|
Hexactinellida
Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma. Some experts believe glass sponges are thlongest-lived animals on earth these scientists tentatively estimate a maximum age of up to 15,000 years. Biology Glass sponges are relatively uncommon and are mostly found at depths from below the sea level. Although the species '' Oopsacas minuta'' has been found in shallow water, others have been found much deeper. They are found in all oceans of the world, although they are particularly common in Antarctic and Northern Pacific waters. They are more-or-less cup-shaped animals, ranging from in height, with sturdy lattice-like internal skeletons made up of fused spicules of silica. The body is relatively symmetrical, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porifera
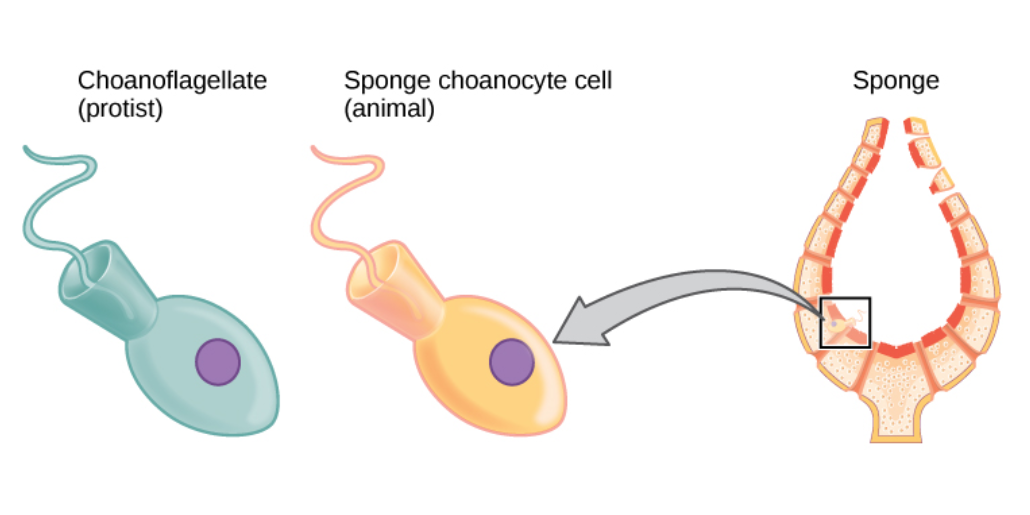
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spicule (sponge)
Spicules are structural elements found in most sponges. The meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators. Sponge spicules are made of calcium carbonate or silica. Large spicules visible to the naked eye are referred to as megascleres, while smaller, microscopic ones are termed microscleres. The composition, size, and shape of spicules are major characters in sponge systematics and taxonomy. Overview Sponges are a species-rich clade of the earliest-diverging (most basal) animals. They are distributed globally, with diverse ecologies and functions, and a record spanning at least the entire Phanerozoic. Most sponges produce skeletons formed by spicules, structural elements that develop in a wide variety of sizes and three dimensional shapes. Among the four sub-clades of Porifera, three ( Demospongiae, Hexactinellida, and Homoscleromorpha) produce skeletons of amorphous sil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staurocalyptus
''Staurocalyptus'' is a genus of sponge. It was circumscribed in 1897 by Isao Ijima. Taxonomy Ijima circumscribed ''Staurocalyptus'' as a genus in the family Rossellidae. His initial taxonomy included three newly described species and two transferred from ''Rhabdocalyptus''. Ijimi did not designate a type species; in 1967 V. M. Koltun designated ''Rhabdocalyptus dowlingi'' as the type species. A 2002 revision of Rossellidae by K. R. Tabachnick demoted ''Staurocalyptus'' to be a subgenus of '' Acanthascus'' and designated a new type species: ''Staurocalyptus glaber'' . However, , WoRMS Worms may refer to: *Worm, an invertebrate animal with a tube-like body and no limbs Places *Worms, Germany Worms () is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, situated on the Upper Rhine about south-southwest of Frankfurt am Main. It had ... still classifies ''Staurocalyptus'' as a genus and follows Koltun's type species designation, not that of Tabachnick. Distribution Its species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus' Flower Basket
The Venus' flower basket (''Euplectella aspergillum'') is a glass sponge in the phylum Porifera. It is a marine sponge found in the deep waters of the Pacific ocean, usually at depths below 500 meters. Like other sponges, they feed by filtering sea water to capture plankton and marine snow. Similar to other glass sponges, they build their skeletons out of silica, which forms a unique lattice structure of spicules. The sponges are usually between 10 cm and 30 cm tall, and their bodies act as refuge for their mutualist shrimp partners. This body structure is of great interest in materials science as the optical and mechanical properties are in some ways superior to man-made materials. Little is known regarding their reproduction habits, however fluid dynamics of their body structure likely influence reproduction and it is hypothesized that they may be hermaphroditic. Habitat Venus' flower baskets are found in the western Pacific Ocean nearby the Philippine Islands. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus Flower Basket
The Venus' flower basket (''Euplectella aspergillum'') is a glass sponge in the phylum Porifera. It is a marine sponge found in the deep waters of the Pacific ocean, usually at depths below 500 meters. Like other sponges, they feed by filtering sea water to capture plankton and marine snow. Similar to other glass sponges, they build their skeletons out of silica, which forms a unique lattice structure of spicules. The sponges are usually between 10 cm and 30 cm tall, and their bodies act as refuge for their mutualist shrimp partners. This body structure is of great interest in materials science as the optical and mechanical properties are in some ways superior to man-made materials. Little is known regarding their reproduction habits, however fluid dynamics of their body structure likely influence reproduction and it is hypothesized that they may be hermaphroditic. Habitat Venus' flower baskets are found in the western Pacific Ocean nearby the Philippine Islands. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)