|
Geoid
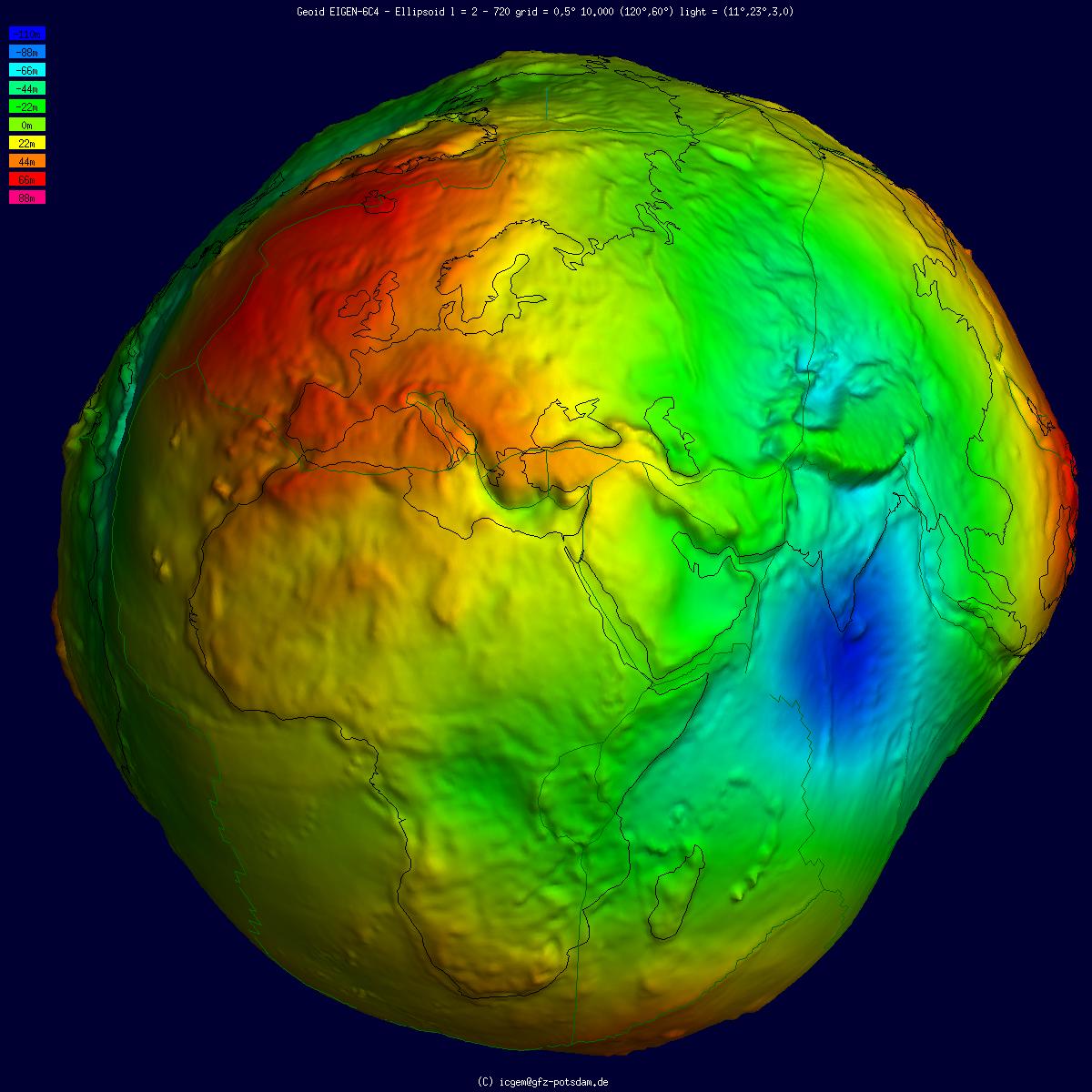
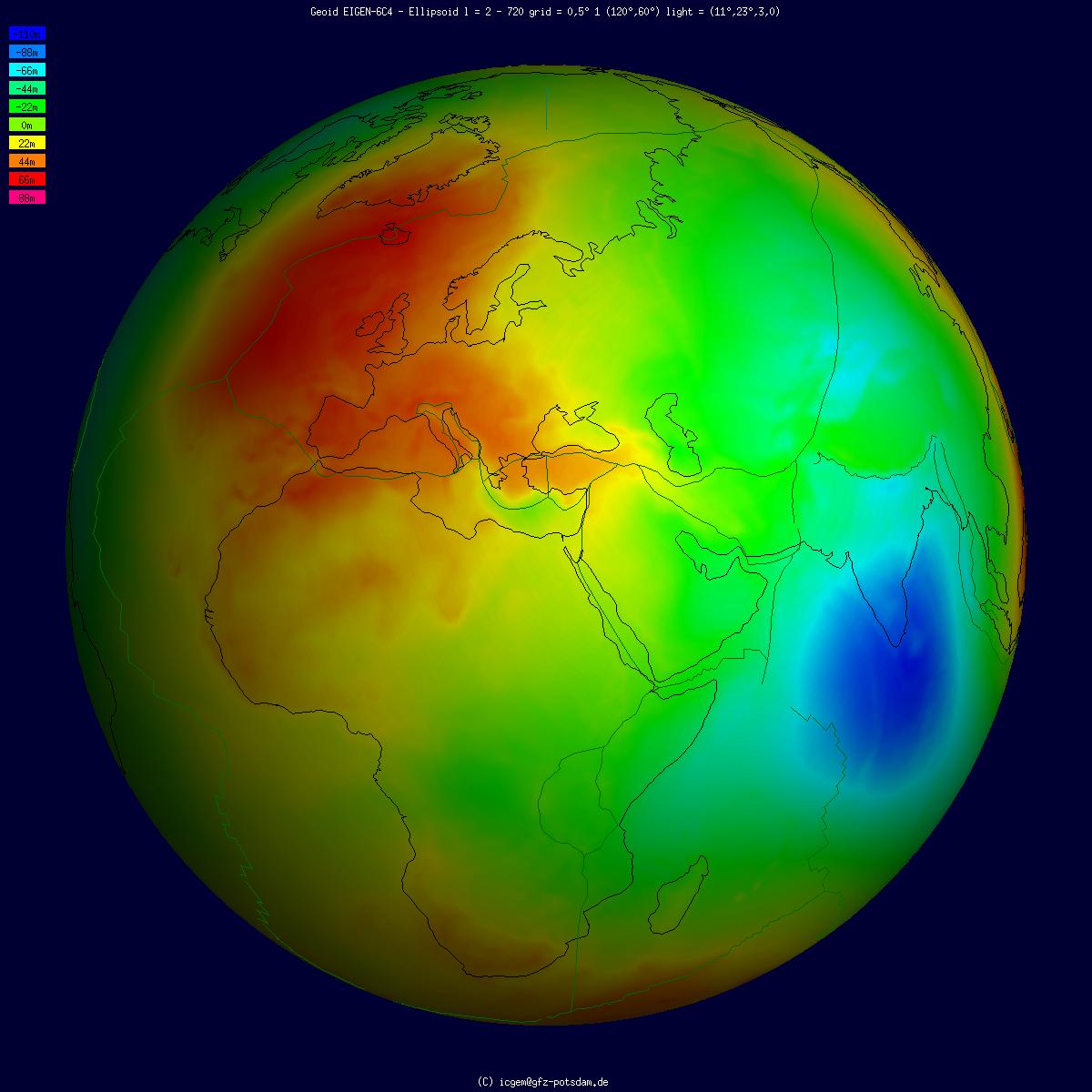
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Carl Friedrich Gauss, Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. All points on a geoid surface have the same geopotential (the sum of gravitational energy, gravitational potential energy and centrifugal force, centrifug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEOID
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Carl Friedrich Gauss, Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. All points on a geoid surface have the same geopotential (the sum of gravitational energy, gravitational potential energy and centrifugal force, centrifug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoid Undulation 10k Scale
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. All points on a geoid surface have the same geopotential (the sum of gravitational potential energy and centrifugal potential energy). The force of gravity acts everywhere per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoid Undulation To Scale
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Carl Friedrich Gauss, Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. All points on a geoid surface have the same geopotential (the sum of gravitational energy, gravitational potential energy and centrifugal force, centrifug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure Of The Earth
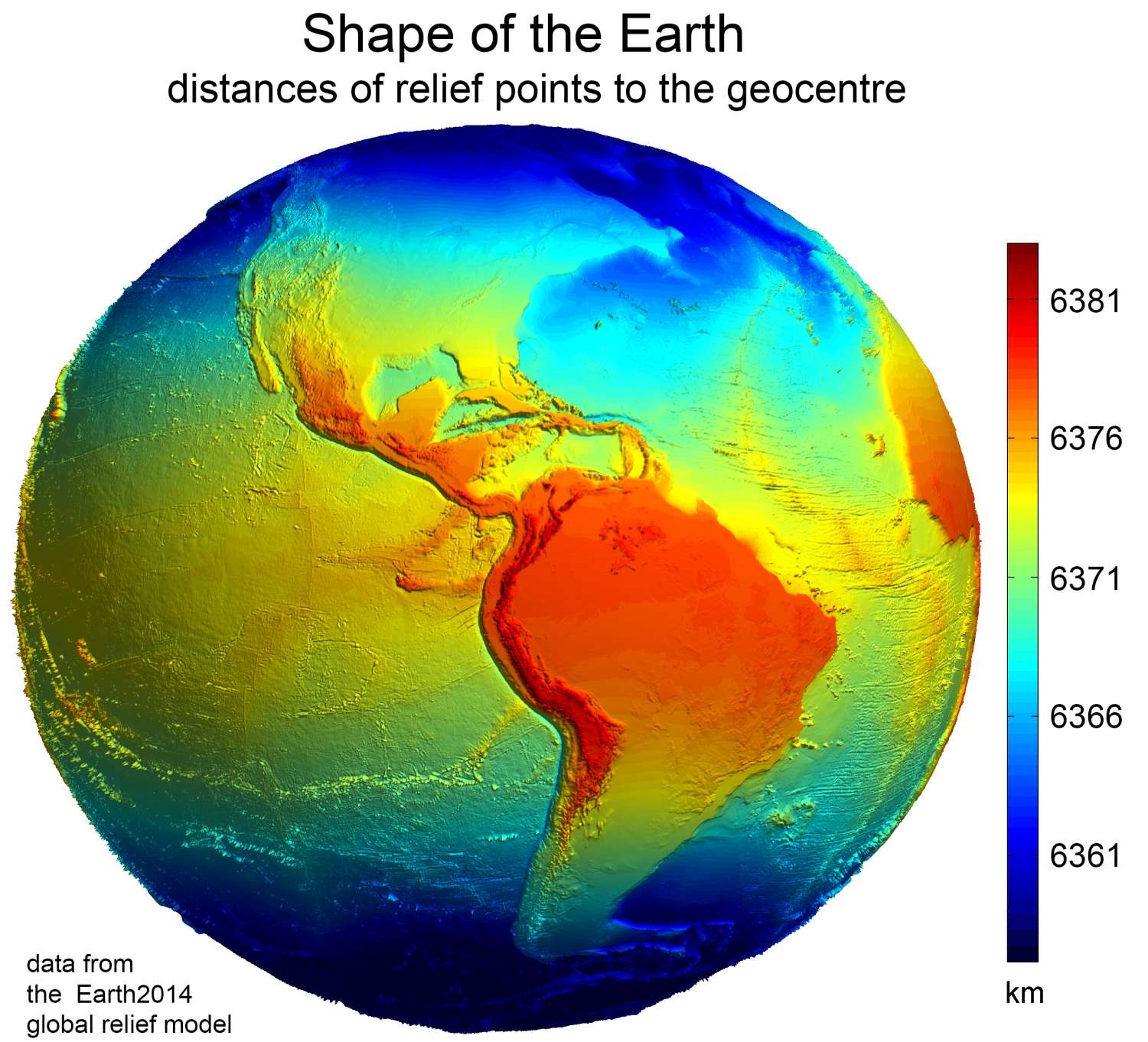
Figure of the Earth is a Jargon, term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A Spherical Earth, sphere is a well-known historical approximation of the figure of the Earth that is satisfactory for many purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including Earth ellipsoid, ellipsoid) have been developed so that Geographic coordinate system, coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's Topography, topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, Hydrography, hydrographers, and Geophysics, geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivalent measurements for other planets (known as '' planetary geodesy''). Geodynamical phenomena, including crustal motion, tides and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques and relying on datums and coordinate systems. The job title is geodesist or geodetic surveyor. History Definition The word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). It is primarily concerned with positioning within the temporally varying gravitational field. Geodesy in the German-speaking world is divided into "higher geodesy" ( or ), which is concerned with measuring Earth on the global scale, and "practical geodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Of Earth
The gravity of Earth, denoted by , is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). It is a vector quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude is given by the norm g=\, \mathit\, . In SI units this acceleration is expressed in metres per second squared (in symbols, m/ s2 or m·s−2) or equivalently in newtons per kilogram (N/kg or N·kg−1). Near Earth's surface, the gravity acceleration is approximately , which means that, ignoring the effects of air resistance, the speed of an object falling freely will increase by about per second every second. This quantity is sometimes referred to informally as ''little '' (in contrast, the gravitational constant is referred to as ''big ''). The precise strength of Earth's gravity varies depending on location. The nominal "average" value at Earth's surface, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geopotential
Geopotential is the potential of the Earth's gravity field. For convenience it is often defined as the ''negative'' of the potential energy per unit mass, so that the gravity vector is obtained as the gradient of this potential, without the negation. In addition to the actual potential (the geopotential), a hypothetical normal potential and their difference, the disturbing potential, can also be defined. Concept For geophysical applications, gravity is distinguished from gravitation. Gravity is defined as the resultant force of gravitation and the centrifugal force caused by the Earth's rotation. Likewise, the respective scalar potentials can be added to form an effective potential called the geopotential, W. Global mean sea surface is close to one of the isosurfaces of the geopotential. This ''equipotential surface'', or surface of constant geopotential, is called the ''geoid''. How the gravitational force and the centrifugal force add up to a force orthogonal to the geoid is ill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Everest
Mount Everest (; Tibetan: ''Chomolungma'' ; ) is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border runs across its summit point. Its elevation (snow height) of was most recently established in 2020 by the Chinese and Nepali authorities. Mount Everest attracts many climbers, including highly experienced mountaineers. There are two main climbing routes, one approaching the summit from the southeast in Nepal (known as the "standard route") and the other from the north in Tibet. While not posing substantial technical climbing challenges on the standard route, Everest presents dangers such as altitude sickness, weather, and wind, as well as hazards from avalanches and the Khumbu Icefall. , over 300 people have died on Everest, many of whose bodies remain on the mountain. The first recorded efforts to reach Everest's summit were made by British mountaineers. As Nepal did not allow foreigners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Ellipsoid
An Earth ellipsoid or Earth spheroid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximations. It is a spheroid (an ellipsoid of revolution) whose minor axis (shorter diameter), which connects the geographical North Pole and South Pole, is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation. The ellipsoid is defined by the ''equatorial axis'' (''a'') and the ''polar axis'' (''b''); their radial difference is slightly more than 21 km, or 0.335% of ''a'' (which is not quite 6,400 km). Many methods exist for determination of the axes of an Earth ellipsoid, ranging from meridian arcs up to modern satellite geodesy or the analysis and interconnection of continental geodetic networks. Amongst the different set of data used in national surveys are several of special importance: the Bessel ellipsoid of 1841, the international H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirit Level
A spirit level, bubble level, or simply a level, is an instrument designed to indicate whether a surface is horizontal (level) or vertical (plumb). Different types of spirit levels may be used by carpenters, stonemasons, bricklayers, other building trades workers, surveyors, millwrights and other metalworkers, and in some photographic or videographic work. Construction Early tubular spirit levels had very slightly curved glass vials with constant inner diameter at each viewing point. These vials are incompletely filled with a liquid, usually a colored spirit or alcohol, leaving a bubble in the tube. They have a slight upward curve, so that the bubble naturally rests in the center, the highest point. At slight inclinations the bubble travels away from the marked center position. Where a spirit level must also be usable upside-down or on its side, the curved constant-diameter tube is replaced by an uncurved barrel-shaped tube with a slightly larger diameter in its middle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |