|
HIV Drug Resistance Database
HIV Drug Resistance Database, also known as ''Stanford HIV RT and Protease Sequence Database'', is a database at Stanford University that tracks 93 common mutations of HIV. It has been recompiled in 2008 listing 93 common mutations, after its initial mutation compilation in 2007 of 80 mutations. The latest list utilizes data from other laboratories in Europe, Canada and the United States including more than 15,000 sequences from untreated individuals. See also * Subtypes of HIV * HIV drug resistance HIV drug resistance occurs when microevolution causes virions to become tolerant to antiretroviral treatments (ART). ART can be used to successfully manage HIV infection, but a number of factors can contribute to the virus mutating and becoming re ... References External links HIV Drug Resistance Database {{HIV/AIDS HIV/AIDS research Medical databases Epidemiology Stanford University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost of Stanford Frederick Terman inspired and supported faculty and graduates' entrepreneu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtypes Of HIV
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey, a vulnerable West African primate. HIV-1 viruses can be further divided into groups M, N, O and P. The HIV-1 group M viruses predominate and are responsible for the AIDS pandemic. Group M can be further subdivided into subtypes based on genetic sequence data. Some of the subtypes are known to be more virulent or are resistant to different medications. Likewise, HIV-2 viruses are thought to be less virulent and transmissible than HIV-1 M group viruses, although HIV-2 is also known to cause AIDS. One of the obstacles to treatment of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is its high genetic variability. Major types HIV-1 HIV-1 is the most common and pathogenic strain of the virus. Over 2 million such infections occur annually. Scientists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
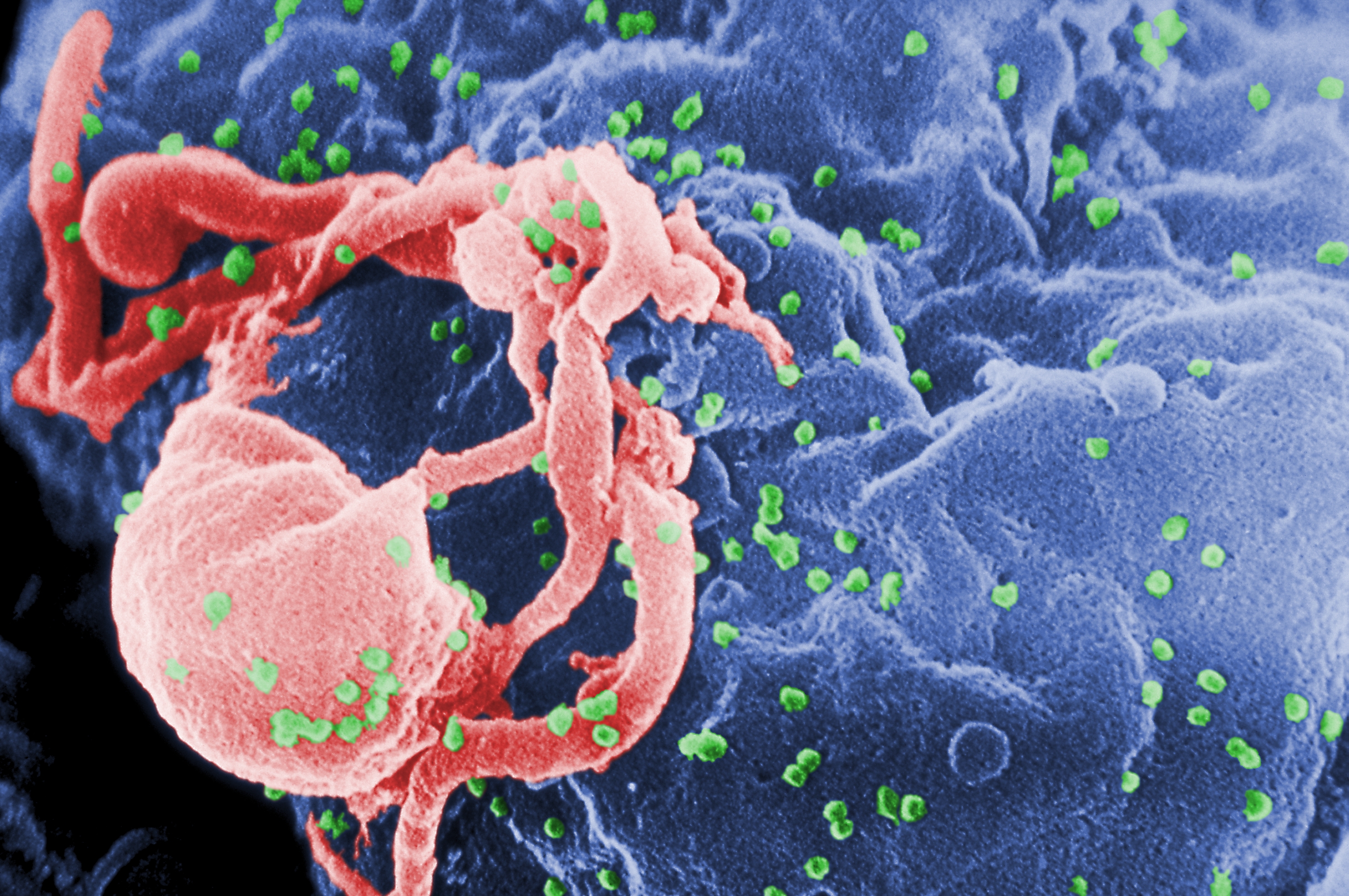
HIV Drug Resistance
HIV drug resistance occurs when microevolution causes virions to become tolerant to antiretroviral treatments (ART). ART can be used to successfully manage HIV infection, but a number of factors can contribute to the virus mutating and becoming resistant. Drug resistance occurs as bacterial or viral populations evolve to no longer respond to medications that previously worked. In the case of HIV, there have been recognized cases of treatment resistant strains since 1989, with drug resistance being a major contributor to treatment failure. While global incidence varies greatly from region to region, there has been a general increase in overall HIV drug resistance. The two main types of resistance, primary and induced, differ mostly in causation, with the biggest cause of resistance being a lack of adherence to the specific details of treatment. These newly created resistant strains of HIV pose a public health issue as they infect a growing number of people because they are harder to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV/AIDS Research
HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV. Transmission A body of scientific evidence has shown that men who are circumcised are less likely to contract HIV than men who are uncircumcised. Research published in 2014 concludes that the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone selectively impact HIV transmission. Pre- and post-exposure prophylaxis "Pre-exposure prophylaxis" refers to the practice of taking some drugs before being exposed to HIV infection, and having a decreased chance of contracting HIV as a result of taking that drug. Post-exposure prophylaxis refers to taking some drugs quickly after being exposed to HIV, while the virus is in a person's body but before the virus has established itself. In both cases, the drugs would be the same as those used to treat persons with HIV, and the intent of tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Databases
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |