|
Fourth Coalition
The Fourth Coalition fought against Napoleon's French Empire and were defeated in a war spanning 1806–1807. The main coalition partners were Prussia and Russia with Saxony, Sweden, and Great Britain also contributing. Excluding Prussia, some members of the coalition had previously been fighting France as part of the Third Coalition, and there was no intervening period of general peace. On 9 October 1806, Prussia declared war on France and joined a renewed coalition, fearing the rise in French power after the defeat of Austria and establishment of the French-sponsored Confederation of the Rhine in addition to having learned of French plans to cede Prussian-desired Hannover to Britain in exchange for peace. Prussia and Russia mobilized for a fresh campaign with Prussia massing troops in Saxony. Napoleon decisively defeated the Prussians in an expeditious campaign that culminated at the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt on 14 October 1806. French forces under Napoleon occupied Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electorate Of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles IV designated the Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg an electorate, a territory whose ruler was one of the prince-electors who chose the Holy Roman emperor. After the extinction of the male Saxe-Wittenberg line of the House of Ascania in 1422, the duchy and the electorate passed to the House of Wettin. The electoral privilege was tied only to the Electoral Circle, specifically the territory of the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg. In the 1485 Treaty of Leipzig, the Wettin noble house was divided between the sons of Elector Frederick II into the Ernestine and Albertine lines, with the electoral district going to the Ernestines. In 1547, when the Ernestine elector John Frederick I was defeated in the Schmalkaldic War, the electoral district and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles William Ferdinand, Duke Of Brunswick
Charles William Ferdinand (german: Karl Wilhelm Ferdinand; 9 October 1735 – 10 November 1806) was the Prince of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel and Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg and a military leader. His titles are usually shortened to Duke of Brunswick in English-language sources. He succeeded his father as sovereign prince of the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, one of the princely states of the Holy Roman Empire. The duke was a cultured and benevolent despot in the model of his uncle, Frederick the Great, and was married to Princess Augusta, a sister of George III of Great Britain. He was also a recognized master of 18th century warfare, serving as a Field Marshal in the Prussian Army. During the Napoleonic Wars, he was mortally wounded by a musket ball at the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt in 1806. Early life Charles William Ferdinand was born in the town of Wolfenbüttel on 9 October 1735, probably in Wolfenbüttel Castle. He was the first-born son of Charles I, Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick William III Of Prussia
Frederick William III (german: Friedrich Wilhelm III.; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, when the Empire was dissolved. Frederick William III ruled Prussia during the difficult times of the Napoleonic Wars. The king reluctantly joined the coalition against Napoleon in the . Following Napoleon's defeat, he took part in the Congress of Vienna, which assembled to settle the political questions arising from the new, post-Napoleonic order in Europe. His primary interests were internal – the reform of Prussia's Protestant churches. He was determined to unify the Protestant churches to homogenize their liturgy, organization, and architecture. The long-term goal was to have fully centralized royal control of all the Protestant churches in the Prussian Union of Churches. The king was said to be extremely shy and indecisive. His wife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Poland Uprising (1806)
Greater Poland uprising of 1806 was a Polish military insurrection which occurred in the region of Wielkopolska, also known as Greater Poland, against the occupying"In 1772, before the Prussian occupation, only four Jewish families had lived there; in 1815, it numbered 233 Jewish inhabitants" ''A History of Modern Jewry: 1780–1815'', Raphael Mahler, page 364. Schocken Books Prussian forces after the Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1772–1795). The uprising was organized by General Jan Henryk Dąbrowski to help advancing French forces under Napoleon in liberating Poland from Prussian occupation. The Wielkopolska Uprising was a decisive factor that allowed the formation of the Duchy of Warsaw (1807) and the inclusion of Wielkopolska in the Duchy of Warsaw. Historical background While the Kingdom of Prussia already possessed large Polish population in Upper Silesia, it gained additional Polish citizens during the partitions of Poland. From the begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Spain (1700–1808)
The Kingdom of Spain ( es, Reino de España, links=no) entered a new era with the death of Charles II, the last Spanish Hapsburg monarch, who died childless in 1700. The War of the Spanish Succession was fought between proponents of a Bourbon prince, Philip of Anjou, and an Austrian Hapsburg claimant. After the wars were ended with the Treaty of Utrecht, Philip V's rule began in 1715, although he had to renounce his place in the succession of the French throne. Spain entered a period of reform and renewal, as well as continued decline. Ideas of the Age of Enlightenment entered Spain and Spanish America during the eighteenth century. The invasion of the Iberian Peninsula by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807–1808 upended political arrangements of the Spanish Empire and the Portuguese Empire. The eighteenth century in Spanish historiography is often referred to as Bourbon Spain, but the Spanish Bourbons continued to reign from 1814 to 1868 (following the restoration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
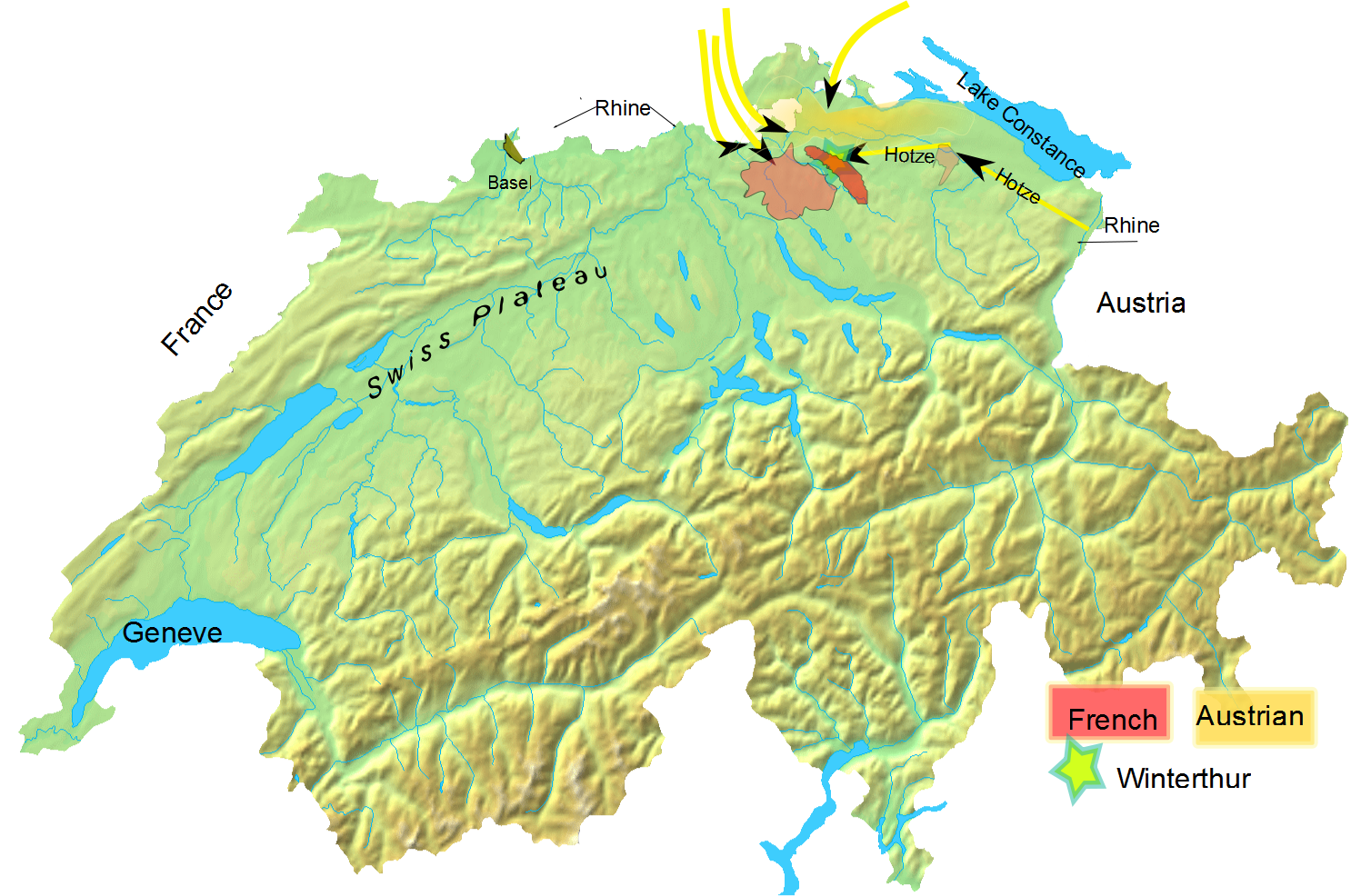
Switzerland In The Napoleonic Era
During the French Revolutionary Wars, the revolutionary armies marched eastward, enveloping Switzerland in their battles against Austria. In 1798, Switzerland was completely overrun by the French and was renamed the Helvetic Republic. The Helvetic Republic encountered severe economic and political problems. In 1798 the country became a battlefield of the Revolutionary Wars, culminating in the Battles of Zürich in 1799. In 1803 Napoleon's Act of Mediation reestablished a Swiss Confederation that partially restored the sovereignty of the cantons, and the former tributary and allied territories of Aargau, Thurgau, Graubünden, St. Gallen, Vaud and Ticino became cantons with equal rights. The Congress of Vienna of 1815 fully re-established Swiss independence and the European powers agreed to permanently recognise Swiss neutrality. At this time, the territory of Switzerland was increased for the last time, by the new cantons of Valais, Neuchâtel and Geneva. The Restoration, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Legions (Napoleonic Period)
The Polish Legions ( pl, Legiony Polskie we Włoszech; also known as the Dąbrowski Legions) in the Napoleonic period, were several Polish military units that served with the French Army, mainly from 1797 to 1803, although some units continued to serve until 1815. After the Third Partition of Poland in 1795, many Poles believed that Revolutionary France and her allies would come to Poland's aid. France's enemies included Poland's partitioners, Prussia, Austria and Russia. Many Polish soldiers, officers, and volunteers therefore emigrated, especially to the parts of Italy under French rule or serving as client states or sister republics to France (leading to the expression, "the Polish Legions in Italy") and to France itself, where they joined forces with the local military. The number of Polish recruits soon reached many thousands. With support from Napoleon Bonaparte, Polish military units were formed, bearing Polish military ranks and commanded by Polish officers. They b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Naples (Napoleonic)
The Kingdom of Naples ( it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule; french: Royaume de Naples) was a French client state in southern Italy created in 1806 when the Bourbon Ferdinand IV & VII of Naples and Sicily sided with the Third Coalition against Napoleon and was in return ousted from his kingdom by a French invasion. Joseph Bonaparte, elder brother of Napoleon I, was installed in his stead: Joseph conferred the title "Prince of Naples" to be hereditary to his children and grandchildren. When Joseph became King of Spain in 1808, Napoleon appointed his brother-in-law Joachim Murat to take his place. Murat was later deposed by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 after striking at Austria in the Neapolitan War, in which he was decisively defeated at the Battle of Tolentino. History Although the Napoleonic kings were officially styled King of Naples and Sicily, British domination of the Mediterranean made it impossible for the French to gain control of Sicily, where Ferdinand ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy (Napoleonic)
The Kingdom of Italy (1805–1814; it, Regno d'Italia; french: Royaume d'Italie) was a kingdom in Northern Italy (formerly the Italian Republic) in personal union with Napoleon I's French Empire. It was fully influenced by revolutionary France and ended with Napoleon's defeat and fall. Its government was assumed by Napoleon as King of Italy and the viceroyalty delegated to his stepson Eugène de Beauharnais. It covered some of Piedmont and the modern regions of Lombardy, Veneto, Emilia-Romagna, Friuli Venezia Giulia, Trentino, South Tyrol, and Marche. Napoleon I also ruled the rest of northern and central Italy in the form of Nice, Aosta, Piedmont, Liguria, Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, but directly as part of the French Empire, rather than as part of a vassal state. Constitutional statutes The Kingdom of Italy was born on 17 March 1805, when the Italian Republic, whose president was Napoleon Bonaparte, became the Kingdom of Italy, with the same man (now styled Napoleon I) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Holland
The Kingdom of Holland ( nl, Holland (contemporary), (modern); french: Royaume de Hollande) was created by Napoleon Bonaparte, overthrowing the Batavian Republic in March 1806 in order to better control the Netherlands. Since becoming Emperor in 1804, Napoleon sought to extirpate republican tendencies in territories France controlled, and placed his third brother, Louis Bonaparte, on the throne of the puppet kingdom.Jonathan Israel, ''The Dutch Republic: Its Rise, Greatness, and Fall 1477-1806''. Oxford: Oxford University Press 1995, 1128. The name of the leading province, Holland, now designated the whole country. In 1807, East Frisia and Jever were added to the kingdom. In 1809, after the Walcheren Campaign, Holland had to surrender all territories south of the river Rhine to France. Also in 1809, Dutch forces fighting on the French side participated in defeating the anti-Bonapartist German rebellion led by Ferdinand von Schill, at the battle of Stralsund. King Louis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Etruria
The Kingdom of Etruria (; it, Regno di Etruria) was an Italian kingdom between 1801 and 1807 that made up a large part of modern Tuscany. It took its name from Etruria, the old Roman name for the land of the Etruscans. History The kingdom was created by the Treaty of Aranjuez, signed at Aranjuez, Spain on 21 March 1801. In the context of a larger agreement between Napoleonic France and Spain, the Bourbons of Parma were compensated for the loss of their territory in northern Italy (which had been occupied by French troops since 1796). Ferdinand, Duke of Parma ceded his duchy to France, and in return his son Louis I was granted the Kingdom of Etruria (which was created from the Grand Duchy of Tuscany). To make way for the Bourbons, the Habsburg Grand Duke of Tuscany Ferdinand III was ousted and compensated with the Electorate of Salzburg. Originally the Grand Duchy of Tuscany, Etruria had been ceded to the Bourbons in 1801 in the person of Charles IV's eldest daughter and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_crop.jpg)

.jpg)
