|
Helmholtz Resonance
Helmholtz resonance or wind throb is the phenomenon of air resonance in a cavity, such as when one blows across the top of an empty bottle. The name comes from a device created in the 1850s by Hermann von Helmholtz, the ''Helmholtz resonator'', which he used to identify the various frequencies or musical pitches present in music and other complex sounds.Helmholtz, Hermann von (1885), ''On the sensations of tone as a physiological basis for the theory of music'' Second English Edition, translated by Alexander J. Ellis. London: Longma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz Resonator
Helmholtz resonance or wind throb is the phenomenon of air resonance in a cavity, such as when one blows across the top of an empty bottle. The name comes from a device created in the 1850s by Hermann von Helmholtz, the ''Helmholtz resonator'', which he used to identify the various frequencies or musical pitches present in music and other complex sounds.Helmholtz, Hermann von (1885), ''On the sensations of tone as a physiological basis for the theory of music'' Second English Edition, translated by Alexander J. Ellis. London: Longman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance Frequency
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buell Motorcycle Company
Buell Motorcycles is an American motorcycle manufacturer based in Grand Rapids, Michigan, United States. It was founded in 1983 by ex-Harley-Davidson engineer Erik Buell. Harley-Davidson acquired 49% of Buell in 1993, and Buell became a wholly owned subsidiary of Harley-Davidson by 2003. On November 17, 2006, Buell announced that it had produced and shipped its 100,000th motorcycle. On October 15, 2009, Harley-Davidson announced the discontinuation of the Buell product line as part of its strategy to focus on the Harley-Davidson brand. The last Buell motorcycle produced through Harley-Davidson was in October 30, 2009, bringing the number manufactured to 136,923. In November 2009, Erik Buell announced the launch of Erik Buell Racing, an independent company run by Erik Buell which initially produced race-only versions of the 1125R model, then subsequently offered an updated 1190RS model for the street or the track, and produced further improved 1190RX and 1190SX models which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, craft, science and technology have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subwoofers
A subwoofer (or sub) is a loudspeaker designed to reproduce low-pitched audio frequencies known as bass and sub-bass, lower in frequency than those which can be (optimally) generated by a woofer. The typical frequency range for a subwoofer is about 20–200 Hz for consumer products, below 100 Hz for professional live sound, and below 80 Hz in THX-certified systems. Subwoofers are never used alone, as they are intended to ''augment'' the low-frequency range of loudspeakers that cover the higher frequency bands. While the term "subwoofer" technically only refers to the speaker driver, in common parlance, the term often refers to a subwoofer driver mounted in a speaker enclosure (cabinet), often with a built-in amplifier. Subwoofers are made up of one or more woofers mounted in a loudspeaker enclosure—often made of wood—capable of withstanding air pressure while resisting deformation. Subwoofer enclosures come in a variety of designs, including bass reflex (wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbox
An airbox is an empty chamber on the inlet of most combustion engines. It collects air from outside and feeds it to the intake hoses of each cylinder. Older engines drew air directly from the surroundings into each individual carburetor. Modern engines instead draw air into an airbox, which is connected by individual hoses to each carburetor or directly to the intake ports in fuel-injected engines, thus avoiding an extra intake manifold. The airbox allows the use of one air filter instead of multiples, reducing complexity. Developments arising from concerns about engine emissions during the late 1970s allow the airbox to collect pump gases from the crankcase and the tank air vent and re-feed them to the engine. Developments Since the 1990s, engine designers also sought to exploit the properties of oscillating gas to improve performance. Many high-performance motorcycles have the airbox fed from funnels in the front of the bike, where increased pressure forces more air into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jalopnik
G/O Media Inc. is an American media holding company that runs ''Gizmodo'', ''Kotaku'', ''Jalopnik'', '' Deadspin'', ''Lifehacker'', '' Jezebel'', '' The Root'', '' The A.V. Club'', ''The Takeout'', '' The Onion'', and ''The Inventory''. History G/O was formed in April 2019 when Great Hill Partners, a private equity firm, purchased the websites from Univision for $20.6 million. Prior to the sale, the former Gawker Media properties had operated as Gizmodo Media Group after being acquired by Univision following the conclusion of the '' Bollea v. Gawker'' lawsuit and subsequent bankruptcy in 2016. Former ''Forbes'' executive Jim Spanfeller became the CEO of G/O Media. Conflict with leadership G/O Media's leadership, introduced after the purchase from Univision, has been subject to frequent criticism by employees. Complaints include closer advertiser relationships, a lack of diversity, and suppression of reporting about the company itself. In October 2019 Deadspin's editor-in-ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
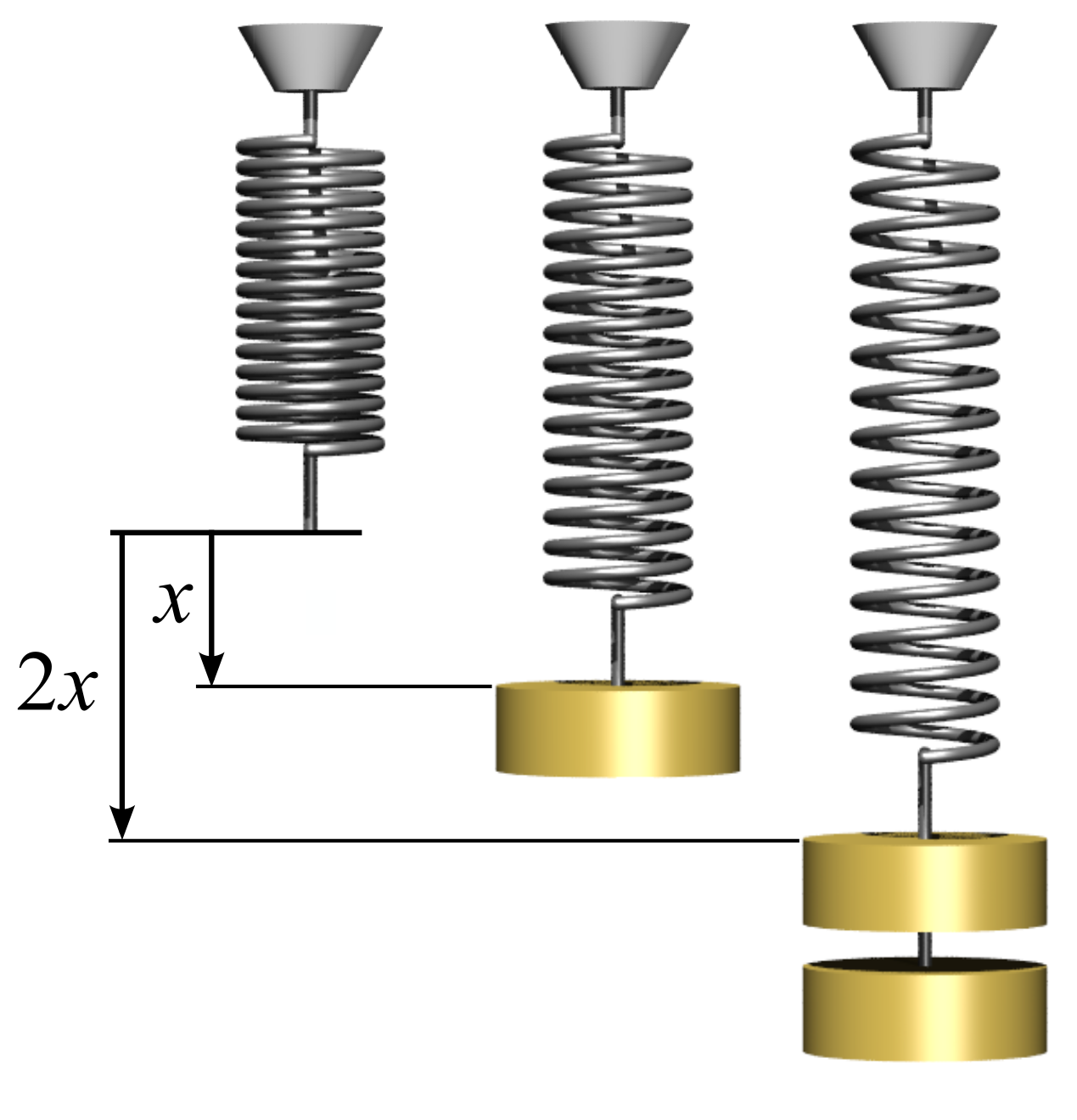
Spring Constant
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance () scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elastic body is deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string of a guitar. An elastic body or material for which this equation can be assumed is said to be linear-elastic or Hookean. Hooke's law is on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or one kilometre in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At , the speed of sound in air is about . The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in ordinary air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In colloquial speech, ''speed of sound'' refers to the speed of sound waves in air. However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at in air, it travels at in water (almost 4.3 times as fast) and at in iron (almost 15 times as fast). In an exceptionally stiff material such as diamond, sound travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter, , is a commonly used term when handling flow in non-circular tubes and channels. Using this term, one can calculate many things in the same way as for a round tube. When the cross-section is uniform along the tube or channel length, it is defined as : D_\text = \frac, where : is the cross-sectional area of the flow, : is the wetted perimeter of the cross-section. More intuitively, the hydraulic diameter can be understood as a function of the hydraulic radius , which is defined as the cross-sectional area of the channel divided by the wetted perimeter. Here, the wetted perimeter includes all surfaces acted upon by shear stress from the fluid. : R_\text = \frac, : D_\text = 4R_\text, Note that for the case of a circular pipe, : D_\text =\frac=2R The need for the hydraulic diameter arises due to the use of a single dimension in case of dimensionless quantity such as Reynolds number, which prefer a single variable for flow analysis rather than the set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Correction
Whenever a wave forms through a medium/object (organ pipe) with a closed/open end, there is a chance of error in the formation of the wave, i.e. it may not actually start from the opening of the object but instead before the opening, thus resulting on an error when studying it theoretically. Hence an end correction is sometimes required to appropriately study its properties. The end correction depends on the radius of the object. An acoustic pipe, such as an organ pipe, marimba, or flute resonates at a specific pitch or frequency. Longer pipes resonate at lower frequencies, producing lower-pitched sounds. The details of acoustic resonance are taught in many elementary physics classes. In an ideal tube, the wavelength of the sound produced is directly proportional to the length of the tube. A tube which is open at one end and closed at the other produces sound with a wavelength equal to four times the length of the tube. A tube which is open at both ends produces sound whose wavelen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_-_filtered.jpg)