|
Hemosiderin
Hemosiderin image of a kidney viewed under a microscope. The brown areas represent hemosiderin Hemosiderin or haemosiderin is an iron-storage complex that is composed of partially digested ferritin and lysosomes. The breakdown of heme gives rise to biliverdin and iron. The body then traps the released iron and stores it as hemosiderin in tissues. Hemosiderin is also generated from the abnormal metabolic pathway of ferritin. It is only found within cells (as opposed to circulating in blood) and appears to be a complex of ferritin, denatured ferritin and other material. The iron within deposits of hemosiderin is very poorly available to supply iron when needed. Hemosiderin can be identified histologically with ''Perls' Prussian blue stain''; iron in hemosiderin turns blue to black when exposed to potassium ferrocyanide. In normal animals, hemosiderin deposits are small and commonly inapparent without special stains. Excessive accumulation of hemosiderin is usually detected within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. It is the primary ''intracellular iron-storage protein'' in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, keeping iron in a soluble and non-toxic form. In humans, it acts as a buffer against iron deficiency and iron overload. Ferritin is found in most tissues as a cytosolic protein, but small amounts are secreted into the serum where it functions as an iron carrier. Plasma ferritin is also an indirect marker of the total amount of iron stored in the body; hence, serum ferritin is used as a diagnostic test for iron-deficiency anemia. Aggregated ferritin transforms into a toxic form of iron called hemosiderin. Ferritin is a globular protein complex consisting of 24 protein subunits forming a hollow nanocage with multiple metal–protein interactions. Ferritin th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
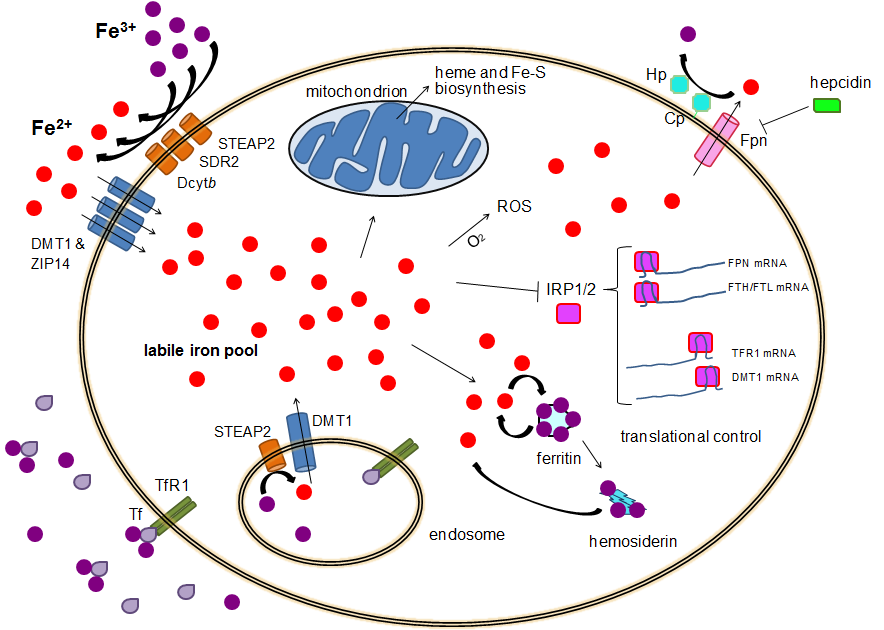
Iron Metabolism
Human iron metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that maintain human homeostasis of iron at the systemic and cellular level. Iron is both necessary to the body and potentially toxic. Controlling iron levels in the body is a critically important part of many aspects of human health and disease. Hematologists have been especially interested in systemic iron metabolism because iron is essential for red blood cells, where most of the human body's iron is contained. Understanding iron metabolism is also important for understanding diseases of iron overload, such as hereditary hemochromatosis, and iron deficiency, such as iron-deficiency anemia. Importance of iron regulation Iron is an essential bioelement for most forms of life, from bacteria to mammals. Its importance lies in its ability to mediate electron transfer. In the ferrous state (Fe2+), iron acts as an electron donor, while in the ferric state (Fe3+) it acts as an acceptor. Thus, iron plays a vital role in the catalys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perls' Prussian Blue
In histology, histopathology, and clinical pathology, Perls Prussian blue is a commonly used method to detect the presence of iron in tissue or cell samples. Perls Prussian Blue derives its name from the German pathologist Max Perls (1843–1881), who described the technique in 1867. The method does not involve the application of a dye, but rather causes the pigment Prussian blue to form directly within the tissue. The method stains mostly iron in the ferric state which includes ferritin and hemosiderin, rather than iron in the ferrous state. Uses Perls's method is used to indicate "non-heme" iron in tissues such as ferritin and hemosiderin, the procedure does not stain iron that is bound to porphyrin forming heme such as hemoglobin and myoglobin. The stain is an important histochemical stain used to demonstrate the distribution and amount of iron deposits in liver tissue, often in the form of a biopsy. Perls's procedure may be used to identify excess iron deposits such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biliverdin
Biliverdin ( latin for green bile) is a green tetrapyrrolic bile pigment, and is a product of heme catabolism.Boron W, Boulpaep E. Medical Physiology: a cellular and molecular approach, 2005. 984-986. Elsevier Saunders, United States. It is the pigment responsible for a greenish color sometimes seen in bruises. Metabolism Biliverdin results from the breakdown of the heme moiety of hemoglobin in erythrocytes. Macrophages break down senescent erythrocytes and break the heme down into biliverdin along with hemosiderin, in which biliverdin normally rapidly reduces to free bilirubin. Biliverdin is seen briefly in some bruises as a green color. In bruises, its breakdown into bilirubin leads to a yellowish color. Role in disease Biliverdin has been found in excess in the blood of humans suffering from hepatic diseases. Jaundice is caused by the accumulation of biliverdin or bilirubin (or both) in the circulatory system and tissues. Jaundiced skin and sclera (whites of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononuclear Phagocyte System
In immunology, the mononuclear phagocyte system or mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS) also known as the reticuloendothelial system or macrophage system is a part of the immune system that consists of the phagocytic cells located in reticular connective tissue. The cells are primarily monocytes and macrophages, and they accumulate in lymph nodes and the spleen. The Kupffer cells of the liver and tissue histiocytes are also part of the MPS. The mononuclear phagocyte system and the monocyte macrophage system refer to two different entities, often mistakenly understood as one. "Reticuloendothelial system" is an older term for the mononuclear phagocyte system, but it is used less commonly now, as it is understood that most endothelial cells are not macrophages. The mononuclear phagocyte system is also a somewhat dated concept trying to combine a broad range of cells, and should be used with caution. Cell types and locations The spleen is the second largest unit of the mononuclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense ( innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the rup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocytes) of almost all vertebrates (the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (''e.g.'' lungs or gills) to the rest of the body (''i.e.'' tissues). There it releases the oxygen to permit aerobic respiration to provide energy to power functions of an organism in the process called metabolism. A healthy individual human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. In mammals, the chromoprotein makes up about 96% of the red blood cells' dry content (by weight), and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL O2 per gram, which increases the total blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology Of Siderophage In Chronic Pulmonary Congestion
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία ''-logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can result in feeling tired and pale skin. There may also be bone problems, an enlarged spleen, yellowish skin, and dark urine. Slow growth may occur in children. Thalassemias are genetic disorders inherited from a person's parents. There are two main types, alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia. The severity of alpha and beta thalassemia depends on how many of the four genes for alpha globin or two genes for beta globin are missing. Diagnosis is typically by blood tests including a complete blood count, special hemoglobin tests, and genetic tests. Diagnosis may occur before birth through prenatal testing. Treatment depends on the type and severity. Treatment for those with more severe disease often includes regular blood transfusions, iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years. Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene (''HBB'') that makes haemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each haemoglobin gene. An attack can be set off by temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |