|
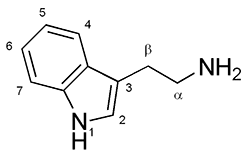
Ibogamine
Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga'' and Crepe Jasmine (''Tabernaemontana divaricata''). Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical. Ibogamine persistently reduced the self-administration of cocaine and morphine in rats. The same study found that ibogamine (40 mg/kg) and coronaridine (40 mg/kg) did not produce "any tremor effects in rats that differ significantly from saline control". While the related alkaloids ibogaine (20–40 mg/kg), harmaline (10–40 mg/kg) and desethylcoronaridine (10–40 mg/kg) were "obviously tremorgenic". Chemistry Synthesis Ibogamine can be prepared from one-step demethoxycarbonylation process through coronaridine. Pharmacology Like ibogaine, it has seems to have similar pharmacology. It has effects on KOR, NMDAR, nAChR and serotonin sites. It also inhibits acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase See a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabernanthine
Tabernanthine is an alkaloid found in '' Tabernanthe iboga''. It has been used in laboratory experiments to study how addiction affects the brain. Tabernanthine persistently reduced the self-administration of cocaine and morphine in rats. Pharmacology It is kappa opioid agonist (Ki = 0.15 μM) and NMDA receptor (Ki = 10.5 μM) antagonist. Compared to ibogaine, it binds weakly to σ1 and σ2 receptor. See also * Coronaridine Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga'' and related species, including ''Tabernaemontana divaricata'' for which (under the now obsolete synonym ''Ervatamia coronaria'') it was named. Li ... * Ibogamine * Voacangine * Tabernaemontanine * Tabernanthalog References Alkaloids found in Iboga NMDA receptor antagonists Azepines Quinuclidine alkaloids Tryptamine alkaloids {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibogaine
Ibogaine is a naturally occurring psychoactive substance found in plants in the family Apocynaceae such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', '' Voacanga africana'', and '' Tabernaemontana undulata''. It is a psychedelic with dissociative properties. Preliminary research indicates that it may help counter drug addiction. Its use has been associated with serious side effects and death. Between the years 1990 and 2008, a total of 19 fatalities temporally associated with the ingestion of ibogaine were reported, from which six subjects died of acute heart failure or cardiopulmonary arrest. The total number of subjects who have used it without major side effects during this period remains unknown. It is used as an alternative medicine treatment for drug addiction in some countries. Its prohibition in other countries has slowed scientific research. Ibogaine is also used to facilitate psychological introspection and spiritual exploration. Various derivatives of ibogaine designed to lack psychede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibogaine
Ibogaine is a naturally occurring psychoactive substance found in plants in the family Apocynaceae such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', '' Voacanga africana'', and '' Tabernaemontana undulata''. It is a psychedelic with dissociative properties. Preliminary research indicates that it may help counter drug addiction. Its use has been associated with serious side effects and death. Between the years 1990 and 2008, a total of 19 fatalities temporally associated with the ingestion of ibogaine were reported, from which six subjects died of acute heart failure or cardiopulmonary arrest. The total number of subjects who have used it without major side effects during this period remains unknown. It is used as an alternative medicine treatment for drug addiction in some countries. Its prohibition in other countries has slowed scientific research. Ibogaine is also used to facilitate psychological introspection and spiritual exploration. Various derivatives of ibogaine designed to lack psychede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including bacteria, fungi, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabernanthe Iboga
''Tabernanthe iboga'' (iboga) is an evergreen rainforest shrub native to Central Africa. A member of the Apocynaceae family indigenous to Gabon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the Republic of Congo, it is cultivated across Central Africa for its medicinal and other effects. In African traditional medicine and rituals, the yellowish root or bark is used to produce hallucinations and near-death outcomes, with some fatalities occurring. In high doses, ibogaine is considered to be toxic, and has caused serious comorbidities when used with opioids or prescription drugs. The United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) lists ibogaine as a controlled substance of the Controlled Substances Act. Description Iboga is native to tropical forests, preferring moist soil in partial shade. It bears dark green, narrow leaves and clusters of white tubular flowers on an erect and branching stem, with yellow-orange fruits resembling Chili pepper , Normally growing to a height of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids Found In Iboga
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , |
Harmaline
Harmaline is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and beta-carbolines. It is the partly hydrogenated form of harmine. Occurrence in nature Various plants contain harmaline including ''Peganum harmala'' (Syrian rue) as well as the hallucinogenic beverage ayahuasca, which is traditionally brewed using ''Banisteriopsis caapi''. Present at 3% by dry weight, the harmala alkaloids may be extracted from the Syrian rue seeds. Effects Harmaline is a central nervous system stimulant and a "reversible inhibitor of MAO-A ( RIMA)". This means that the risk of a hypertensive crisis, a dangerous high blood pressure crisis from eating tyramine-rich foods such as cheese, is likely lower with harmaline than with irreversible MAOIs such as phenelzine. The harmala alkaloids are psychoactive in humans. Harmaline is shown to act as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Harmaline also stimulates striatal dopamine release in rats at very high dose levels. Since harmaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronaridine
Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga'' and related species, including ''Tabernaemontana divaricata'' for which (under the now obsolete synonym ''Ervatamia coronaria'') it was named. Like ibogaine, (''R'')-coronaridine and (''S'')-coronaridine can decrease intake of cocaine and morphine intake in animals and it may have muscle relaxant and hypotensive activity. Chemistry Congeners Coronaridine congers are important in drug discovery and development due to multiple actions on different targets. They have ability to inhibit Cav2.2 channel, modulate and inhibit subunits of nAChr selectively such as α9α10, α3β4 and potentiate GABAA activity. Pharmacology Coronaridine has been reported to bind to an assortment of molecular sites, including: μ-opioid (Ki = 2.0 μM), δ-opioid (Ki = 8.1 μM), and κ-opioid receptors (Ki = 4.3 μM), NMDA receptor (Ki = 6.24 μM) (as an antagonist), and nAChRs (as an antagonist). It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmaline
Harmaline is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and beta-carbolines. It is the partly hydrogenated form of harmine. Occurrence in nature Various plants contain harmaline including ''Peganum harmala'' (Syrian rue) as well as the hallucinogenic beverage ayahuasca, which is traditionally brewed using ''Banisteriopsis caapi''. Present at 3% by dry weight, the harmala alkaloids may be extracted from the Syrian rue seeds. Effects Harmaline is a central nervous system stimulant and a "reversible inhibitor of MAO-A ( RIMA)". This means that the risk of a hypertensive crisis, a dangerous high blood pressure crisis from eating tyramine-rich foods such as cheese, is likely lower with harmaline than with irreversible MAOIs such as phenelzine. The harmala alkaloids are psychoactive in humans. Harmaline is shown to act as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Harmaline also stimulates striatal dopamine release in rats at very high dose levels. Since harmaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronaridine
Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga'' and related species, including ''Tabernaemontana divaricata'' for which (under the now obsolete synonym ''Ervatamia coronaria'') it was named. Like ibogaine, (''R'')-coronaridine and (''S'')-coronaridine can decrease intake of cocaine and morphine intake in animals and it may have muscle relaxant and hypotensive activity. Chemistry Congeners Coronaridine congers are important in drug discovery and development due to multiple actions on different targets. They have ability to inhibit Cav2.2 channel, modulate and inhibit subunits of nAChr selectively such as α9α10, α3β4 and potentiate GABAA activity. Pharmacology Coronaridine has been reported to bind to an assortment of molecular sites, including: μ-opioid (Ki = 2.0 μM), δ-opioid (Ki = 8.1 μM), and κ-opioid receptors (Ki = 4.3 μM), NMDA receptor (Ki = 6.24 μM) (as an antagonist), and nAChRs (as an antagonist). It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-convulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs may block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to the voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GAT-1 GABA transporter, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gated calcium channels, SV2A, and α2δ. By blocking sodium or calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The International Journal Of Biochemistry & Cell Biology
''The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier, covering research in all areas of biochemistry and cell biology. The editor-in-chief is Geoffrey J. Laurent (University of Western Australia). The journal was established in 1970 as ''International Journal of Biochemistry'' and obtained its current title in 1995. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2013 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 4.240. References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, The Publications established in 1970 Biochemistry journals Monthly journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_CIPN21501.jpg)

