|
Hypoesthesia
Hypoesthesia or numbness is a common side effect of various medical conditions that manifests as a reduced sense of touch or sensation, or a partial loss of sensitivity to sensory stimuli. In everyday speech this is generally referred to as numbness. Hypoesthesia primarily results from damage to nerves, and from blockages in blood vessels, resulting in ischemic damage to tissues supplied by the blocked blood vessels. This damage is detectable through the use of various imaging studies. Damage in this way is caused by a variety of different illnesses and diseases. A few examples of the most common illnesses and diseases that can cause hypoesthesia as a side effect are as follows: * Decompression sickness * Trigeminal schwannoma * Rhombencephalitis * Intradural extramedullary tuberculoma of the spinal cord * Cutaneous sensory disorder * Beriberi Diseases Decompression sickness Decompression sickness occurs during rapid ascent, spanning 20 or more feet (typically from under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysesthesia
Dysesthesia is an unpleasant, abnormal sense of touch. Its etymology comes from the Greek word "dys," meaning "bad," and "aesthesis," which means "sensation" (abnormal sensation). It often presents as pain Joseph J. Marbach, Joseph Marbach hypothesized that the symptoms were rooted in psychiatric disorders. Marbach suggested that occlusal dysesthesia would occur in patients with underlying psychological problems (such as schizophrenia) after having undergone dental treatment. More recently, two studies have found that occlusal dysesthesia is associated with somatoform disorders in which the patients obsess over the oral sensations. Similarly, Marbach later proposed that occlusal dysesthesia may be caused by the brain “talking to itself,” causing abnormal oral sensations in the absence of external stimuli. According to this model, the symptoms of dysesthesia are catalyzed by dental “amputation,” for example the extraction of a tooth, whereby the brain loses the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the '' International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM ( DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
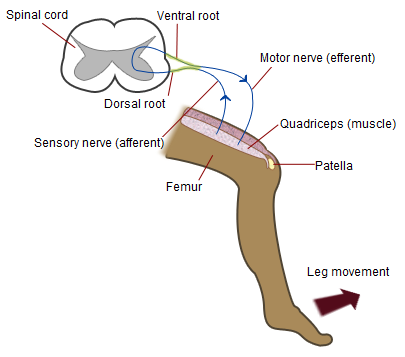
Spinal Nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve fibers from its dorsal and ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent sensory root and carries sensory information to the brain. The ventral root is the efferent motor root and carries motor information from the brain. The spinal nerve emerges from the spinal column through an opening ( intervertebral foramen) between adjacent verteb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paresthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias are usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occur in the arms and legs. The most familiar kind of paresthesia is the sensation known as "pins and needles" after having a limb "fall asleep". A less well-known and uncommon paresthesia is formication, the sensation of insects crawling on the skin. Causes Transient Paresthesias of the hands, feet, legs, and arms are common transient symptoms. The briefest electric shock type of paresthesia can be caused by tweaking the ulnar nerve near the elbow; this phenomenon is colloquially known as bumping one's "funny bone". Similar brief shocks can be experienced when any other nerve is tweaked (e.g. a pinched neck nerve may cause a brief shock-like paresthesia toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperesthesia
Hyperesthesia is a condition that involves an abnormal increase in sensitivity to stimuli of the sense. Stimuli of the senses can include sound that one hears, foods that one tastes, textures that one feels, and so forth. Increased touch sensitivity is referred to as "tactile hyperesthesia", and increased sound sensitivity is called "auditory hyperesthesia". In the context of pain hyperaesthesia can refer to an increase in sensitivity where there is both allodynia and hyperalgesia. In psychology, Jeanne Siaud-Facchin uses the term by defining it as an "exacerbation des sens" that characterizes gifted individuals: for them, the sensory information reaches the brain much faster than the average, and the information is processed in a significantly shorter time. Other animals Feline hyperesthesia syndrome is an uncommon but recognized condition in cats, particularly Siamese, Burmese, Himalayan, and Abyssinian cats. It can affect cats of all ages, though it is most prevalent durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphia
Anaphia, also known as tactile anesthesia, is a medical symptom in which there is a total or partial absence of the sense of touch. Anaphia is a common symptom of spinal cord injury and neuropathy. See also * Dysesthesia * Hyperesthesia * Hypoesthesia Hypoesthesia or numbness is a common side effect of various medical conditions that manifests as a reduced sense of touch or sensation, or a partial loss of sensitivity to sensory stimuli. In everyday speech this is generally referred to as nu ... References Symptoms and signs of mental disorders Symptoms and signs: Nervous and musculoskeletal systems Neurological disorders Anesthesia {{symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patellar Reflex
The patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord. Mechanism Striking of the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer just below the patella stretches the muscle spindle in the quadriceps muscle. This produces a signal which travels back to the spinal cord and synapses (without interneurons) at the level of L3 or L4 in the spinal cord, completely independent of higher centres. From there, an alpha motor neuron conducts an efferent impulse back to the quadriceps femoris muscle, triggering contraction. This contraction, coordinated with the relaxation of the antagonistic flexor hamstring muscle causes the leg to kick. There is a latency of around 18 ms between stretch of the patellar tendon and the beginning of contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle. This is a reflex of proprioception which helps maintain posture and balance, allowing to keep one's balance with little effort or cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, physician assistant, a certified nur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiamine are required for some metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of glucose and amino acids. Food sources of thiamine include whole grains, legumes, and some meats and fish. Grain processing removes much of the vitamin content, so in many countries cereals and flours are enriched with thiamine. Supplements and medications are available to treat and prevent thiamine deficiency and disorders that result from it include beriberi and Wernicke encephalopathy. They are also used to treat maple syrup urine disease and Leigh syndrome. Supplements and medications are typically taken by mouth, but may also be given by intravenous or intramuscular injection. Thiamine supplements are generally well tolerated. Allergic reactions, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beriberi
Thiamine deficiency is a medical condition of low levels of thiamine (Vitamin B1). A severe and chronic form is known as beriberi. The two main types in adults are wet beriberi and dry beriberi. Wet beriberi affects the cardiovascular system, resulting in a fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and leg swelling. Dry beriberi affects the nervous system, resulting in numbness of the hands and feet, confusion, trouble moving the legs, and pain. A form with loss of appetite and constipation may also occur. Another type, acute beriberi, found mostly in babies, presents with loss of appetite, vomiting, lactic acidosis, changes in heart rate, and enlargement of the heart. Risk factors include a diet of mostly white rice, alcoholism, dialysis, chronic diarrhea, and taking high doses of diuretics. In rare cases, it may be due to a genetic condition that results in difficulties absorbing thiamine found in food. Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome are forms of dry beri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |