|
Freedom Of Association
Freedom of association encompasses both an individual's right to join or leave groups voluntarily, the right of the group to take collective action to pursue the interests of its members, and the right of an association to accept or decline membership based on certain criteria. It can be described as the right of a person coming together with other individuals to collectively express, promote, pursue and/or defend common interests. Freedom of association is both an individual right and a collective right, guaranteed by all modern and democratic legal systems, including the United States Bill of Rights, article 11 of the European Convention on Human Rights, section 2 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, and international law, including articles 20 and 23 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and article 22 of International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. The Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work by the International Labour Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Action
Collective action refers to action taken together by a group of people whose goal is to enhance their condition and achieve a common objective. It is a term that has formulations and theories in many areas of the social sciences including psychology, sociology, anthropology, political science and economics. The social identity model Researchers Martijn van Zomeren, Tom Postmes, and Russell Spears conducted a meta-analysis of over 180 studies of collective action, in an attempt to integrate three dominant socio-psychological perspectives explaining antecedent conditions to this phenomenon – injustice, efficacy, and identity. In their resultant 2008 review article, an integrative Social Identity Model of Collective Action (SIMCA) was proposed which accounts for interrelationships among the three predictors as well as their predictive capacities for collective action. An important assumption of this approach is that people tend to respond to subjective states of disadvantage, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
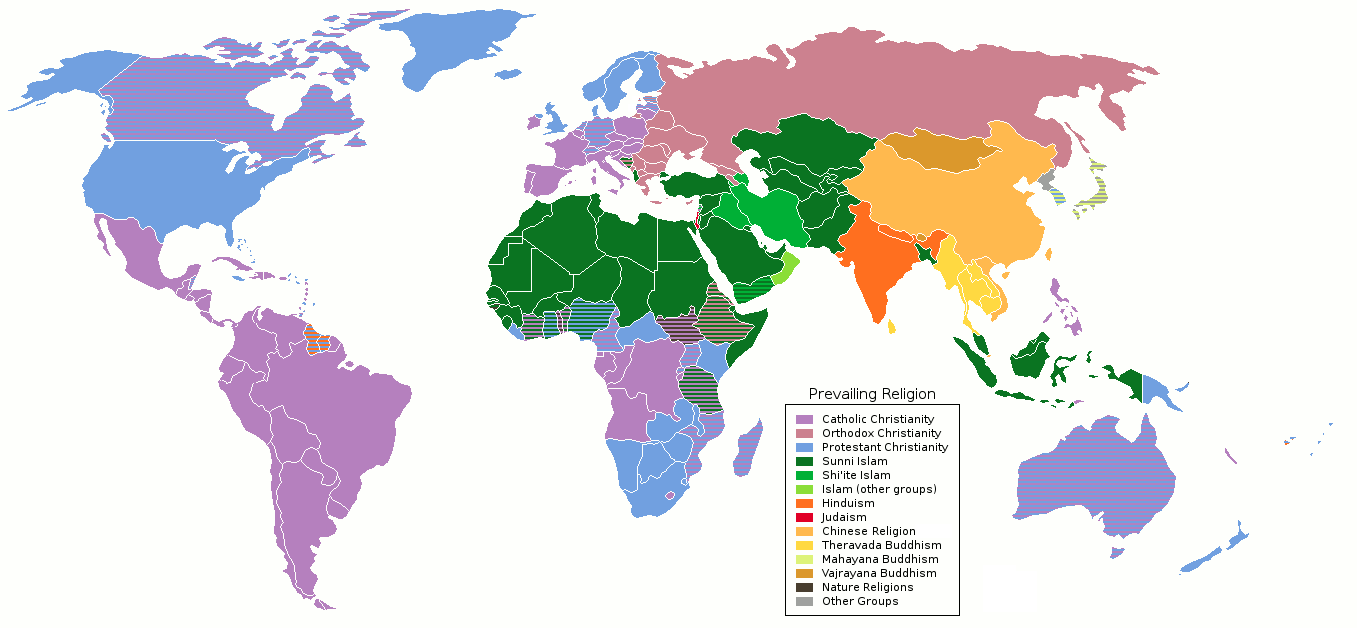
Religious Denominations
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion that operates under a common name and tradition among other activities. The term refers to the various Christian denominations (for example, Eastern Orthodox, Catholic, and the many varieties of Protestantism). It is also used to describe the five major branches of Judaism (Karaite Judaism, Orthodox, Conservative, Reform, and Reconstructionist). Within Islam, it can refer to the branches or sects (such as Sunni, Shia), as well as their various subdivisions such as sub-sects, schools of jurisprudence, schools of theology and religious movements. The world's largest religious denominations are Sunni Islam and Catholic Church. Christianity A Christian denomination is a generic term for a distinct religious body identified by traits such as a common name, structure, leadership and doctrine. Individual bodies, however, may use alternative terms to describe themselves, such as church or fellowship. Divisions between o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companies Act 1856
The Joint Stock Companies Act 1856 (19 & 20 Vict c 47) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was a consolidating statute, recognised as the founding piece of modern United Kingdom company law legislation. Overview Unlike other Acts of Parliament that preceded it, the 1856 Act provided a simple administrative procedure by which any group of seven people could register a limited liability company for themselves. Companies involved in banking and insurance were explicitly excluded from the provisions of the Act. Debate The Joint Stock Companies Bill was introduced to Parliament by the then Vice President of the Board of Trade, Robert Lowe. In doing so he proclaimed the right of every citizen to have freedom of contract and with it obtain limited liability for operating a business. Companies had until recently been prohibited, as a result of the Bubble Act and the stock market panics of the early 18th century. There was still a lot of suspicion of companies, but Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combination Act 1825
The Combinations of Workmen Act 1825 (6 Geo 4 c. 129) was an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom, which prohibited trade unions from attempting to collectively bargain for better terms and conditions at work, and suppressed the right to strike. Background The 1825 Act followed on from the Combination Act 1799 and the Combination of Workmen Act 1824 (5 Geo. 4 c. 95). The 1824 Act repealed the Acts of 1799 and 1800, but this led to a wave of strikes. Accordingly, the Combinations of Workmen Act 1825 was passed to reimpose criminal sanctions for picketing and other methods of persuading workers not to work. Content This law made illegal any combinations not for the purposes of pressing for wage increases or for a change in working hours. Repeal The 1825 Act was recommended for amendment by the majority report of the ''Eleventh and Final Report of the Royal Commissioners appointed to Inquire into the Organisation and Rules of Trade Unions and Other Associations''.(1868-1869) Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search And Seizure
Search and seizure is a procedure used in many civil law and common law legal systems by which police or other authorities and their agents, who, suspecting that a crime has been committed, commence a search of a person's property and confiscate any relevant evidence found in connection to the crime. Some countries have certain provisions in their constitutions that provide the public with the right to be free from "unreasonable searches and seizures". This right is generally based on the premise that everyone is entitled to a reasonable right to privacy. Though specific interpretation may vary, this right can often require law enforcement to obtain a search warrant or consent of the owner before engaging in any form of search and seizure. In cases where evidence is seized in a search, that evidence might be rejected by court procedures, such as with a motion to suppress the evidence under the exclusionary rule. Italy In Italy protection from search and seizure is enshrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, society, culture, nation, religion, or social treatment within their residing area. The term ethnicity is often times used interchangeably with the term nation, particularly in cases of ethnic nationalism, and is separate from the related concept of races. Ethnicity may be construed as an inherited or as a societally imposed construct. Ethnic membership tends to be defined by a shared cultural heritage, ancestry, origin myth, history, homeland, language, or dialect, symbolic systems such as religion, mythology and ritual, cuisine, dressing style, art, or physical appearance. Ethnic groups may share a narrow or broad spectrum of genetic ancestry, depending on group identification, with many groups having mixed genetic ancestry. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race (human Categorization)
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of various kinds, including those characterized by close kinship relations. By the 17th century, the term began to refer to physical ( phenotypical) traits, and then later to national affiliations. Modern science regards race as a social construct, an identity which is assigned based on rules made by society. While partly based on physical similarities within groups, race does not have an inherent physical or biological meaning. The concept of race is foundational to racism, the belief that humans can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. Social conceptions and groupings of races have varied over time, often involving folk taxonomies that define essential types of individuals based on perceived traits. Today, scientists co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Act Of 1968
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a landmark law in the United States signed into law by United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots. Titles II through VII comprise the Indian Civil Rights Act, which applies to the Native American tribes of the United States and makes many but not all of the guarantees of the U.S. Bill of Rights applicable within the tribes. (that Act appears today in Title 25, sections 1301 to 1303 of the United States Code). Titles VIII and IX are commonly known as the Fair Housing Act, which was meant as a follow-up to the Civil Rights Act of 1964 (this is different legislation than the Housing and Urban Development Act of 1968, which expanded housing funding programs). While the Civil Rights Act of 1866 prohibited discrimination in housing, there were no federal enforcement provisions. The 1968 act expanded on previous acts and prohibited discrimination concerning the sale, rental, and financing of housing based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights Instruments
International human rights instruments are the treaties and other international texts that serve as legal sources for international human rights law and the protection of human rights in general. There are many varying types, but most can be classified into two broad categories: ''declarations'', adopted by bodies such as the United Nations General Assembly, which are by nature declaratory, so not legally-binding although they may be politically authoritative and very well-respected soft law;, and often express guiding principles; and ''conventions'' that are multi-party treaties that are designed to become legally binding, usually include prescriptive and very specific language, and usually are concluded by a long procedure that frequently requires ratification by each states' legislature. Lesser known are some "recommendations" which are similar to conventions in being multilaterally agreed, yet cannot be ratified, and serve to set common standards. There may also be administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The U
"The U" is a nickname often given to a university. Specifically, it has been used to refer to: * The University of Miami ** ''The U'' (film), a 2009 documentary about the University of Miami football team. * The University of Utah Other uses * WCIU-TV WCIU-TV (channel 26) is a television station in Chicago, Illinois, United States, affiliated with The CW. It is the flagship television property of locally based Weigel Broadcasting, which has owned the station since its inception, and is sister ..., a television station that was formerly branded as "The U"; * WMEU-CD, a television station that currently carries "The U" branding. {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Of Assembly
Freedom of peaceful assembly, sometimes used interchangeably with the freedom of association, is the individual right or ability of people to come together and collectively express, promote, pursue, and defend their collective or shared ideas. The right to freedom of association is recognized as a human right, a political right and a civil liberty. The terms ''freedom of assembly'' and ''freedom of association'' may be used to distinguish between the freedom to assemble in public places and the freedom to join an association. Freedom of assembly is often used in the context of the right to protest, while freedom of association is used in the context of labor rights and in the Constitution of the United States is interpreted to mean both the freedom to assemble and the freedom to join an association. Human rights instruments Freedom of assembly is included in, among others, the following human rights instruments: * Universal Declaration of Human Rights – Article 20 * In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |