|
Hedge End
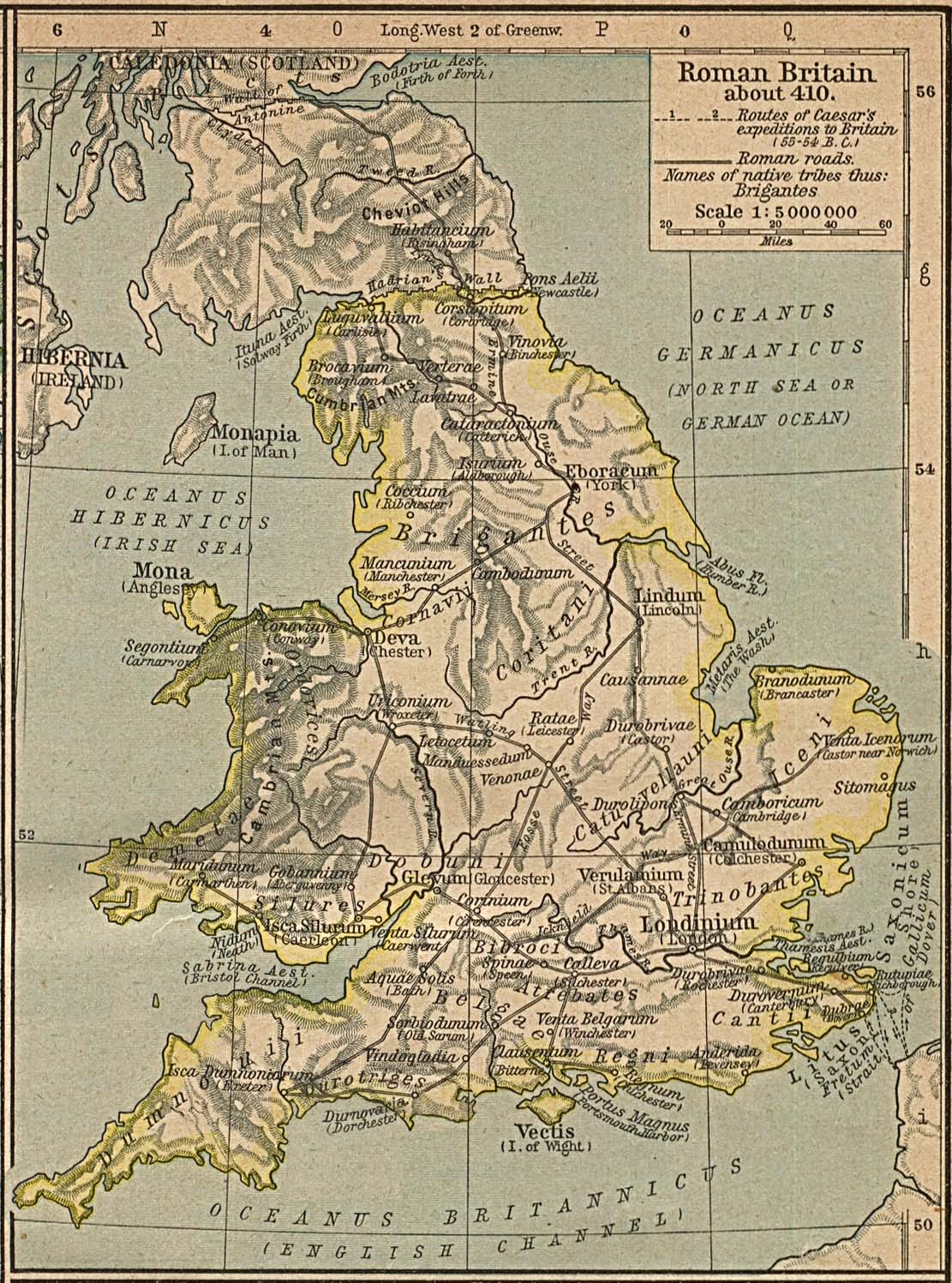
Hedge End is a town and civil parish in Hampshire, England. Situated to the east of the City of Southampton, it adjoins the districts of West End and Botley. Hedge End lies within the Borough of Eastleigh and is part of the Southampton Urban Area. The original hamlet developed on Botley Common after 1250 when it was granted to the men of Botley as common pasture. In 1267, royal charters allowed Botley to hold an annual fair and a weekly market on the common which eventually became a market town. History Origins The Belgae tribe inhabited the Hedge End area prior to the Roman conquest. A Roman road from Clausentum (a fortified harbour in what is now Bitterne, Southampton) passed through the area on route to Portus Adurni (Portchester Castle) and Noviomagus Reginorum (Chichester).The Changing Face of Hedge End. Joyce B Blyth The crossing of the River Itchen at Mansbridge and the crossing of the River Hamble at Botley date to AD932. The road that linked those two rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastleigh (UK Parliament Constituency)
Eastleigh is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2019 by Paul Holmes, a Conservative. Constituency profile The seat forms part of the South Hampshire conurbation between Southampton and Portsmouth, including the railway town of Eastleigh itself, the postwar Hedge End and the Hamble peninsula which is known for boat building and sailing. Residents' health and wealth are around average for the UK. Boundaries 1955–1974: The Borough of Eastleigh, in the Rural District of New Forest the parishes of Eling and Netley Marsh, in the Rural District of Romsey and Stockbridge the parishes of Ampfield, Chilworth, North Baddesley, and Nursling and Rownhams, and in the Rural District of Winchester the parishes of Botley, Bursledon, Hamble, Hedge End, Hound, and West End. 1974–1983: The Boroughs of Eastleigh and Romsey, in the Rural District of Romsey and Stockbridge the parishes of Ampfield, Braishfield, Chilworth, Melchet Park and Plaitford, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Itchen, Hampshire
The River Itchen in Hampshire, England, rises to the south of New Alresford and flows to meet Southampton Water below the Itchen Bridge. The Itchen Navigation was constructed in the late 17th and early 18th centuries to enable barges to reach Winchester from Southampton Docks, but ceased to operate in the mid-19th century and is largely abandoned today. The river is one of the world's premier chalk streams for fly fishing, amenable to dry fly or nymphing. The local chalk aquifer has excellent storage and filtration and the river has long been used for drinking water. Watercress thrives in its upper reaches. Much of the river from its source to Swaythling is classified as a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), and a Special Area of Conservation, of which the Hockley Meadows nature reserve is a part. The Itchen estuary is part of the separate Lee-on-The Solent to Itchen Estuary SSSI. Etymology and other name The name is likely from a Brittonic language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St John's Church, Hedge End
Hedge End is a town and civil parish in Hampshire, England. Situated to the east of the City of Southampton, it adjoins the districts of West End and Botley. Hedge End lies within the Borough of Eastleigh and is part of the Southampton Urban Area. The original hamlet developed on Botley Common after 1250 when it was granted to the men of Botley as common pasture. In 1267, royal charters allowed Botley to hold an annual fair and a weekly market on the common which eventually became a market town. History Origins The Belgae tribe inhabited the Hedge End area prior to the Roman conquest. A Roman road from Clausentum (a fortified harbour in what is now Bitterne, Southampton) passed through the area on route to Portus Adurni (Portchester Castle) and Noviomagus Reginorum (Chichester).The Changing Face of Hedge End. Joyce B Blyth The crossing of the River Itchen at Mansbridge and the crossing of the River Hamble at Botley date to AD932. The road that linked those two rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolston Ferry
The Woolston Floating Bridge was a cable ferry that crossed the River Itchen in England between hards at Woolston and Southampton from 23 November 1836 until 11 June 1977. It was taken out of service after the new Itchen Bridge was opened. Initially there was one ferry, built and owned by the Floating Bridge Company, increased to two in 1881. In 1934 they were sold to Southampton Corporation.''The Illustrated History of Southampton's Suburbs''. Jim Brown. 2004. . In the 1970s two diesel ferries operated side by side during the day with a single ferry late in the evening. There was a bus terminus at both hards on either side of the crossing, connecting foot passengers with the centre of Southampton and the road to Portsmouth. A maintenance slipway and cradle were built to the North of the Woolston hard to enable the ferries (or "Bridges") to be hauled out of the water. The third (or spare) diesel ferry was often to be found moored off the wires on the Southampton side of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolston, Hampshire
Woolston is a suburb of Southampton, Hampshire, located on the eastern bank of the River Itchen. It is bounded by the River Itchen, Sholing, Peartree Green, Itchen and Weston. The area has a strong maritime and aviation history. The former hamlet grew as new industries, roads and railways came to the area in the Victorian era with Woolston formally incorporated into the borough of Southampton in 1920. History Woolston is believed to originate from ''Olafs tun'', a fortified tun on the East bank of the River Itchen established by the Viking leader Olaf I of Norway in the 10th Century. In the Domesday Book of 1086, the area is recorded as ''Olvestune''. The area now known as Woolston is certain to have received consignments of wool to be ferried across the River Itchen, Hampshire by the inhabitants of Itchen Ferry village. The evolution of ''Olvestune'' into "Woolston" is a result of that trade. The former hamlet grew as new industries, roads and railways came to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northam Bridge
The Northam Bridge is a road bridge across the River Itchen in Southampton, England, linking the suburbs of Northam and Bitterne Manor. The current bridge was the first major prestressed concrete road bridge to be built in the United Kingdom. The bridge carries the A3024 road as a dual carriageway, with two lanes on each carriageway. History Prior to the construction of the Northam Bridge, the southernmost bridge across the River Itchen was at Mansbridge. Mansbridge was the lowest crossing point of the river until the early 18th century, when the Itchen Ferry began operating between Woolston and St Mary's, downriver of Northam. The Northam Bridge was the idea of David Lance, who acquired land in Bitterne and built Chessel House there in 1796. Realising that access to his land was poor, he encouraged the building of a bridge linking Bitterne Manor to Northam, together with roads from the bridge to Botley and a further bridge over the River Hamble in Bursledon (and onwards to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enclosure Acts
The Inclosure Acts, which use an archaic spelling of the word now usually spelt "enclosure", cover enclosure of open fields and common land in England and Wales, creating legal property rights to land previously held in common. Between 1604 and 1914, over 5,200 individual enclosure acts were passed, affecting 28,000 km2. History Before the enclosures in England, a portion of the land was categorized as "common" or "waste". "Common" land was under the control of the lord of the manor, but certain rights on the land such as pasture, pannage, or estovers were held variously by certain nearby properties, or (occasionally) ''in gross'' by all manorial tenants. "Waste" was land without value as a farm strip – often very narrow areas (typically less than a yard wide) in awkward locations (such as cliff edges, or inconveniently shaped manorial borders), but also bare rock, and so forth. "Waste" was not officially used by anyone, and so was often farmed by landless peasants. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th Century
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Land
Common land is land owned by a person or collectively by a number of persons, over which other persons have certain common rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect wood, or to cut turf for fuel. A person who has a right in, or over, common land jointly with another or others is usually called a commoner. In the New Forest, the New Forest Commoner is recognised as a minority cultural identity as well as an agricultural vocation, and members of this community are referred to as Commoners. In Great Britain, common land or former common land is usually referred to as a common; for instance, Clapham Common and Mungrisdale Common. Due to enclosure, the extent of common land is now much reduced from the millions of acres that existed until the 17th century, but a considerable amount of common land still exists, particularly in upland areas. There are over 8,000 registered commons in England alone. Origins Originally in medieval England the common wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |