|
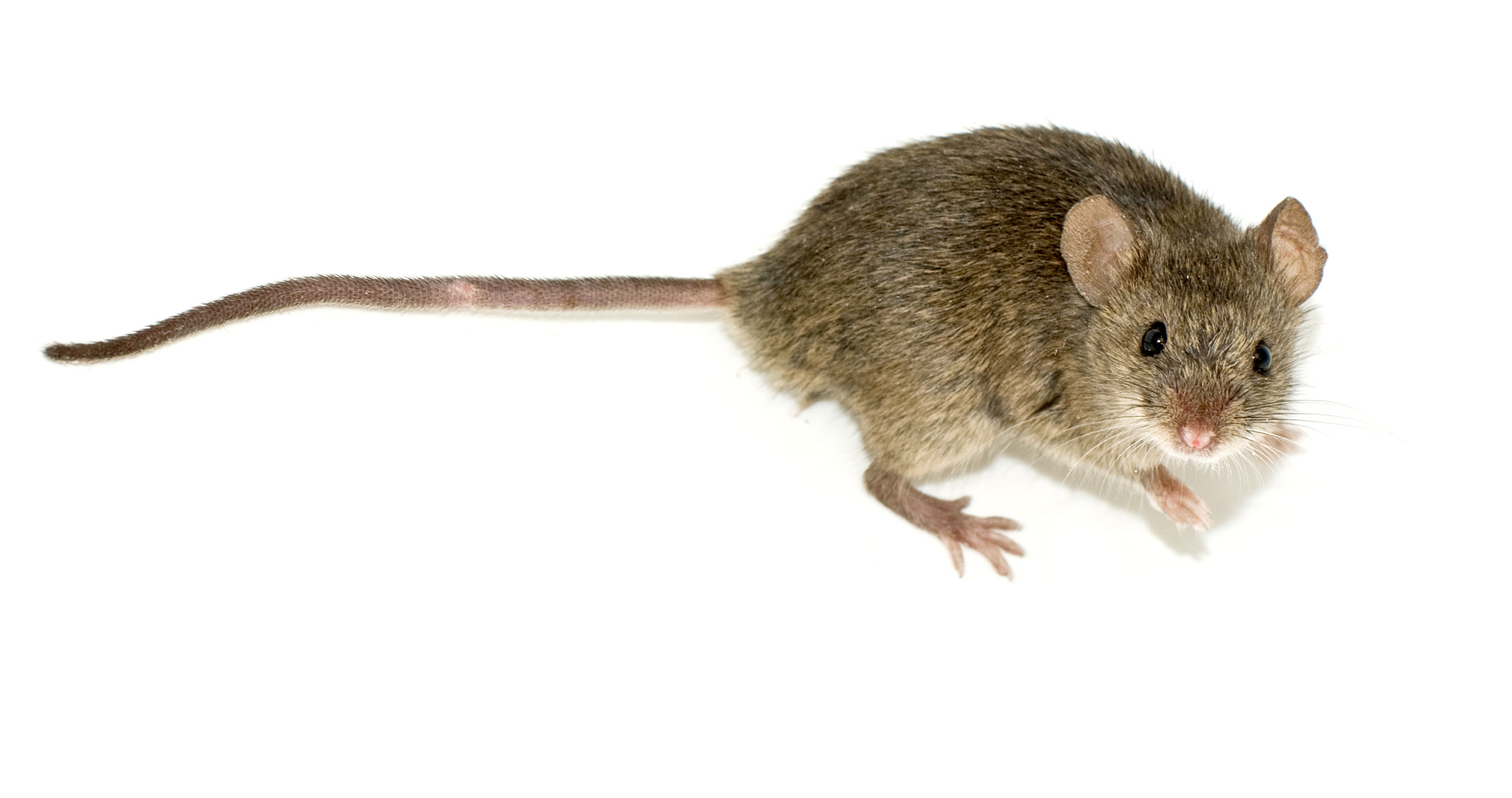
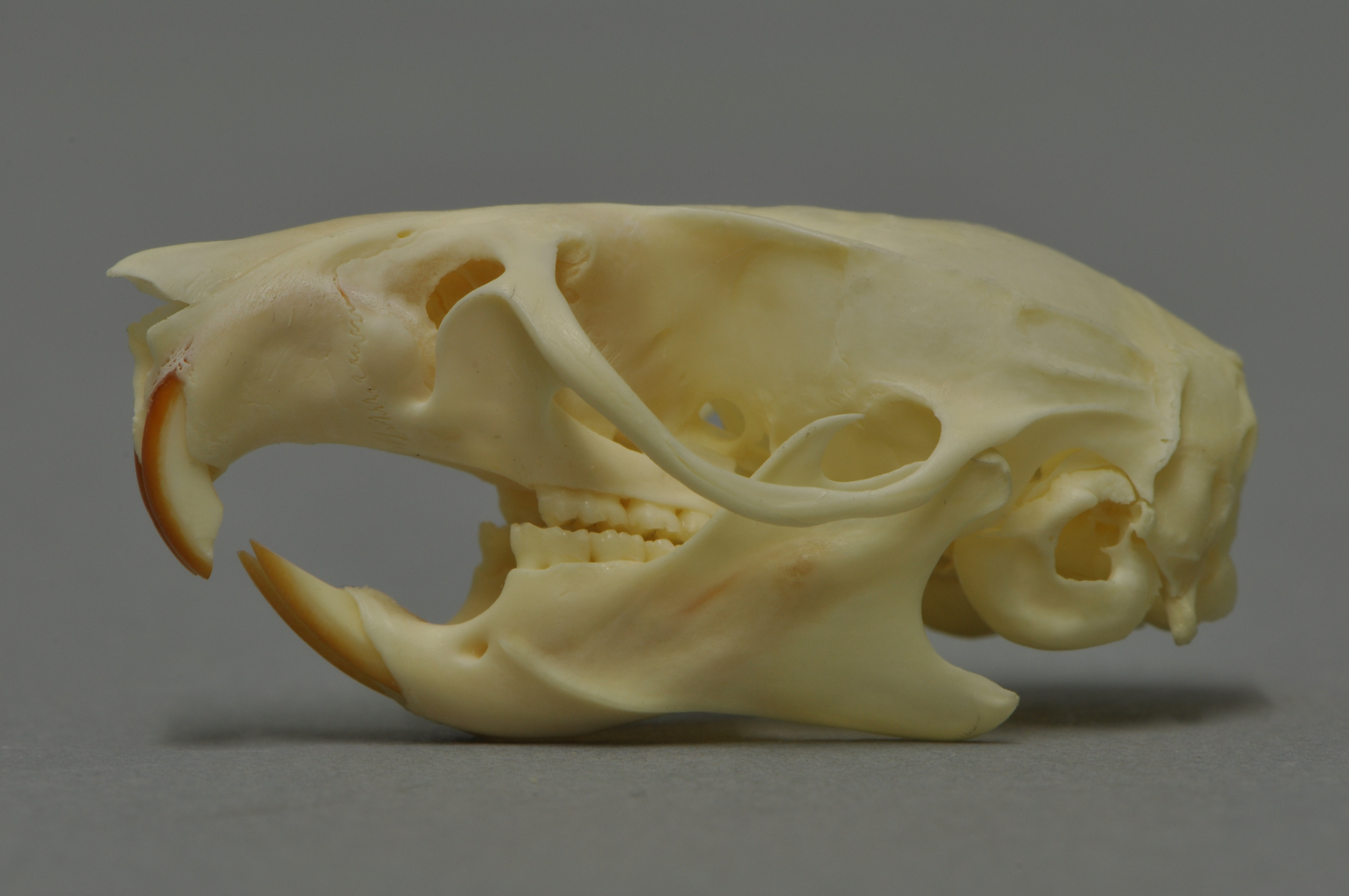
Gerbil
The Mongolian gerbil or Mongolian jird (''Meriones unguiculatus'') is a small rodent belonging to the subfamily Gerbillinae. Their body size is typically , with a tail, and body weight , with adult males larger than females. The animal is used in science and kept as a small house pet. Their use in science dates back to the latter half of the 19th century, but they only started to be kept as pets in the English-speaking world after 1954, when they were brought to the United States. However, their use in scientific research has fallen out of favor. Habitat Mongolian gerbils inhabit grassland, shrubland and desert, including semidesert and steppes in China, Mongolia, and the Russian Federation. Soil on the steppes is sandy and is covered with grasses, herbs, and shrubs. The steppes have cool, dry winters and hot summers. The temperature can get up to , but the average temperature for most of the year is around . In the wild, these gerbils live in patriarchal groups generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerbillinae
Gerbillinae is one of the subfamilies of the rodent family Muridae and includes the gerbils, jirds, and sand rats. Once known as desert rats, the subfamily includes about 110 species of African, Indian, and Asian rodents, including sand rats and jirds, all of which are adapted to arid habitats. Most are primarily active during the day, making them diurnal (but some species, including the common household pet, exhibit crepuscular behavior), and almost all are omnivorous. The gerbil got its name as a diminutive form of "jerboa," an unrelated group of rodents occupying a similar ecological niche. Gerbils are typically between long, including the tail, which makes up about half of their total length. One species, the great gerbil (''Rhombomys opimus''), originally native to Turkmenistan, can grow to more than . The average adult gerbil weighs about . One species, the Mongolian gerbil ('' Meriones unguiculatus''), also known as the ''clawed jird'', is a gentle and hardy anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pocket Pet
The most common rodents kept as household pets are hamsters (golden hamsters and dwarf hamsters), gerbils (Mongolian jirds and duprasi gerbils), common degus, fancy mice, fancy rats, common chinchillas, and guinea pigs (cavies). The domestication of small mammals is a relatively recent development, arising only after large-scale industrialization. Historically, Western society was more agrarian than today, with rodents as a whole seen as vermin that were carriers for disease and a threat to crops. Animals that hunted such pests (e.g. terriers and cats) were prized. Some of these small rodents are prohibited from being kept as pets in certain areas for being invasive; California, Hawaii, and New Zealand have strict regulations to protect their native environments and agricultural operations. Gerbils, degus, and domesticated rats have various prohibitions on their ownership. Characteristics Guinea pig Guinea pigs (cavy) have perhaps been kept the longest as pets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fat Sand Rat
The fat sand rat (''Psammomys obesus'') is a terrestrial mammal from the gerbil subfamily that is mostly found in North Africa and the Middle East, ranging from Mauritania to the Arabian Peninsula. This species usually lives in sandy deserts, but may also be found in rocky terrain or saline marsh areas. Fat sand rats are very selective in their diet, only eating stems and leaves of plants from the family Amaranthaceae, more commonly known as the amaranth family. In captivity, fat sand rats can become obese and rapidly develop diabetes-like symptoms when fed the diet typically given to other rodents. ''P. obesus'' has an average lifespan of 14 months in the wild and 3–4 years in captivity. Ecology Activity patterns The fat sand rat is diurnal, but its activity on the surface fluctuates depending on the ambient temperature. Its period of activity is shortest in the summer, starting in the early morning and finishing an hour to several hours after. As the year progresses and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken language, and in adults it can create difficulties with social interaction and at work. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Hearing loss related to age usually affects both ears and is due to cochlear hair cell loss. In some people, particularly older people, hearing loss can result in loneliness. Deaf people usually have little to no hearing. Hearing loss may be caused by a number of factors, including: genetics, ageing, exposure to noise, some infections, birth complications, trauma to the ear, and certain medications or toxins. A common condition that results in hearing loss is chronic ear infections. Certain infections during pregnancy, such as cytomegalovirus, syphilis and rubella, may also cause hearing loss in the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burrow
An Eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion. Burrows provide a form of shelter against predation and exposure to the elements, and can be found in nearly every biome and among various biological interactions. Many animal species are known to form burrows. These species range from small invertebrates, such as the '' Corophium arenarium'', to very large vertebrate species such as the polar bear. Burrows can be constructed into a wide variety of substrates and can range in complexity from a simple tube a few centimeters long to a complex network of interconnecting tunnels and chambers hundreds or thousands of meters in total length; an example of the latter level of complexity, a well-developed burrow, would be a rabbit warren. Vertebrate burrows A large variety of vertebrates construct or use burrows in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus''). Mice are also popular as pets. In some places, certain kinds of field mice are locally common. They are known to invade homes for food and shelter. Mice are typically distinguished from rats by their size. Generally, when a muroid rodent is discovered, its common name includes the term ''mouse'' if it is smaller, or ''rat'' if it is larger. The common terms ''rat'' and ''mouse'' are not taxonomically specific. Typical mice are classified in the genus ''Mus'', but the term ''mouse'' is not confined to members of ''Mus'' and can also apply to species from other genera such as the deer mouse, ''Peromyscus''. Domestic mice sold as pets often differ substantially in size from the common house mouse. This is attributable to breeding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meriones Unguiculatus - Wilhelma
Meriones may refer to: *Meriones (mythology) In Greek mythology, Meriones ( grc, Μηριόνης, Mēriónēs) was the Cretan son of Molus and Melphis or Euippe. Molus was a half-brother of Idomeneus. Like other heroes of mythology, Meriones was said to be a descendant of gods. As a gran ..., a hero of the Trojan War * ''Meriones'' (genus), a genus of gerbil that includes the species most commonly kept as a pet * ''Meriones'' (subgenus) a subgenus of the genus ''Meriones'' that contains a single species: the Tamarisk Jird * 3596 Meriones, a Trojan asteroid {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles River Laboratories
Charles River Laboratories International, Inc., is an American pharmaceutical company specializing in a variety of preclinical and clinical laboratory, gene therapy and cell therapy services for the Pharmaceutical, Medical device and Biotechnology industries. It also supplies assorted biomedical products, outsourcing services, and animals for research and development in the pharmaceutical industry (for example, contract research organization services) and offer support in the fields of basic research, drug discovery, safety and efficacy, clinical support, and manufacturing. The company's broad portfolio allowed them to support the development of approximately 85% of FDA-approved drugs in 2018. Its customers include leading pharmaceutical, biotechnology, agrochemical, government, and academic organization around the globe. The company has over 90 facilities, operates in 20 countries, and employs approximately 18,400 people worldwide. Charles River Laboratories is often criticize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphonse Milne-Edwards
Alphonse Milne-Edwards (Paris, 13 October 1835 – Paris, 21 April 1900) was a French mammalogist, ornithologist, and carcinologist. He was English in origin, the son of Henri Milne-Edwards and grandson of Bryan Edwards, a Jamaican planter who settled at Bruges (then in France). Milne-Edwards obtained a medical degree in 1859 and became assistant to his father at the ' in 1876. He became the director of the in 1891, devoting himself especially to fossil birds and deep-sea exploration. In 1881, he undertook a survey of the Gulf of Gascony with Léopold de Folin and worked aboard the ''Travailleur'' and the ''Talisman,'' researching the seas off the Canary Islands, the Cape Verde Islands, and the Azores. For this, he received a gold medal of the Royal Geographical Society. His major ornithological works include ' published in two parts in 1867 and 1872, ' 1866–1874 and ' 1868–1874. His study of fossils led to the discovery of tropical birds such as trogons and parrots from pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rattus Rattus Domesticus
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A typical adult black rat is lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)