|
Grand Magne
Grand Ma ne ("Great Maina", in el, Μεγάλη Μαΐνη) or Vieux Ma ne ("Old Maina", in el, Παλαιά Μαΐνη) was a Frankish castle in the Mani Peninsula, Greece. It was built, according to the ''Chronicle of the Morea'', ca. 1248–1250 AD by William II Villehardouin, the Prince of Achaea in order to control the Slavic tribe of the Melingoi, living on Mount Taygetos. He was captured by the Byzantines in 1259 at the Battle of Pelagonia, and had to give up the castle as part of his ransom. The location of the castle is not clear. Modern usage refers to the castle of Porto Kagio as "Mani", but medieval portolans place the castle of Grand Magne on the western shore of the peninsula and its fortification was not mentioned by portolans or travelers before about 1568. Another candidate is the settlement of Tigani, but although a sizeable medieval town it shows no traces of having been the site of a Crusader fortress. Antoine Bon preferred the nearby site of Cavo Grosso (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
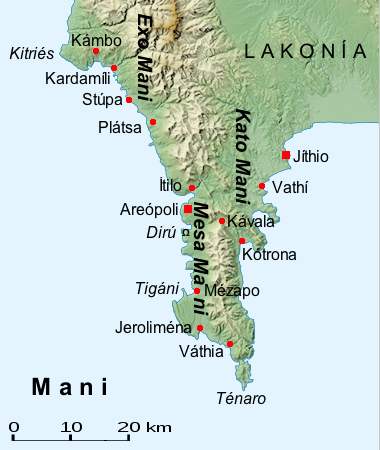
Mani Peninsula
The Mani Peninsula ( el, Μάνη, Mánē), also long known by its medieval name Maina or Maïna (Μαΐνη), is a geographical and cultural region in Southern Greece that is home to the Maniots (Mανιάτες, ''Maniátes'' in Greek), who claim descent from the ancient Spartans. The capital city of Mani is Areopoli. Mani is the central peninsula of the three which extend southwards from the Peloponnese in southern Greece. To the east is the Laconian Gulf, to the west the Messenian Gulf. The Mani peninsula forms a continuation of the Taygetos mountain range, the western spine of the Peloponnese. Etymology The name "Mani" may come from the albanian word mani meaning mullbery Geography The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible. Until recent years many Mani villages could be reached only by sea. Today a narrow and winding road extends along the west coast from Kalamata to Areopoli, then south to Akrotainaro (the pointed cape, which is the southernmost point of contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pelagonia
The Battle of Pelagonia or Battle of Kastoriae.g. ; . took place in early summer or autumn 1259, between the Empire of Nicaea and an anti-Nicaean alliance comprising Despotate of Epirus, Sicily and the Principality of Achaea. It was a decisive event in the history of the Eastern Mediterranean, ensuring the eventual reconquest of Constantinople and the end of the Latin Empire in 1261. The rising power of Nicaea in the southern Balkans, and the ambitions of its ruler, Michael VIII Palaiologos, to recover Constantinople, led the formation of a coalition between the Epirote Greeks, under Michael II Komnenos Doukas, and the chief Latin rulers of the time, the Prince of Achaea, William of Villehardouin, and Manfred of Sicily. The details of the battle, including its precise date and location, are disputed as the primary sources give contradictory information; modern scholars usually place it either in July or in September, somewhere in the plain of Pelagonia or near Kastoria. It appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles And Fortifications Of The Principality Of Achaea
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelefa
Kelefa ( el, Κελεφά) is a castle and village in Mani, Laconia, Greece. It is part of the municipal unit of Oitylo. History The castle of Kelefa is located about half-way between the current village of Kelefa and the Bay of Oitylo. It was built in 1679 by the Ottomans, in order to contain the Inner Mani region. Some years later, in 1685, the Maniots besieged the castle. They sent messengers to Venice so the Doge could send a fleet to help them capture the castle. The Venetians were currently at war with the Ottomans so they agreed and sent a fleet under Francesco Morosini. As soon the fleets bearing the symbol of St Mark the Ottoman garrison surrendered. A year later the Ottomans returned with a strong force and laid siege to the castle but were driven back. Along with the rest of the Peloponnese, the castle remained in Venetian hands for about 30 years, but in 1715 the Ottomans recaptured the Peloponnese. Around 1780 the Ottomans abandoned the castle, which became der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastro Tis Orias, Mani
Dryalos (Δρύαλος) or Dry (Δρυ) is a village in the municipal unit of Oitylo, Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. A nearby hilltop, high, is named "Kastro tis Orias" ("Castle of the Fair Maiden"), and is sometimes given as the site of the medieval castle the Grand Magne Grand Ma ne ("Great Maina", in el, Μεγάλη Μαΐνη) or Vieux Ma ne ("Old Maina", in el, Παλαιά Μαΐνη) was a Frankish castle in the Mani Peninsula, Greece. It was built, according to the ''Chronicle of the Morea'', ca. 1248–1 ..., but it has no remains of a castle.J. M. Wagstaff, "Further Observations on the Location of Grand Magne", ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers'' 45:141-148 (1991) , p. 143-144. Notes External links Official site Populated places in Laconia Populated places in the Mani Peninsula East Mani {{Peloponnese-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigani
Tigani (Τηγάνι) is a small peninsula in the landscape of Mani in southern Greece. The name is Greek for "frying pan". Tigani is surrounded by the sea except for a narrow strip of land that connects to the mainland. The ruins of a probable medieval In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ... castle can be found there. Its position and its walls made it extremely hard to capture. Megali Maina Many historians believe that Tigani is the location of the castle ''Megali Maina'' (also called ''Grande Magne'') because Tigani fits elements of historic descriptions of ''Megali Maina''. External links Where is the castle of the Grand Magne?Exploring mysterious Tigani (in German) {{coord, 36.54484, N, 22.36584, E, type:landmark_region:GR_dim:2500, display=title Peninsulas of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portolan
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portulano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and which since at least the 17th century designates "a collection of sailing directions". Definition The term “portolan chart” was coined in the 1890s because at the time it was assumed that these maps were related to portolani, medieval or early modern books of sailing directions. Other names that have been proposed include rhumb line charts, compass charts or loxodromic charts whereas modern French scholars prefer to call them nautical charts to avoid any relationship with portolani. Several definitions of portolan chart coexist in the literature. A narrow definition includes only medieval or, at the latest, early modern sea charts (i.e. maps that primarily cover maritime rather than inland regions) that include a network of rhumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porto Kagio
Porto Kagio or Porto Káyio (Πόρτο Κάγιο) is a seaside village in the East Mani municipality on the eastern side of the Mani Peninsula, Greece. It faces a small bay off the Laconian Gulf and is about three miles north of Cape Matapan, the southernmost tip of the Mani Peninsula and of mainland Greece. History The site was that of the ancient port of Psamathous, mentioned by Pausanias. The modern name comes from the Venetian ''Porto Quaglio'' and the French (Frankish) ''Port des Cailles'' (Quail Port).Paul Cartledge, ''Sparta and Lakonia: A Regional History 1300-362 BC'', 2013, p. 19/ref> Some 17th- and 18th-century maps called it "Maina", so some authors consider it to be a possible location for the castle of Grand Magne, but medieval portolans mention no such castle here. The Ottomans built a castle here in about 1568, to protect the port, which was used for galleys patrolling the Kythera Channel. The Venetians attacked the castle in 1570, and the Ottomans surren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankokratia
The ''Frankokratia'' ( el, Φραγκοκρατία, la, Francocratia, sometimes anglicized as Francocracy, "rule of the Franks"), also known as ''Latinokratia'' ( el, Λατινοκρατία, la, Latinocratia, "rule of the Latins") and, for the Venetian domains, ''Venetokratia'' or ''Enetokratia'' ( el, Βενετοκρατία or Ενετοκρατία, la, Venetocratia, "rule of the Venetians"), was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French and Italian states were established by the '' Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae'' on the territory of the dissolved Byzantine Empire. The terms Frankokratia and Latinokratia derive from the name given by the Orthodox Greeks to the Western French and Italians who originated from territories that once belonged to the Frankish Empire. The Frankish Empire being the political entity which ruled much of the former Western Roman Empire after the collapse of Roman authority and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Taygetos
The Taygetus, Taugetus, Taygetos or Taÿgetus ( el, Ταΰγετος, Taygetos) is a mountain range on the Peloponnese peninsula in Southern Greece. The highest mountain of the range is Mount Taygetus, also known as "Profitis Ilias", or "Prophet Elias" (Elijah). The name is one of the oldest recorded in Europe, appearing in the Odyssey. In classical mythology, it was associated to the nymph Taygete and it was named after her. During Byzantine times and up until the 19th century, the mountain was also known as Pentadaktylos (Πενταδάκτυλος; Greek for ''five-fingered'', a common name during that period). Geography Physical The Taygetus Massif is about long, extending from the center of the Peloponnese to Cape Matapan, its southernmost extremity. It contains the tallest mountain in the Peloponnese, the Profitis Ilias summit, reaching ; this is probably the classical Mount Taléton mentioned by Pausanias. The summit is an ultra-prominent peak. It is prominent above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





