|
Grímnismál
''Grímnismál'' (Old Norse: ; 'The Lay of Grímnir') is one of the mythological poems of the ''Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in the Codex Regius manuscript and the AM 748 I 4to fragment. It is spoken through the voice of ''Grímnir'', one of the many guises of the god Odin. The very name suggests guise, or mask or hood. Through an error, King Geirröth tortured Odin-as-Grímnir, a fatal mistake, since Odin caused him to fall upon his own sword. The poem is written mostly in the ljóðaháttr metre, typical for wisdom verse. Structure and history The work starts out with a lengthy prose section describing the circumstances leading up to Grímnir's monologue. The monologue itself comprises 54 stanzas of poetic verse describing the worlds and Odin's many guises. The third and last part of the poem is also prose, a brief description of Geirröth's demise, his son's ascension, and Odin's disappearance. The prose sections were most likely not part of the original oral versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigg
Frigg (; Old Norse: ) is a goddess, one of the Æsir, in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about her, she is associated with marriage, prophecy, clairvoyance and motherhood, and dwells in the wetland halls of Fensalir. In wider Germanic mythology, she is known in Old High German as , in Langobardic as , in Old English as , in Old Frisian as ''Frīa'', and in Old Saxon as , all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *'' Frijjō''. Nearly all sources portray her as the wife of the god Odin. In Old High German and Old Norse sources, she is specifically connected with Fulla, but she is also associated with the goddesses Lofn, Hlín, Gná, and ambiguously with the Earth, otherwise personified as an apparently separate entity Jörð (Old Norse: 'Earth'). The children of Frigg and Odin include the gleaming god Baldr. The English weekday name Friday (ultimately meaning 'Frigg's Day') bears her name. After Christianiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddic Poetry
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic medieval manuscript known as the ''Codex Regius'', which contains 31 poems. The ''Codex Regius'' is arguably the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends. Since the early 19th century, it has had a powerful influence on Scandinavian literature, not only through its stories, but also through the visionary force and the dramatic quality of many of the poems. It has also been an inspiration for later innovations in poetic meter, particularly in Nordic languages, with its use of terse, stress-based metrical schemes that lack final rhymes, instead focusing on alliterative devices and strongly concentrated imagery. Poets who have acknowledged their debt to the ''Codex Regius'' include Vilhelm Ekelund, August Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
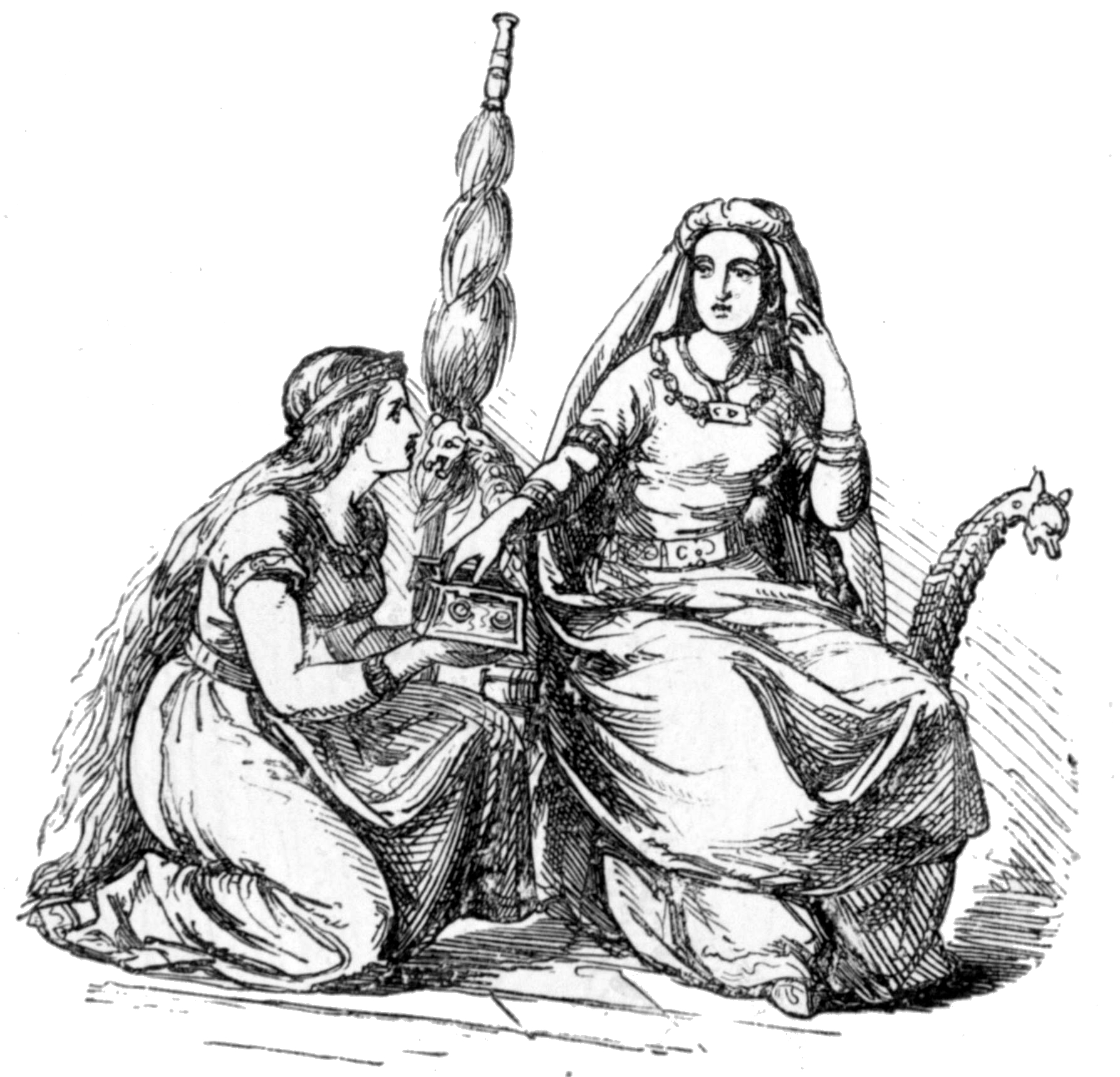
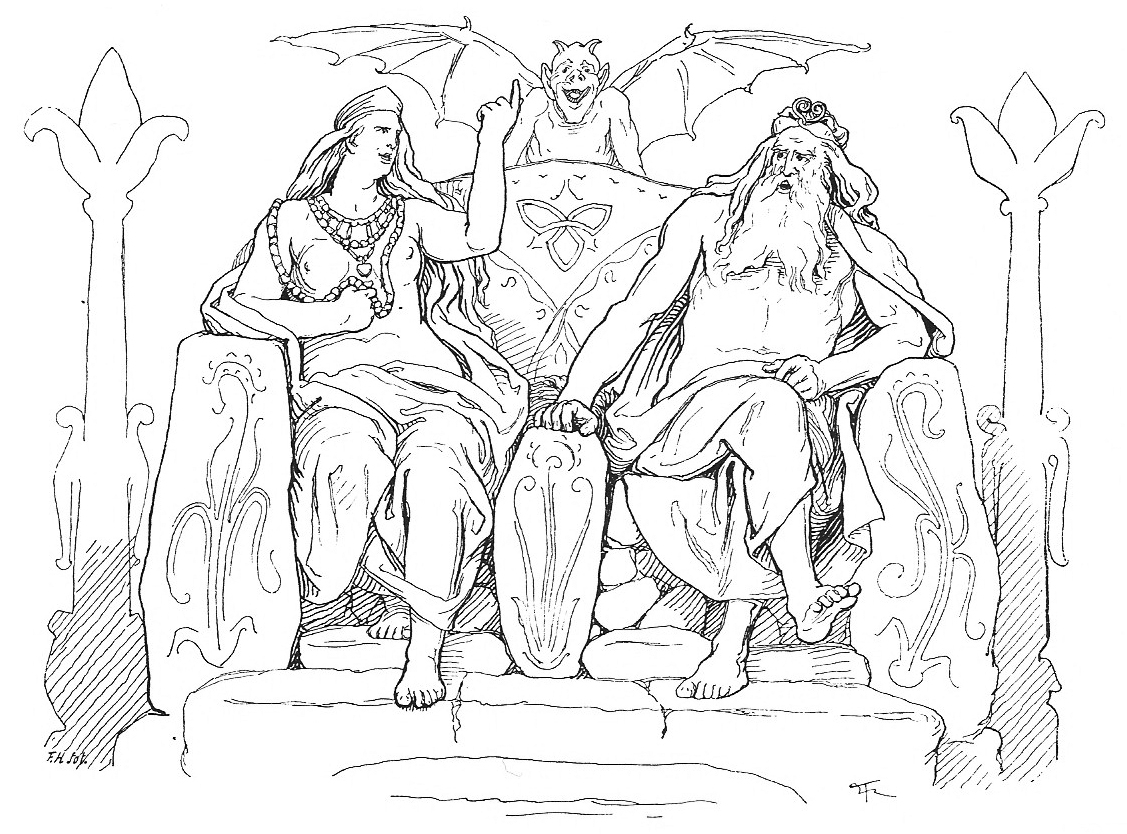
Hlidskjalf
In Norse mythology, Hliðskjálf is the high seat of the god Odin allowing him to see into all realms. ''Poetic Edda'' In ''Grímnismál'', Odin and Frigg are both sitting in Hliðskjálf when they see their foster sons Agnarr and Geirröðr, one living in a cave with a giantess and the other a king. Frigg then made the accusation to her husband that Geirröðr was miserly and inhospitable toward guests, so after wagering with one another over the veracity of the statement, Odin set out to visit Geirröðr in order to settle the matter. In '' Skírnismál'', Freyr sneaks into Hliðskjálf when he looks into Jötunheimr and sees the beautiful giant maiden Gerðr, with whom he instantly falls in love. ''Prose Edda'' In ''Gylfaginning'', Snorri mentions the high seat on four occasions. In the first instance he seems to refer to it rather as a dwelling place: "There is one abode called Hliðskjálf, and when Allfather sat in the high seat there, he looked out over the whole w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic medieval manuscript known as the '' Codex Regius'', which contains 31 poems. The ''Codex Regius'' is arguably the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends. Since the early 19th century, it has had a powerful influence on Scandinavian literature, not only through its stories, but also through the visionary force and the dramatic quality of many of the poems. It has also been an inspiration for later innovations in poetic meter, particularly in Nordic languages, with its use of terse, stress-based metrical schemes that lack final rhymes, instead focusing on alliterative devices and strongly concentrated imagery. Poets who have acknowledged their debt to the ''Codex Regius'' include Vilhelm Ekelund, August S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Regius
Codex Regius ( la, Cōdex Rēgius, "Royal Book" or "King's Book"; is, Konungsbók) or GKS 2365 4º is an Icelandic codex in which many Old Norse poems from the ''Poetic Edda'' are preserved. Thought to have been written during the 1270s, it is made up of 45 vellum leaves. The work originally contained a further eight leaves, which are now missing. It is the sole source for most of the poems it contains. In scholarly texts, this manuscript is commonly abbreviated as for Codex Regius, or as for Konungsbók. The codex was discovered in 1643, when it came into the possession of Brynjólfur Sveinsson, then Bishop of Skálholt in Iceland, who in 1662 sent it as a gift to King Frederick III of Denmark; hence the name. It was then kept in the Royal Library in Copenhagen until April 21, 1971, when it was brought back to Reykjavík, and is now kept in the Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies. Because air travel at the time was not entirely trustworthy with such preciou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valhalla (comics)
Valhalla is a Danish comic series, which offers a comedic view of the gods of Norse mythology. Originally commissioned for and published by Interpresse, it has been published by Carlsen Comics since 1978. In 1986, ''Valhalla'' was adapted into an animated feature film the studio A Film. On October 10, 2019, a more serious and dark live action adaptation was released. History During 1976 and 1977, Henning Kure and Arne Stenby at Interpresse, a Danish publishing house, were planning to create a comic series based on the world of the Vikings. They offered the place of illustrating the comic to the young cartoonist Peter Madsen, who accepted, and also enlisted Hans Rancke-Madsen. The team set out to draw the first album (similar format as ''Tintin'' and ''Asterix'') in a series of the adventures of the Norse gods, based on the Elder Eddas. Thor would very much be the hero of this series, along with Odin and Loki. Valhalla started in 1978 as a strip running in the Danish newspa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulla
Fulla (Old Norse: , possibly 'bountiful') or Volla (Old High German, 'plenitude') is a goddess in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, Fulla is described as wearing a golden band and as tending to the ashen box and the footwear owned by the goddess Frigg, and, in addition, Frigg confides in Fulla her secrets. Fulla is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; the ''Prose Edda'', written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson; and in skaldic poetry. Volla (''Folla'') is attested in the "Horse Cure" Merseburg Incantation, recorded anonymously in the 10th century in Old High German, in which she assists in healing the wounded foal of Phol and is referred to as Frigg's sister. Scholars have proposed theories about the implications of the goddess. Name The Old Norse name ''Fulla'' has been translated as 'bountiful'. It stems from Proto-Germanic ''*fullōn'' ('fullness, plenitude'; cf. Gothic ''fullo'' 'fullness', OHG ''foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AM 748 I 4to
AM 748 I 4to is an Icelandic vellum manuscript fragment containing several Eddaic poems. It dates to the beginning of the 14th century. AM 748 I is split into two parts. AM 748 I a 4to is kept in the Arnamagnæan Institute in Copenhagen. AM 748 I b 4to is kept at the Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies in Reykjavík. The six sheets which have been preserved of AM 748 I a 4to contain the following poems, all mythological. *'' Grímnismál'' (complete) *''Hymiskviða'' (complete) *''Baldrs draumar'' (complete) *''Skírnismál'' (partial) *''Hárbarðsljóð'' (partial) *''Vafþrúðnismál'' (partial) *''Völundarkviða'' (only the beginning of the prose prologue) AM 748 I a 4to is the only mediaeval manuscript to preserve ''Baldrs draumar''. The other poems are also preserved in Codex Regius Codex Regius ( la, Cōdex Rēgius, "Royal Book" or "King's Book"; is, Konungsbók) or GKS 2365 4º is an Icelandic codex in which many Old Norse poems from the ''Poetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odin
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the runic alphabet, and depicts him as the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, the god was also known in Old English as ', in Old Saxon as , in Old Dutch as ''Wuodan'', in Old Frisian as ''Wêda'', and in Old High German as , all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *''Wōðanaz'', meaning 'lord of frenzy', or 'leader of the possessed'. Odin appears as a prominent god throughout the recorded history of Northern Europe, from the Roman occupation of regions of Germania (from BCE) through movement of peoples during the Migration Period (4th to 6th centuries CE) and the Viking Age (8th to 11th centuries CE). In the modern period, the rural folklore of Germanic E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grímnir And Agnar By George Wright
{{disambig ...
Grimnir may refer to: *One of Odin's names, specifically the one he uses in ''Grímnismál'' (''Sayings of Grímnir''), see list of names of Odin *A character in the children's novel, '' The Weirdstone of Brisingamen'' *An "ancestor god" of the dwarfs in ''Warhammer Fantasy'' (setting) *Name of soul reapers for Goddess Hel in Runes books, YA novels by Ednah Walters *The fictional terrorist group that serves as the main antagonists of the '' Front Mission'' series. See also * * * Grimnirson (surname) * Grim (other) * Grim (surname) * Grimnitzsee Grimnitzsee () is a lake in Landkreis Barnim, Brandenburg, Germany. At an elevation of 64 m, its surface area is 7.8 km². It is situated in the municipality of Joachimsthal, Brandenburg, Joachimsthal. See also *Werbellinsee External lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ljóðaháttr
In prosody, alliterative verse is a form of verse that uses alliteration as the principal ornamental device to help indicate the underlying metrical structure, as opposed to other devices such as rhyme. The most commonly studied traditions of alliterative verse are those found in the oldest literature of the Germanic languages, where scholars use the term 'alliterative poetry' rather broadly to indicate a tradition which not only shares alliteration as its primary ornament but also certain metrical characteristics. The Old English epic ''Beowulf'', as well as most other Old English poetry, the Old High German ''Muspilli'', the Old Saxon '' Heliand'', the Old Norse ''Poetic Edda'', and many Middle English poems such as ''Piers Plowman'', ''Sir Gawain and the Green Knight'', and the '' Alliterative Morte Arthur'' all use alliterative verse. While alliteration can be found in many poetic traditions, it is 'relatively infrequent' as a structured characteristic of poetic form.Frog, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monologue
In theatre, a monologue (from el, μονόλογος, from μόνος ''mónos'', "alone, solitary" and λόγος ''lógos'', "speech") is a speech presented by a single character, most often to express their thoughts aloud, though sometimes also to directly address another character or the audience. Monologues are common across the range of dramatic media ( plays, films, etc.), as well as in non-dramatic media such as poetry. Monologues share much in common with several other literary devices including soliloquies, apostrophes, and asides. There are, however, distinctions between each of these devices. Similar literary devices Monologues are similar to poems, epiphanies, and others, in that, they involve one 'voice' speaking but there are differences between them. For example, a soliloquy involves a character relating their thoughts and feelings to themself and to the audience without addressing any of the other characters. A monologue is the thoughts of a person spoken out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |