|
Geocode
A geocode is a code that represents a geographic entity ( location or object). It is a unique identifier of the entity, to distinguish it from others in a finite set of geographic entities. In general the ''geocode'' is a human-readable and short identifier. Typical geocodes and entities represented by it: * ''Country code'' and subdivision code. Polygon of the administrative boundaries of a country or a subdivision. The main examples are ISO codes: ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code (e.g. AF for Afghanistan or BR for Brazil), and its subdivision conventions, such as subdivision codes (e.g. AF-GHO for Ghor province) or subdivision codes (e.g. BR-AM for Amazonas state). * ''DGG cell ID''. Identifier of a cell of a discrete global grid: a Geohash code (e.g. ~0.023 km2 cell 6vjyngd at the Brazilian's center) or an OLC code (e.g. ~0.004 km2 cell 58PJ642P+4 at the same point). * ''Postal code''. Polygon of a postal area: a CEP code (e.g. 70040 represents a Brazil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocode System
A geocode is a code that represents a geographic entity (location or Geographical feature, object). It is a unique identifier of the entity, to distinguish it from others in a finite set of geographic entities. In general the ''geocode'' is a human-readable and short identifier. Typical geocodes and entities represented by it: * ''Country code'' and subdivision code. Polygon of the administrative boundaries of a country or a subdivision. The main examples are ISO codes: ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code (e.g. AF for Afghanistan or BR for Brazil), and its subdivision conventions, such as ISO 3166-2:AF, subdivision codes (e.g. AF-GHO for Ghor province) or ISO 3166-2:BR, subdivision codes (e.g. BR-AM for Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas state). * ''DGG cell ID''. Identifier of a cell of a discrete global grid: a Geohash code (e.g. ~0.023 km2 cell 6vjyngd at the National Congress of Brazil, Brazilian's center) or an Open Location Code, OLC code (e.g. ~0.004 km2 cell 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Global Grid
A discrete global grid (DGG) is a mosaic that covers the entire Earth's surface. Mathematically it is a space partitioning: it consists of a set of non-empty regions that form a partition of the Earth's surface. In a usual grid-modeling strategy, to simplify position calculations, each region is represented by a point, abstracting the grid as a set of region-points. Each region or region-point in the grid is called a cell. When each cell of a grid is subject to a recursive partition, resulting in a "series of discrete global grids with progressively finer resolution", forming a hierarchical grid, it is called a hierarchical DGG (sometimes "global hierarchical tessellation" or "DGG system"). Discrete global grids are used as the geometric basis for the building of geospatial data structures. Each cell is related with data objects or values, or (in the hierarchical case) may be associated with other cells. DGGs have been proposed for use in a wide range of geospatial applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
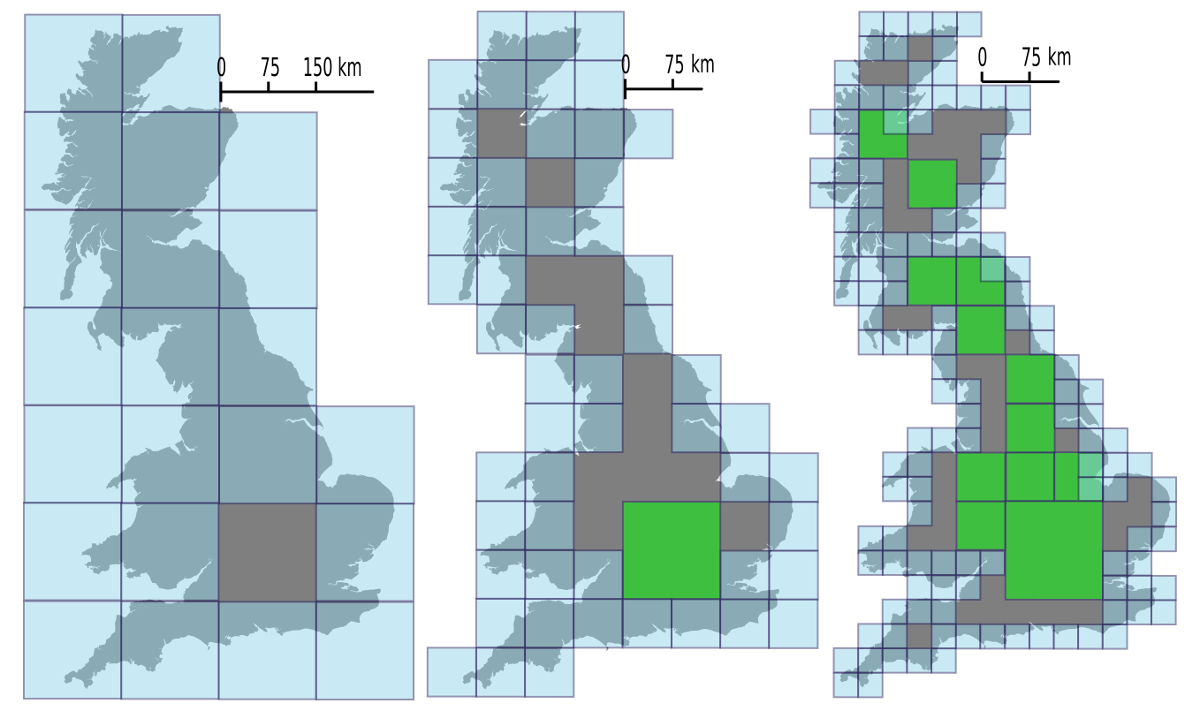
Geohash
Geohash is a public domain geocode system invented in 2008 by Gustavo NiemeyerEvidences at the Wayback Machine: labix.org in 2008, the G. Niemeyer's blog announcing Geohash *an article about Geohash witnessing and citing G. Niemeyer works, before 2012 G. Niemeyer's post at forums.geocaching.com announcing Geohash in Feb. 2008 which encodes a geographic location into a short string of letters and digits. Similar ideas were introduced by G.M. Morton in 1966.G. M. Morton (196''"A Computer Oriented Geodetic Data Base and a New Technique in File Sequencing"''. Report in IBM Canada. It is a hierarchical spatial data structure which subdivides space into buckets of grid shape, which is one of the many applications of what is known as a Z-order curve, and generally space-filling curves. Geohashes offer properties like arbitrary precision and the possibility of gradually removing characters from the end of the code to reduce its size (and gradually lose precision). Geohashing guarantees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Location
In geography, location or place are used to denote a region (point, line, or area) on Earth's surface or elsewhere. The term ''location'' generally implies a higher degree of certainty than ''place'', the latter often indicating an entity with an ambiguous boundary, relying more on human or social attributes of place identity and sense of place than on geometry. Types Locality A locality, settlement, or populated place is likely to have a well-defined name but a boundary that is not well defined varies by context. London, for instance, has a legal boundary, but this is unlikely to completely match with general usage. An area within a town, such as Covent Garden in London, also almost always has some ambiguity as to its extent. In geography, location is considered to be more precise than "place". Relative location A relative location, or situation, is described as a displacement from another site. An example is "3 miles northwest of Seattle". Absolute location An absolute locati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geotagging
Geotagging, or GeoTagging, is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to various media such as a geotagged photograph or video, websites, SMS messages, QR Codes or RSS feeds and is a form of geospatial metadata. This data usually consists of latitude and longitude coordinates, though they can also include altitude, bearing, distance, accuracy data, and place names, and perhaps a time stamp. Geotagging can help users find a wide variety of location-specific information from a device. For instance, someone can find images taken near a given location by entering latitude and longitude coordinates into a suitable image search engine. Geotagging-enabled information services can also potentially be used to find location-based news, websites, or other resources. Geotagging can tell users the location of the content of a given picture or other media or the point of view, and conversely on some media platforms show media relevant to a given location. The geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Location Code
The Open Location Code (OLC) is a geocode based in a system of regular grids for identifying an area anywhere on the Earth. It was developed at Google's Zürich engineering office, and released late October 2014. Location codes created by the OLC system are referred to as "plus codes". Open Location Code is a way of encoding location into a form that is easier to use than showing coordinates in the usual form of latitude and longitude. Plus codes are designed to be used like street addresses, and may be especially useful in places where there is no formal system to identify buildings, such as street names, house numbers, and post codes. Plus codes are derived from latitude and longitude coordinates, so they already exist everywhere. They are similar in length to a telephone number – 849VCWC8+R9, for example – but can often be shortened to only four or six digits when combined with a locality (CWC8+R9, Mountain View). Locations close to each other have similar cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Computer Science
computer science (TCS) is a subset of general computer science and mathematics that focuses on mathematical aspects of computer science such as the theory of computation, lambda calculus, and type theory. It is difficult to circumscribe the theoretical areas precisely. The ACM's Special Interest Group on Algorithms and Computation Theory (SIGACT) provides the following description: History While logical inference and mathematical proof had existed previously, in 1931 Kurt Gödel proved with his incompleteness theorem that there are fundamental limitations on what statements could be proved or disproved. Information theory was added to the field with a 1948 mathematical theory of communication by Claude Shannon. In the same decade, Donald Hebb introduced a mathematical model of learning in the brain. With mounting biological data supporting this hypothesis with some modification, the fields of neural networks and parallel distributed processing were established. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Database
A spatial database is a general-purpose database (usually a relational database) that has been enhanced to include spatial data that represents objects defined in a geometric space, along with tools for querying and analyzing such data. Most spatial databases allow the representation of simple geometric objects such as points, lines and polygons. Some spatial databases handle more complex structures such as 3D objects, topological coverages, linear networks, and triangulated irregular networks (TINs). While typical databases have developed to manage various numeric and character types of data, such databases require additional functionality to process spatial data types efficiently, and developers have often added ''geometry'' or ''feature'' data types. The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) developed the Simple Features specification (first released in 1997) and sets standards for adding spatial functionality to database systems. The '' SQL/MM Spatial'' ISO/IEC standard is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communication channel or storage in a storage medium. An early example is an invention of language, which enabled a person, through speech, to communicate what they thought, saw, heard, or felt to others. But speech limits the range of communication to the distance a voice can carry and limits the audience to those present when the speech is uttered. The invention of writing, which converted spoken language into visual symbols, extended the range of communication across space and time. The process of encoding converts information from a source into symbols for communication or storage. Decoding is the reverse process, converting code symbols back into a form that the recipient understands, such as English or/and Spanish. One reason for coding is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locality-sensitive Hashing
In computer science, locality-sensitive hashing (LSH) is an algorithmic technique that hashes similar input items into the same "buckets" with high probability. (The number of buckets is much smaller than the universe of possible input items.) Since similar items end up in the same buckets, this technique can be used for data clustering and nearest neighbor search. It differs from conventional hashing techniques in that hash collisions are maximized, not minimized. Alternatively, the technique can be seen as a way to reduce the dimensionality of high-dimensional data; high-dimensional input items can be reduced to low-dimensional versions while preserving relative distances between items. Hashing-based approximate nearest neighbor search algorithms generally use one of two main categories of hashing methods: either data-independent methods, such as locality-sensitive hashing (LSH); or data-dependent methods, such as locality-preserving hashing (LPH). Definitions An ''LSH family'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Integrity
Data integrity is the maintenance of, and the assurance of, data accuracy and consistency over its entire life-cycle and is a critical aspect to the design, implementation, and usage of any system that stores, processes, or retrieves data. The term is broad in scope and may have widely different meanings depending on the specific context even under the same general umbrella of computing. It is at times used as a proxy term for data quality, while data validation is a prerequisite for data integrity. Data integrity is the opposite of data corruption. The overall intent of any data integrity technique is the same: ensure data is recorded exactly as intended (such as a database correctly rejecting mutually exclusive possibilities). Moreover, upon later retrieval, ensure the data is the same as when it was originally recorded. In short, data integrity aims to prevent unintentional changes to information. Data integrity is not to be confused with data security, the discipline of prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission. As examples, the works of William Shakespeare, Ludwig van Beethoven, Leonardo da Vinci and Georges Méliès are in the public domain either by virtue of their having been created before copyright existed, or by their copyright term having expired. Some works are not covered by a country's copyright laws, and are therefore in the public domain; for example, in the United States, items excluded from copyright include the formulae of Newtonian physics, cooking recipes,Copyright Protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |