|
Genryaku
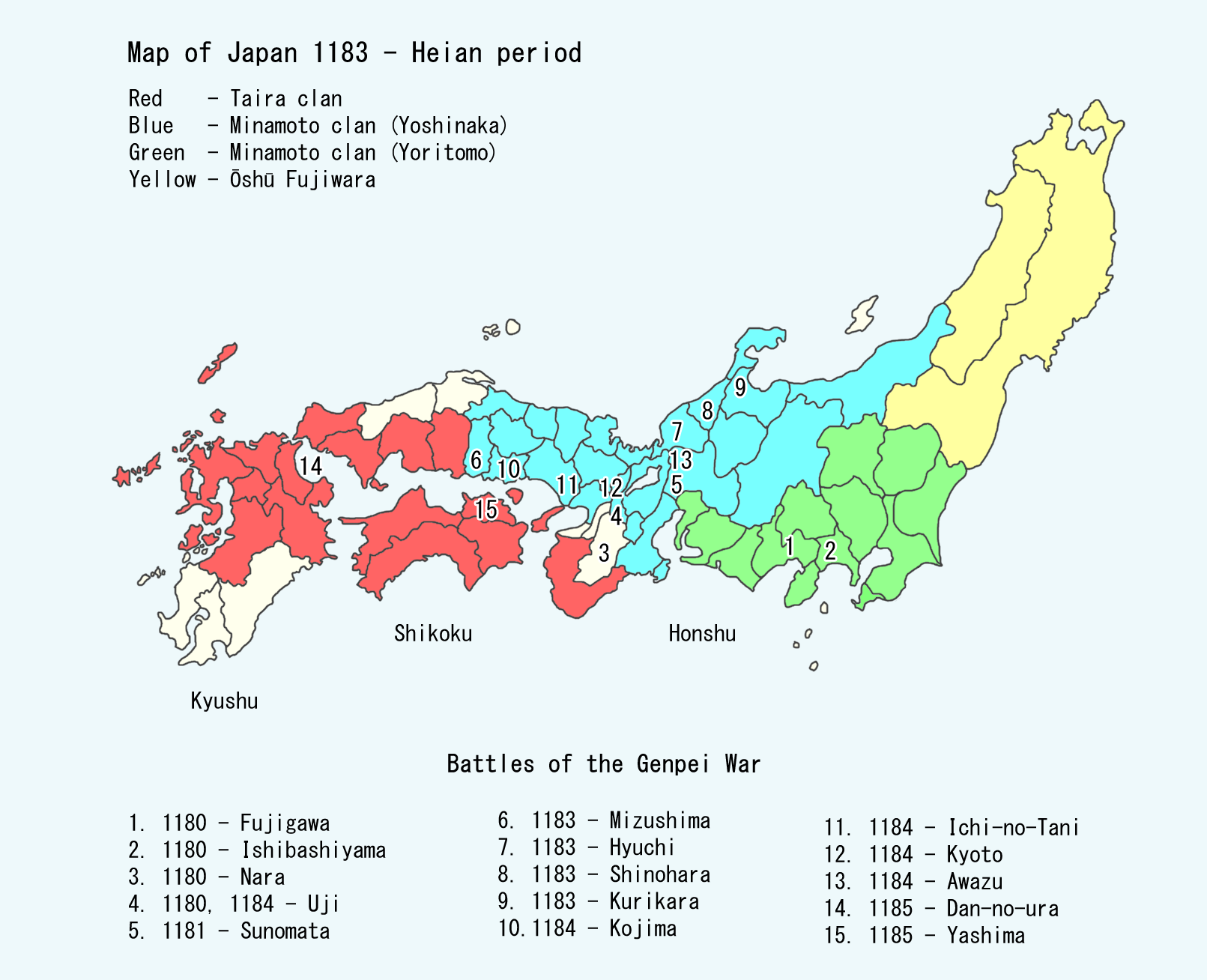
was a after '' Juei'' and before '' Bunji.'' This period spanned the years from April 1184 through August 1185. The reigning emperors were and . Change of era * 1184 : The new era name was created to mark an event or a number of events. The previous era ended and a new one commenced in ''Juei'' 3, on the 16th day of the 4th month of 1184.Brown, p. 337. Events of the ''Genryaku'' era * 1185 (''Genryaku 2, 24th day of the 3rd month''): the Taira (also known as the Heike) and the Minamoto clashed in the Battle of Dan-no-ura; and the Heike were utterly defeated.Kitagawa, Hiroshi ''et al.'' (1975). ''The Tale of the Heike'', p. 787. * 1185 (''Genryaku 2, 9th day of the 7th month''): Great earthquake caused turmoil in the capital and in the neighboring provinces. References ;Sources * Brown, Delmer M. and Ichirō Ishida, eds. (1979) ''Gukanshō: The Future and the Past.''Berkeley: University of California Press. OCLC 251325323* Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunji (Japanese Era)
was a after ''Genryaku'' and before ''Kenkyū.'' This period spanned the years from August 1185 through April 1190. The reigning emperor was . Change of era * 1185 : The new era name was created to mark an event or a number of events. The previous era ended and a new one commenced in ''Genryaku'' 2, on the 16th day of the 4th month of 1184.Brown, p. 337. Events of the ''Bunji'' era * 1185 (''Bunji 1, 29th day of the 11th month''): The court formally approves of establishment of a shogunate government at Kamakura in the Kantō region.Kitagawa, p. 787. * 1186 (''Bunji 2, 4th month''): Go-Shirakawa visits Kenrei-mon In, mother of the late Emperor Antoku and last Imperial survivor of the Battle of Dan-no-ura, at her humble retreat in the nunnery of , near , Sakyō-ku, Kyoto. Notes References * Brown, Delmer and Ichiro Ishida. (1979). ''The Future and the Past: a translation and study of the 'Gukanshō', an interpretative history of Japan written in 1219.'' Berkeley: Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunji (era)
was a after '' Genryaku'' and before '' Kenkyū.'' This period spanned the years from August 1185 through April 1190. The reigning emperor was . Change of era * 1185 : The new era name was created to mark an event or a number of events. The previous era ended and a new one commenced in ''Genryaku'' 2, on the 16th day of the 4th month of 1184.Brown, p. 337. Events of the ''Bunji'' era * 1185 (''Bunji 1, 29th day of the 11th month''): The court formally approves of establishment of a shogunate government at Kamakura in the Kantō region.Kitagawa, p. 787. * 1186 (''Bunji 2, 4th month''): Go-Shirakawa visits Kenrei-mon In, mother of the late Emperor Antoku and last Imperial survivor of the Battle of Dan-no-ura, at her humble retreat in the nunnery of , near , Sakyō-ku, Kyoto. Notes References * Brown, Delmer and Ichiro Ishida. (1979). ''The Future and the Past: a translation and study of the 'Gukanshō', an interpretative history of Japan written in 1219.'' Berkeley: Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juei
was a after '' Yōwa'' and before '' Genryaku.'' This period spanned the years from May 1182 through March 1184. The reigning emperors were Antoku''-tennō'' (安徳天皇) and . Change of era * 1182 : The new era name was created to mark an event or a number of events. The previous era ended and a new one commenced in ''Yōwa'' 2, on the 27th day of the 5th month of 1182. Events of the ''Juei'' era * 1182 (''Juei 1''): The entire country suffers a famine. * 1183 (''Juei 2, 25th day of 7th month''): The Heike flee the capital with Emperor Antoku and Three Sacred Treasures.Kitagawa, p. 786. * 1183 (''Juei 2, 20th day of the 8th month''): In the 3rd year of Antoku''-tennō''s reign (安徳天皇25年), the emperor fled the capital rather than give in to pressures for his abdication. In Antoku's absence, the cloistered former-Emperor Go-Shirakawa then elevated his young brother by decree; and the young child was given the acceptance of abdication (''juzen'') rites. The anti-Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Antoku
was the 81st emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His reign spanned the years from 1180 through 1185. During this time, the Imperial family was involved in a bitter struggle between warring clans. Minamoto no Yoritomo with his cousin Minamoto no Yoshinaka, led a force from the Minamoto clan against the Taira, who controlled the emperor. During the climactic sea Battle of Dan-no-ura in April 1185, Antoku's grandmother Taira no Tokiko took him and plunged with him into the water in the Shimonoseki Straits, drowning the child emperor rather than allowing him to be captured by the opposing forces. The conflict between the clans led to numerous legends and tales. The story of Emperor Antoku and his mother's family became the subject of the Kamakura period epic poem ''The Tale of the Heike'' (Heike is an alternative reading of the Japanese characters for "House of the Taira"). Antoku's tomb is said to be located in a number of places around western Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Era Name
The , also known as , is the first of the two elements that identify years in the Japanese era calendar scheme. The second element is a number which indicates the year number within the era (with the first year being ""), followed by the literal "" meaning "year". Era names originated in 140 BCE in China, during the reign of the Emperor Wu of Han. As elsewhere in East Asia, the use of era names was originally derived from Chinese imperial practice, although the Japanese system is independent of the Chinese, Korean, and Vietnamese era-naming systems. Unlike these other similar systems, Japanese era names are still in use. Government offices usually require era names and years for official papers. The five era names used since the end of the Edo period in 1868 can be abbreviated by taking the first letter of their romanized names. For example, S55 means Shōwa 55 (i.e. 1980), and H22 stands for Heisei 22 (2010). At 62 years and 2 weeks, Shōwa is the longest era to date. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Go-Toba
was the 82nd emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His reign spanned the years from 1183 through 1198. This 12th-century sovereign was named after Emperor Toba, and ''go-'' (後), translates literally as "later"; and thus, he is sometimes called the "Later Emperor Toba". The Japanese word ''go'' has also been translated to mean the "second one"; and in some older sources, this emperor may be identified as "Toba the Second" or as "Toba II". Genealogy Before his ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name (his ''imina'') was . He was also known as Takanari''-shinnō'' He was the fourth son of Emperor Takakura, and thus grandson of Emperor Go-Shirakawa. His mother was Bōmon ''Shokushi'' (坊門殖子) (Empress Dowager Shichijō-in, 七条院), daughter of Bōmon Nobutaka (坊門信隆) of the Fujiwara clan. Consorts and children *Empress (''chūgū''): ''Fujiwara no Ninshi''/Takako (藤原任子) later Gishūmon-in (宜秋門院), K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Eras
The , also known as , is the first of the two elements that identify years in the Japanese era calendar scheme. The second element is a number which indicates the year number within the era (with the first year being ""), followed by the literal "" meaning "year". Era names originated in 140 BCE in China, during the reign of the Emperor Wu of Han. As elsewhere in East Asia, the use of era names was originally derived from Chinese imperial practice, although the Japanese system is independent of the Chinese, Korean, and Vietnamese era-naming systems. Unlike these other similar systems, Japanese era names are still in use. Government offices usually require era names and years for official papers. The five era names used since the end of the Edo period in 1868 can be abbreviated by taking the first letter of their romanized names. For example, S55 means Shōwa 55 (i.e. 1980), and H22 stands for Heisei 22 (2010). At 62 years and 2 weeks, Shōwa is the longest era to date. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
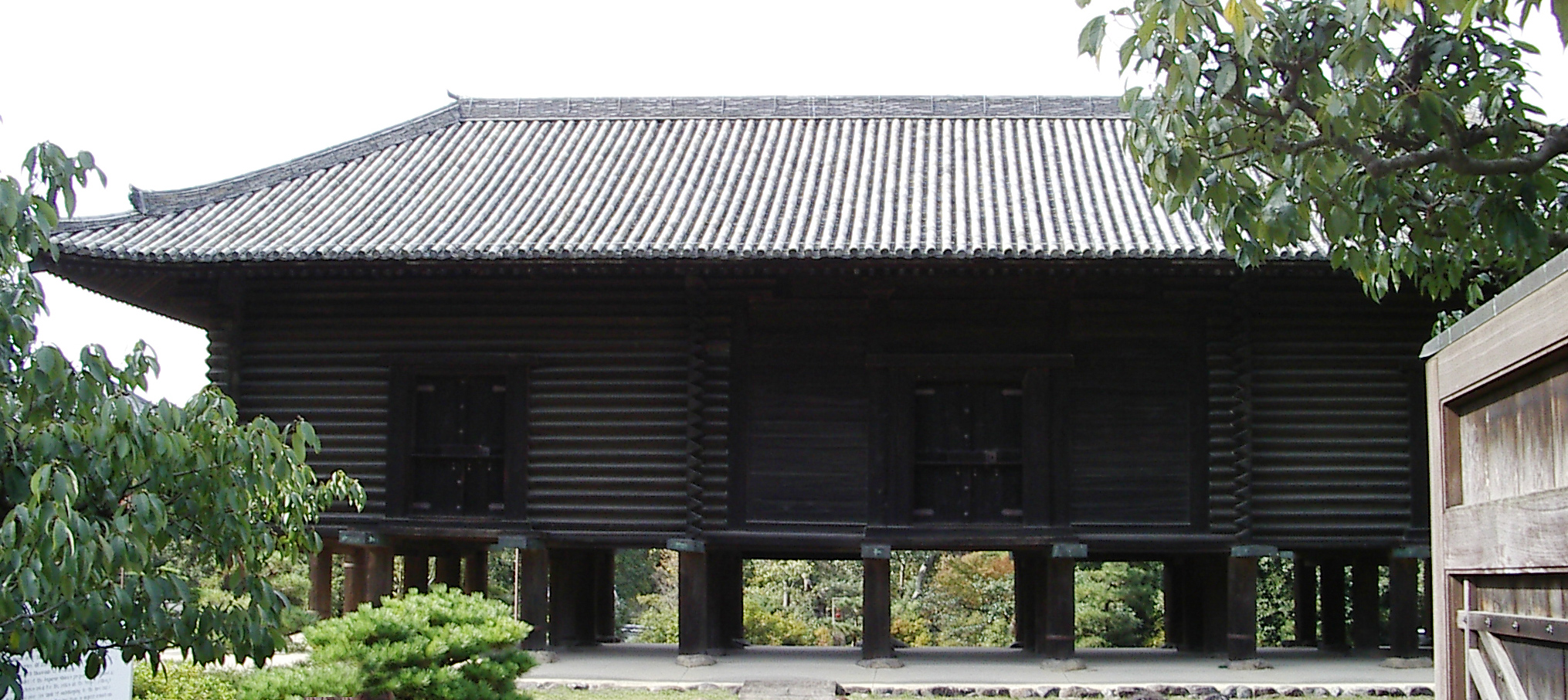
Shōsōin
The is the treasure house of Tōdai-ji Temple in Nara, Japan. The building is in the '' azekura'' ( log-cabin) style with a raised floor. It lies to the northwest of the Great Buddha Hall. The Shōsō-in houses artifacts connected to Emperor Shōmu (聖武天皇)(701–756) and Empress Kōmyō (光明皇后)(701–760), as well as arts and crafts of the Tempyō (天平) era of Japanese history. History The construction of the Tōdai-ji Buddhist temple complex was ordained by Emperor Shōmu as part of a national project of Buddhist temple construction. During the Tempyō period, the years during which Emperor Shōmu reigned, multiple disasters struck Japan as well as political uproar and epidemics. Because of these reasons Emperor Shōmu launched a project of provincial temples. The Tōdai-ji was appointed as the head temple of these provincial temples. Emperor Shōmu was a strong supporter of Buddhism and he thought it would strengthen his central authority as well. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira
The Taira was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian, Kamakura and Muromachi Periods of Japanese history – the others being the Fujiwara, the Tachibana, and the Minamoto. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the emperor they descended from: Kanmu Heishi, Ninmyō Heishi, Montoku Heishi, and Kōkō Heishi. The clan is commonly referred to as or , using the character's On'yomi for ''Taira'', while means "clan", and is used as a suffix for " extended family". History Along with the Minamoto, Taira was one of the honorary surnames given by the emperors of the Heian Period (794–1185 CE) to their children and grandchildren who were not considered eligible for the throne. The clan was founded when the Imperial Court grew too large, and the emperor ordered that the descendants of previous emperors from several generations ago would no longer be princes, but would instead be given noble surnames and ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto
was one of the surnames bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the imperial family who were excluded from the line of succession and demoted into the ranks of the nobility from 1192 to 1333. The practice was most prevalent during the Heian period (794–1185 AD), although its last occurrence was during the Sengoku period. The Taira were another such offshoot of the imperial dynasty, making both clans distant relatives. The Minamoto clan is also called the , or less frequently, the , using the on'yomi reading for Minamoto. The Minamoto were one of four great clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period—the other three were the Fujiwara, the Taira, and the Tachibana. History The first emperor to grant the surname Minamoto was Minamoto no Makoto, seventh son of Emperor Saga. The most prominent of the several Minamoto families, the Seiwa Genji, descended from Minamoto no Tsunemoto (897–961), a grandson of Emperor Seiwa. Tsunemoto went to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dan-no-ura
The was a major sea battle of the Genpei War, occurring at Dan-no-ura, in the Shimonoseki Strait off the southern tip of Honshū. On April 25, 1185 (or March 24, 1185 by the official page of Shimonoseki City), the fleet of the Minamoto clan (Genji), led by Minamoto no Yoshitsune, defeated the fleet of the Taira clan (Heike). The morning rip tide was an advantage to the Taira in the morning but turned to their disadvantage in the afternoon. The young Emperor Antoku was one of those who died among the Taira nobles. History At the time of the battle, the war was not going well for the Taira. They still had the Emperor on their side as well as the Imperial Regalia which symbolized the Emperor's authority, but had lost much of their territory. Still, the coming battle would be fought in their home territory with the trained southerners fighting in their home waters. The Taira were weaker (despite having more ships), but they had the advantage over the Minamoto in unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirement of William P. Sisler in 2017, the university appointed as Director George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)