|
History Of Berlin
The history of Berlin starts with its foundation in the 14th century. It became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1417, and later of Brandenburg-Prussia, and the Kingdom of Prussia. Prussia grew about rapidly in the 18th and 19th centuries and formed the basis of the German Empire in 1871. The empire would survive until 1918 when it was defeated in World War I. After 1900 Berlin became a major world city, known for its leadership roles in science, the humanities, music, museums, higher education, government, diplomacy and military affairs. It also had a role in manufacturing and finance. During World War II, bombing, artillery, and ferocious street-by-street fighting destroyed large parts of Berlin. Berlin was subsequently divided among the four major Allied powers and for over four decades it encapsulated the Cold War confrontation between West and East. With the reunification of Germany in 1990, Berlin was restored as the capital and as a major world city. Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Ludwig Kirchner - Brandenburger Tor
Ernst is both a surname and a given name, the German, Dutch, and Scandinavian form of Ernest. Notable people with the name include: Surname * Adolf Ernst (1832–1899) German botanist known by the author abbreviation "Ernst" * Anton Ernst (1975-) South African Film Producer * Alice Henson Ernst (1880-1980), American writer and historian * Britta Ernst (born 1961), German politician * Cornelia Ernst, German politician * Edzard Ernst, German-British Professor of Complementary Medicine * Emil Ernst, astronomer * Ernie Ernst (1924/25–2013), former District Judge in Walker County, Texas * Eugen Ernst (1864–1954), German politician * Fabian Ernst, German soccer player * Gustav Ernst, Austrian writer * Heinrich Wilhelm Ernst, Moravian violinist and composer * Jim Ernst, Canadian politician * Jimmy Ernst, American painter, son of Max Ernst * Joni Ernst, U.S. Senator from Iowa * K.S. Ernst, American visual poet * Karl Friedrich Paul Ernst, German writer (1866–1933) * Ken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river in the present-day Havelland region of Brandenburg in eastern Germany from the 8th century onwards. West Slavic tribes (" Wends") had settled in the ''Germania Slavica'' region from the 7th century onwards. The ''Hehfeldi'' as they were called by the Bavarian Geographer about 850 built their main fortification at Brenna (later to become Brandenburg an der Havel) and a large eastern outpost at the current site of Spandau. In 906 the Hevelli princess Drahomíra married the Přemyslid duke Vratislaus I of Bohemia. Baçlabič was the prince of Hevelli from 921-936. Brenna was occupied by the German king Henry the Fowler in his 928/29 Slavic campaign and incorporated into the '' Marca Geronis''. Henry's successor Otto I in 948 establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries destabilised the settlement. While most modern commentators accept differences over religion and Imperial authority were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Town Rights
The German town law (german: Deutsches Stadtrecht) or German municipal concerns (''Deutsches Städtewesen'') was a set of early town privileges based on the Magdeburg rights developed by Otto I. The Magdeburg Law became the inspiration for regional town charters not only in Germany, but also in Central and Eastern Europe who modified it during the Middle Ages. The German town law (based on Magdeburg rights) was used in the founding of many German cities, towns, and villages beginning in the 13th century. History As Germans began establishing towns throughout northern Europe as early as the 10th century, they often received town privileges granting them autonomy from local secular or religious rulers. Such privileges often included the right to self-governance, economic autonomy, criminal courts, and militia. Town laws were more or less entirely copied from neighboring towns, such as the Westphalian towns of Soest, Dortmund, Minden, and Münster. As Germans began settling east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Island
The Museum Island (german: Museumsinsel) is a museum complex on the northern part of the Spree Island in the historic heart of Berlin. It is one of the most visited sights of Germany's capital and one of the most important museum sites in Europe. Built from 1830 to 1930 by order of the Prussian Kings according to plans by five architects, Museum Island was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999 because of its testimony to the architectural and cultural development of museums in the 19th and 20th centuries. It consists of the Altes Museum, the Neues Museum, the Alte Nationalgalerie, the Bode-Museum and the Pergamonmuseum. As Museum Island includes all of Spree Island north of the Unter den Linden, the Berliner Dom is also located here, near the Lustgarten. To the south, the reconstructed Berlin Palace houses the Humboldt Forum museum and opened in 2020. Since German reunification, the Museum Island has been rebuilt and extended according to a master plan. In 2019, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
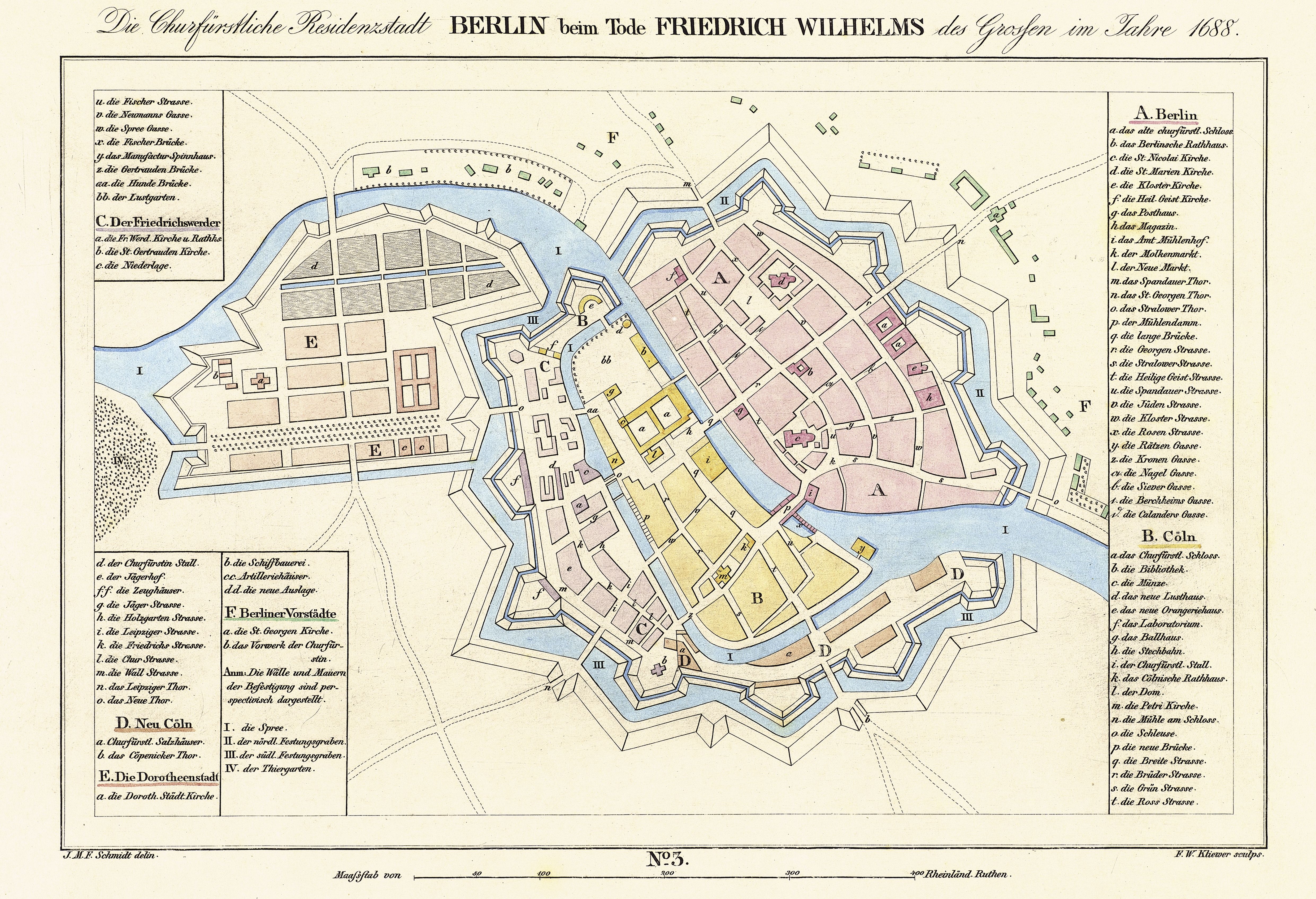
Cölln
Cölln () was the twin city of Old Berlin ( Altberlin) from the 13th century to the 18th century. Cölln was located on the Fisher Island section of Spree Island, opposite Altberlin on the western bank of the River Spree, until the cities were merged by Frederick I of Prussia to form Berlin in 1710. Today, the former site of Cölln is the historic core of the modern Mitte locality of the Berlin-Mitte borough in central Berlin. History Cölln is first mentioned in a 1237 deed, denoting a priest Symeon of Cölln's (Symeon de Colonia) Saint Peter's Church as a witness. This date is commonly regarded as the origin of Berlin, though Altberlin on the eastern bank of the Spree river was not mentioned before 1244 and parts of modern Greater Berlin, such as Spandau and Köpenick, are even older. Cölln and Altberlin were separated only by the river Spree, linked by the ''Mühlendamm'' causeway, hence there was a close connection right from the start. Since the trade route from Magd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolaiviertel
Founded about 1200, the (Nicholas' Quarter) of Alt-Berlin, together with nearby Cölln, jointly make up the reconstructed historical heart of the German capital of Berlin. It is located in Mitte locality (in the homonymous district), five minutes away from Alexanderplatz. Geography Situated on the eastern shore of the river Spree, it is bounded by the streets ''Rathausstraße'', ''Spandauer Straße'' and ''Mühlendamm''. The neighborhood itself is named for the eponymous deconsecrated Nikolaikirche ("Saint Nicholas Church") at its heart, i.e. Berlin's oldest church. History The two settlements of Old Berlin as well as Cölln on the other side of the Spree originated along an old trade route, the ''Mühlendamm'' (Mills Dam), a ford where the river could be easily crossed. The Nicholas' Church, originally a late Romanesque basilica, was erected about 1230. The area around the church with its medieval alleys in the main had been preserved throughout the centuries, until it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alt-Berlin
Alt-Berlin ("Old Berlin"), also spelled ''Altberlin'', is a neighborhood (''Stadtviertel''), situated in the Berliner locality (''Ortsteil'') of Mitte, part of the homonymous borough. In the 13th century it was the sister town of the old Cölln, located on the northern Spree Island in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. It counts in its territory the zone of Nikolaiviertel. History First mentioned in 1244, 7 years after Cölln, it represents the original core of the modern Berlin. The first stone fortification was built, to defend both cities, in 1250 and in 1251 it gained city rights. In 1280 Berlin, gained the right to mint currency. In that period it appeared on a coat of arms for the first time, close to the symbol of the imperial eagle, two stylized bears, antecedents of the bear currently serving as the symbol of the city. On 20 March 1307 the town was united with Cölln (maintaining its name, Berlin) forming a trading union on political and security matters, and parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert The Bear
Albert the Bear (german: Albrecht der Bär; 1100 – 18 November 1170) was the first margrave of Brandenburg from 1157 to his death and was briefly duke of Saxony between 1138 and 1142. Life Albert was the only son of Otto, Count of Ballenstedt, and Eilika, daughter of Magnus Billung, Duke of Saxony. He inherited his father's valuable estates in northern Saxony in 1123, and on his mother's death, in 1142, succeeded to one-half of the lands of the house of Billung. Albert was a loyal vassal of his relation, Lothar I, Duke of Saxony, from whom, about 1123, he received the Margraviate of Lusatia, to the east; after Lothar became King of the Germans, he accompanied him on a disastrous expedition to Bohemia against the upstart, Soběslav I, Duke of Bohemia in 1126 at the Battle of Kulm, where he suffered a short imprisonment. Albert's entanglements in Saxony stemmed from his desire to expand his inherited estates there. After the death of his brother-in-law, Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |