|
Gotha Observatory
Gotha Observatory (''Seeberg Observatory'', ''Sternwarte Gotha'' or ''Seeberg-Sternwarte'') was a German astronomical observatory located on Seeberg hill near Gotha, Thuringia, Germany. Initially the observatory was dedicated to astrometry, geodetic and meteorological observation and tracking the time. The minor planet 1346 Gotha was named after the city of Gotha in recognition of the observatory. History Planning for the observatory began in 1787 by the court astronomer Baron Franz Xaver von Zach, with the financing of Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg. It was based upon the Radcliffe Observatory in Oxford, England. The building was divided into five parts, with the central section holding a revolving dome. There were two wings to provide quarters for the staff. During Peter Andreas Hansen's term, the observatory was dismantled and moved to a less exposed location in Gotha. The observatory was closed in 1934. Instruments Around 1800, the observatory became an internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotha (town)
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the Gotha (district), district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine House of Wettin, Wettins from 1640 until the end of monarchy in Germany in 1918. The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha originating here spawned many European rulers, including the royal houses of the United Kingdom, Belgium, Portugal (until 1910) and Bulgaria (until 1946). In the Middle Ages, Gotha was a rich trading town on the trade route ''Via Regia'' and between 1650 and 1850, Gotha saw a cultural heyday as a centre of sciences and arts, fostered by the dukes of Saxe-Gotha. The first duke, Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha, Ernest the Pious, was famous for his wise rule. In the 18th century, the ''Almanach de Gotha'' was first published in the city. The publisher Justus Perthes (publishing company), Justus Perthes and the encyclopedist Joseph Meyer (publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatic Lens
An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths (typically red and blue) into focus on the same plane. The most common type of achromat is the achromatic doublet, which is composed of two individual lenses made from glasses with different amounts of dispersion. Typically, one element is a negative (concave) element made out of flint glass such as F2, which has relatively high dispersion, and the other is a positive (convex) element made of crown glass such as BK7, which has lower dispersion. The lens elements are mounted next to each other, often cemented together, and shaped so that the chromatic aberration of one is counterbalanced by that of the other. In the most common type (shown), the positive power of the crown lens element is not quite equalled by the negative power of the flint lens element. Together they form a weak positive lens that will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Von Lindenau
Baron Bernhard August von Lindenau (11 June 1779 – 21 May 1854) was a German lawyer, astronomer, politician, and art collector. Lindenau was born in Altenburg, the son of Johann August Lindenau, a regional administrator (''Landschaftsdirektor)''. In 1793, Lindeau began studying law and mathematics at Leipzig, and beginning in 1801 he worked at the astronomical observatory in Seeburg. In 1830 he was the Minister of the Interior during a turbulent period in the history of Saxony. Late in the year he oversaw measures to calm violent protests demanding political reform. From 1831 to 1843 he was Minister-President. He created a collection of Italian artwork from the 14th and 15th centuries by Florentine painters in an effort to create artistic awareness. He gave his art collection to the city of Altenburg on the condition that they create a museum to display the pieces. This museum was finished in 1875, and became the Lindenau-Museum. Lindenau edited the ''Monatliche Correspondenz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometer
A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier. Photometers measure: *Illuminance * Irradiance *Light absorption * Scattering of light * Reflection of light * Fluorescence * Phosphorescence * Luminescence History Before electronic light sensitive elements were developed, photometry was done by estimation by the eye. The relative luminous flux of a source was compared with a standard source. The photometer is placed such that the illuminance from the source being investigated is equal to the standard source, as the human eye can judge equal illuminance. The relative luminous fluxes can then be calculated as the illuminance decreases proportionally to the inverse square of distance. A standard example of such a photometer consists of a piece of paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner
Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner (8 November 1834, Berlin25 April 1882, Leipzig) was a German astrophysicist who studied optical illusions. He was also an early psychical investigator. Biography From 1872 he held the chair of astrophysics at Leipzig University. He wrote numerous papers on photometry and spectrum analysis in Poggendorff's '' Annalen'' and ''Berichte der k. sächsischen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften'', two works on celestial photometry (''Grundzüge einer allgemeinen Photometrie des Himmels'', Berlin, 1861, 4to, and ''Photometrische Untersuchungen'', Leipzig, 1865, 8vo), and a curious book, ''Ueber die Natur der Cometen'' (Leipzig, 1872, 3rd ed. 1883). He discovered the Zöllner illusion where lines that are parallel appear diagonal. He also successfully proved Christian Doppler's theory on the effect of motion of the color of stars, and the resulting shift of absorption lines, via the invention of a very sensitive spectroscope which he named "Reversionspectros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photography
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication. Typically, a lens is used to focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel, which is electronically processed and stored in a digital image file for subsequent display or processing. The result with photographic emulsion is an invisible latent image, which is later chemically "developed" into a visible image, either negative or positive, depending on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utzschneider & Fraunhofer
Georg Merz (26 January 1793 – 12 January 1867) was a Bavarian optician and manufacturer of astronomical telescopes and other optical instruments. Life Merz was born on 26 January 1793 in Bichl, in Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen, now in Bavaria, Germany. At the age of 15 he went to work in the glassworks recently set up by in the nearby deconsecrated monastery of Benediktbeuern. There he became the assistant of Joseph Fraunhofer. From 1826, when Fraunhofer died, Merz was in charge of the optical division of the business. On the death of von Utzschneider in 1839 Merz, in partnership with Joseph Mahler, bought the firm. After Mahler's death he ran the business in partnership with his sons Ludwig and Sigmund. When Ludwig died in 1858 the name was changed to G. & S. Merz. Georg Merz died in Munich on 12 January 1867. In 1882 the firm passed to Jacob and Matthias Merz, Sigmund's cousins, and in 1884 the Benediktbeuern works was closed. The company moved to Munich, and closed in 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
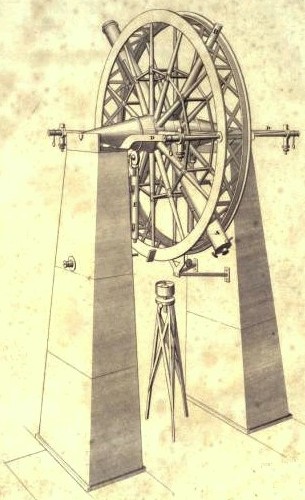
Meridian Circle
The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis. The similar transit instrument, transit circle, or transit telescope is likewise mounted on a horizontal axis, but the axis need not be fixed in the east–west direction. For instance, a surveyor's theodolite can function as a transit instrument if its telescope is capable of a full revolution about the horizontal axis. Meridian circles are often called by these names, alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Von Fraunhofer
Joseph Ritter von Fraunhofer (; ; 6 March 1787 – 7 June 1826) was a German physicist and optical lens manufacturer. He made optical glass, an achromatic telescope, and objective lenses. He also invented the spectroscope and developed diffraction grating. In 1814, he discovered and studied the dark absorption lines in the spectrum of the sun now known as Fraunhofer lines. The German research organization Fraunhofer Society, which is Europe's biggest Society for the advancement of applied research, is named after him. Biography Joseph Fraunhofer was the 11th child, born into a Roman Catholic family in Straubing, in the Electorate of Bavaria, to Franz Xaver Fraunhofer and Maria Anna Fröhlich. He was orphaned at the age of 11 and started working as an apprentice to a harsh glassmaker named Philipp Anton Weichelsberger. In 1801, the workshop in which he was working collapsed, and he was buried in the rubble. The rescue operation was led by Prince-Elector Maximilian Joseph. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Friedrich Von Reichenbach
Georg Friedrich von Reichenbach (24 August 1772 – 21 May 1826), German scientific instrument maker, was born at Durlach in Baden on 24 August 1772. Early life Reichenbach's father was a master mechanic, and a master cannon-borer, who moved to Mannheim when Reichenbach was two, and became manager of the cannon-boring works there. At 14 Georg was admitted to the Military School at Mannheim where he got to know the astronomer at the Mannheim Observatory. He received a knowledge of mathematical instruments and was inspired to try to construct similar instruments in his father's workshop. The Director of the Observatory sent a sextant made by Reichenbach to Count Rumford. When he was 19, Reichenbach received a grant of 500 gulden for a journey to London, and introductions to the engineers James Watt and Matthew Boulton. Reichenbach's first visit to England lasted from 1 June 1791 to January 1792, when he returned home for a short time before returning to England. He made drawings of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodolite
A theodolite () is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but it is also used extensively for building and infrastructure construction, and some specialized applications such as meteorology and rocket launching. It consists of a moveable telescope mounted so it can rotate around horizontal and vertical axes and provide angular readouts. These indicate the orientation of the telescope, and are used to relate the first point sighted through the telescope to subsequent sightings of other points from the same theodolite position. These angles can be measured with accuracies down to microradians or seconds of arc. From these readings a plan can be drawn, or objects can be positioned in accordance with an existing plan. The modern theodolite has evolved into what is known as a total station where angles and distances are measured electronically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |