijing where Ji was believed to be located date to the Spring and Autumn period (771–476BC). The city of Ji served as the capital of the ancient states of Ji and Yan until the unification of China by the Qin dynasty in 221BC. Thereafter, the city was a prefectural capital for Youzhou through the Han dynasty, Three Kingdoms, Western Jin dynasty, Sixteen Kingdoms, Northern Dynasties, and Sui dynasty. With the creation of a Jizhou during the Tang dynasty in what is now Tianjin Municipality, the city of Ji took on the name Youzhou. Youzhou was one of the Sixteen Prefectures ceded to the Khitans during the Five Dynasties. The city then became the southern capital of the Liao dynasty and then main capital of the Jin dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, finance, busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
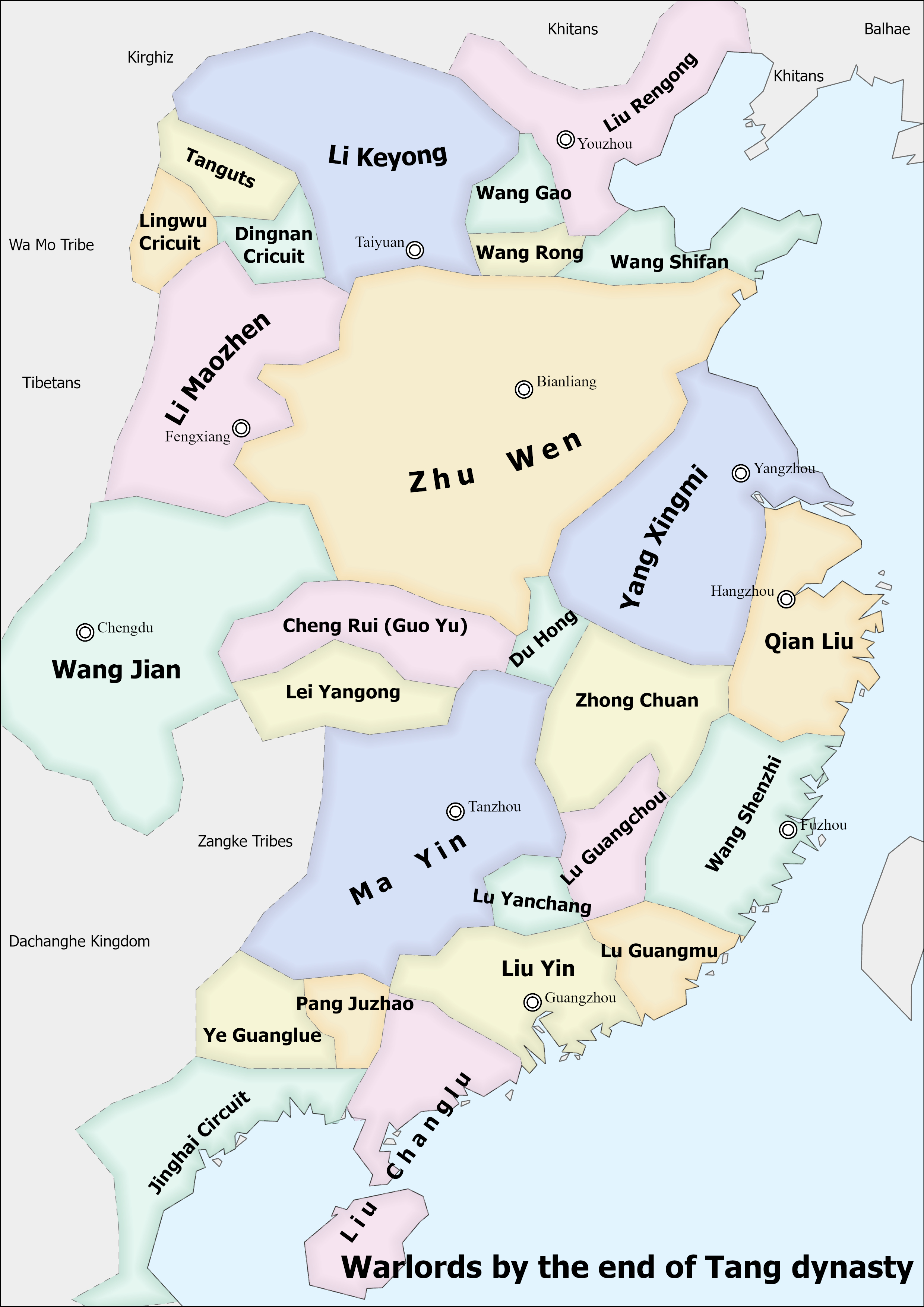
Five Dynasties
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century History of China#Imperial China, Imperial China. Five Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Zhongyuan, Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history. Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the Liao dynasty still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasty), and the Western Xia was eventually established in China's northwest. Many states had been ''de facto'' independent long before 907 as the Tang dynasty' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years beginning from the rise of the legendary Yellow Emperor and the formation of the first Chinese polity to the reigning sovereign of Sima Qian's time, Emperor Wu of Han. As the first universal history of the world as it was known to the ancient Chinese, the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' served as a model for official history-writing for subsequent Chinese dynasties and the Chinese cultural sphere (Korea, Vietnam, Japan) up until the 20th century. Sima Qian's father Sima Tan first conceived of the ambitious project of writing a complete history of China, but had completed only some preparatory sketches at the time of his death. After inheriting his father's position as court historian in the imperial court, he was determined to fulfill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the '' Book of Documents'', '' Bamboo Annals'' and '' Records of the Grand Historian''. According to the traditional chronology based on calculations made approximately 2,000 years ago by Liu Xin, the Shang ruled from 1766 to 1122 BC, but according to the chronology based upon the "current text" of ''Bamboo Annals'', they ruled from 1556 to 1046 BC. Comparing the same text with dates of five-planet conjunctions, David Pankenier, supported by David Nivison, proposed dates of the establishment of the dynasty to 1554 BC. The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project dated the establishment to c. 1600 BC based on the carbon-14 dates of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors and cosmological Five Regions' Highest Deities (). Calculated by Jesuit missionaries on the basis of Chinese chronicles and later accepted by the twentieth-century promoters of a universal calendar starting with the Yellow Emperor, Huangdi's traditional reign dates are 2697–2597 or 2698–2598 BC. Huangdi's cult became prominent in the late Warring States and early Han dynasty, when he was portrayed as the originator of the centralized state, as a cosmic ruler, and as a patron of esoteric arts. A large number of texts – such as the '' Huangdi Neijing'', a medical classic, and the '' Huangdi Sijing'', a group of political treatises – were thus attributed to him. Having waned in influence during most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing City Fortifications
The Beijing city fortifications were Defensive wall, walls with series of towers and gates constructed in the city of Beijing, China in the early 1400s until they were partially demolished in 1965 for the construction of the 2nd Ring Road and Line 2, Beijing Subway, Line 2 of the Beijing Subway. The original walls were preserved in the southeastern part of the city, just south of the Beijing railway station. The entire perimeter of the Inner and Outer city walls stretched for approximately . Beijing was the capital of China for the majority of the Yuan Dynasty, Yuan, Ming Dynasty, Ming, and Qing Dynasty, Qing Dynasties, as well as a secondary capital to the Liao Dynasty, Liao and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin Dynasties. As such, the city required an extensive fortification system around the Forbidden City, the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City, the Inner city, and the Outer city. Fortifications included gate towers, gates, archways, watchtowers, barbicans, barbican towers, bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanbaliq
Khanbaliq or Dadu of Yuan () was the winter capital of the Yuan dynasty of China in what is now Beijing, also the capital of the People's Republic of China today. It was located at the center of modern Beijing. The Secretariat directly administered the Central Region () of the Yuan Empire (comprising present-day Beijing, Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, and parts of Henan and Inner Mongolia) and dictated policies for the other provinces. Kublai and his successors also claimed supremacy over the entire Mongol Empire following the death of Möngke (Kublai's brother and predecessor) in 1259. Over time the unified empire gradually fragmented into a number of khanates. Khanbaliq is the direct predecessor to modern Beijing. Several stations of Line 10 and Line 13 are named after the gates of Dadu. Name The name Khanbaliq comes from the Mongolian and Old Uyghur words ''khan'' and ''balik'' ("town", "permanent settlement"): "City of the Khan". It was actually in use among the Turks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan had been enthroned with the Han-style title of Emperor in 1206 and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other Mongol-led khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from 1260 to 1294, although after the division of the empire this was a nominal position. He proclaimed the empire's dynastic name "Great Yuan" in 1271, and ruled Yuan China until his death in 1294. Kublai was the second son of Tolui by his chief wife Sorghaghtani Beki, and a grandson of Genghis Khan. He was almost 12 when Genghis Khan died in 1227. He had succeeded his older brother Möngke as Khagan in 1260, but had to defeat his younger brother Ariq Böke in the Toluid Civil War lasting until 1264. This episode marked the beginning of the fragmentation of the empire. Kublai's real power was limited to the Yuan Empire, even though as Khagan he still had influence in the Ilkhanate and, to a significantly lesser deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (, ; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin in English to differentiate it from an earlier Jìn dynasty whose name is rendered identically in Hanyu Pinyin without the tone marking. It is also sometimes called the "Jurchen dynasty" or the "Jurchen Jin", because members of the ruling Wanyan clan were of Jurchen descent. The Jin emerged from Wanyan Aguda's rebellion against the Liao dynasty (916–1125), which held sway over northern China until the nascent Jin drove the Liao to the Western Regions, where they became known in historiography as the Western Liao. After vanquishing the Liao, the Jin launched a century-long campaign against the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279), which was based in southern China. Over the course of their rule, the ethnic Jurchen emperors of the Jin dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |