|
Gorbals
The Gorbals is an area in the city of Glasgow, Scotland, on the south bank of the River Clyde. By the late 19th century, it had become densely populated; rural migrants and immigrants were attracted by the new industries and employment opportunities of Glasgow. At its peak, during the 1930s, the wider Gorbals district (which includes the directly adjoined localities of Laurieston and Hutchesontown) had swollen in population to an estimated 90,000 residents. Along with its relatively small size, this gave the area a very high population density of around 40,000/km². Redevelopment after WWII has taken many turns, and the area's population is substantially smaller today. Meaning of placename The name is first documented in the 15th and 16th centuries as ''Gorbaldis'', and its etymology is unclear. It may be related to the Ecclesiastical Latin word ('sheaf'), found in the Scottish Gaelic term ('tenth sheaf'), a tithe of corn given to a parish rector. The taking of was a right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutchesontown
Hutchesontown is an inner-city area in Glasgow, Scotland. Mostly residential, it is situated directly south of the River Clyde and forms part of the wider historic Gorbals district, which is covered by the Southside Central ward under Glasgow City Council. The area is linked to Glasgow Green public park on the north side of the river by St. Andrew's Suspension Bridge and King's Bridge. At its north-western edge, Albert Bridge is the closest crossing point towards Glasgow city centre. In McNeill Street, Hutchesontown has one of Glasgow's original Carnegie libraries, deftly designed by the Inverness-born architect James Robert Rhind. James Stokes, recipient of the Victoria Cross, was from the area. Comprehensive Development Area Following the Second World War, Hutchesontown was declared a Comprehensive Development Area (CDA) in 1957, in the aftermath of the Bruce Report. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
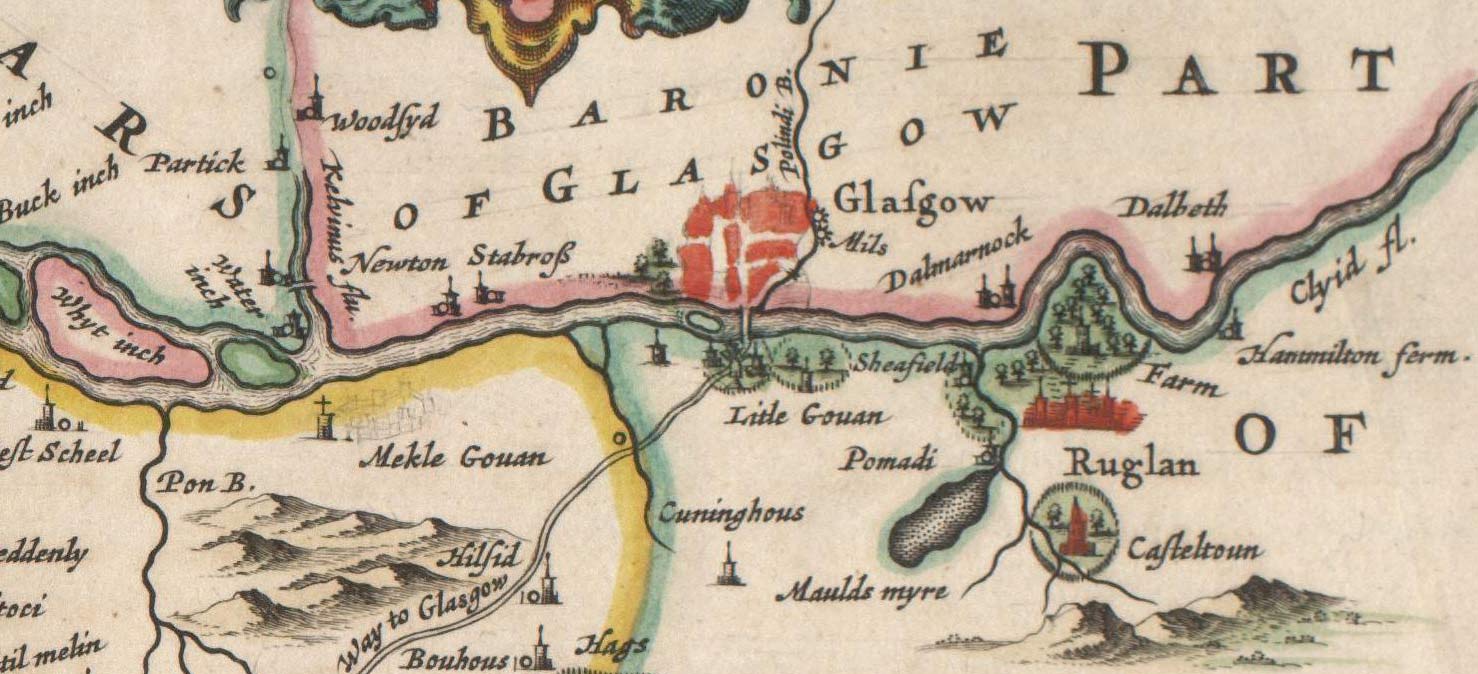
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurieston, Glasgow
Laurieston is a district in the Gorbals area of the Scottish city of Glasgow. It is situated south of the River Clyde. It derives its name from James Laurie who, along with his brother, developed a large part of the district in the early 19th century. History Laurieston is a core part of the Gorbals. Compared to other neighbourhoods in the vicinity, many of its 19th century buildings escaped the slum clearances of the 1960s and 70s, particularly in the north of the district close to the river. However the tenements further south were swept away to be replaced by four black 'slab' tower blocks (which actually consisted of four pairs of towers with separate entrances, joined together externally). Whilst the blocks (''Norfolk Court'' and ''Stirlingfauld Place'') solved a short term housing need and were popular with some residents due to their proximity to central Glasgow, they were expensive to maintain and became increasingly undesirable in terms of their build quality and aesthet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Elphinstone
George Elphinstone of Blythswood (died 1634) was a Scottish landowner, courtier, and Provost of Glasgow. Life George Elphinstone was the son of George Elphinstone of Blythswood (died 2 April 1585), a leading Glasgow merchant and shipowner, and Marion Scott. He was knighted during the celebrations at the baptism of Prince Henry at Stirling Castle on 30 August 1594. He was made a gentleman of the king's bedchamber in 1596. In this role he controlled the access to James VI of Scotland allowed to the English diplomatic agent, George Nicholson, occasionally bringing him secretly into the king's cabinet at Holyroodhouse. He was a member of a "knot of friendship" at the Scottish court that included the Secretary, Sir George Home, Sir Robert Kerr, the younger Sir Robert Melville, and Sir David Murray. These chamber servants paid for the baptism of Princess Margaret in April 1599, because they had displaced the treasurer Walter Stewart of Blantyre. Elphinstone's popularity wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Central (UK Parliament Constituency)
Glasgow Central is a constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (at Westminster). In its current form, the constituency was first used at the 2005 general election, but there was also a ''Glasgow Central'' constituency that existed from 1885 to 1997. The sitting MP is Alison Thewliss of the Scottish National Party (SNP), who was first elected in May 2015. This constituency was also the seat of the former Conservative Prime Minister Bonar Law, who was the shortest-serving UK Prime Minister of the twentieth century. Boundaries 1885–1918: The Seventh, Eighth, Ninth, Twelfth, and Thirteenth Municipal Wards. 1918–1950: "That portion of the city which is bounded by a line commencing at a point at the intersection of the centre lines of Parliamentary Road and Castle Street, thence southward along the centre line of Castle Street to the centre line of Alexandra Parade, thence eastward along the centre line of Alexandra Parade to the centre li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south bank of the River Clyde, opposite the mouth of the River Kelvin and the district of Partick. Historically it was part of the County of Lanark. In the early medieval period, the site of the present Govan Old churchyard was established as a Christian centre for the Brittonic Kingdom of Alt Clut (Dumbarton Rock) and its successor realm, the Kingdom of Strathclyde. This latter kingdom, established in the aftermath of the Viking siege and capture of Alt Clut by Vikings from Dublin in AD 870, created the sandstone sculptures known today as the Govan Stones. Govan was the site of a ford and later a ferry which linked the area with Partick for seasonal cattle drovers. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, textile mills and coal mining we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics Of Glasgow
The politics of Glasgow, Scotland's largest city by population, are expressed in the deliberations and decisions of Glasgow City Council, in elections to the council, the Scottish Parliament and the UK Parliament. Local government As one of the 32 unitary local government areas of Scotland, Glasgow City Council has a defined structure of governance, generally under the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994, controlling matters of local administration such as housing, planning, local transport, parks and local economic development and regeneration. For such purposes the city is currently (as of 2020, since 2017) divided into 23 wards, each returning either three or four councillors via single transferable vote, a proportional representation system. From 1995 until 2007, single members were elected from 79 small wards. Among other appointments, one of the councillors becomes its leader, and one other takes on the ceremonial and ambassadorial role of Lord Provost of Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, which spans roughly 40% of the continent's landmass while accounting for approximately 15% of its total population."The Balkans" , ''Global Perspectives: A Remote Sensing and World Issues Site''. Wheeling Jesuit University/Center for Educational Technologies, 1999–2002. It represents a significant part of ; the main socio-cultural characteristics of Eastern Europe have historically been defined by the trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area's history. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. Central Europe comprised most of the territories of the Holy Roman Empire and those of the two neighboring kingdoms of Poland and Hungary. Hungary and parts of Poland were later part of the Habsburg monarchy, which also significantly shaped the history of Central Europe. Unlike their Western European (Portugal, Spain et al.) and Eastern European (Russia) counterparts, the Central European nations never had any notable colonies (either overseas or adjacent) due to their inland location and other factors. It has often been argued that one of the contributing causes of both World War I and World War II was Germany's lack of original overseas colonies. After Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Street, Gorbals, Looking South (-36) LACMA M
Main may refer to: Geography * Main River (other) **Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany * Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province *"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries *'' The Main'', the diverse core running through Montreal, Quebec, Canada, also separating the Two Solitudes * Main (lunar crater), located near the north pole of the Moon * Main (Martian crater) People and organisations *Main (surname), a list of people with this family name *Ma'in, alternate spelling for the Minaeans, an ancient people of modern-day Yemen * Main (band), a British ambient band formed in 1991 * Chas. T. Main, an American engineering and hydroelectric company founded in 1893 *MAIN (Mountain Area Information Network), former operator of WPVM-LP (MAIN-FM) in Asheville, North Carolina, U.S. Ships * ''Main'' (ship), an iron sailing ship launched in 1884 * SS ''Main'', list of steamships with this name * ''Main'' (A515), a mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Ninian
Ninian is a Christian saint, first mentioned in the 8th century as being an early missionary among the Pictish peoples of what is now Scotland. For this reason he is known as the Apostle to the Southern Picts, and there are numerous dedications to him in those parts of Scotland with a Pictish heritage, throughout the Scottish Lowlands, and in parts of Northern England with a Northumbrian heritage. He is also known as Ringan in Scotland, and as Trynnian in Northern England. Ninian's major shrine was at Whithorn in Galloway, where he is associated with the Candida Casa (Latin for 'White House'). Nothing is known about his teachings, and there is no unchallenged authority for information about his life. The nature of Ninian's identity is uncertain, and historians have identified the name "Ninian" with other historical figures. A popular hypothesis proposed by Thomas Owen Clancy, a researcher and professor of Celtic studies, posits that Ninian can be identified with three other hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Rae (bishop)
William Rae (died 1376) was a 14th-century bishop of Glasgow. His background is obscure, although it is known that before ascending to the bishopric he was a precentor of the diocese of Glasgow. On the death of John Wishart in 1338, William was elected to the see. His election was confirmed by Pope Benedict XII, who on 11 February 1339 ordered Annibald de Ceccano, bishop of Tusculum, to consecrate William. William was consecrated at Avignon a short while later. Curiously, his predecessor Wishart had been consecrated by the same man, in the same location. William's episcopate was comparatively long, and he died on 27 January 1367. He was succeeded by Walter Wardlaw Walter Wardlaw (died ) was a 14th-century bishop of Glasgow in Scotland. Biography Wardlaw was the son of a Sir Henry Wardlaw of Torry, a middling knight of Fife. Before becoming bishop, Walter was a canon of Glasgow, a Master of Theology and .... References * Dowden, John, ''The Bishops of Scotland'', ed. J. Mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |