|
Forschungszentrum Jülich
Forschungszentrum Jülich (FZJ here for short) is a national research institution that pursues interdisciplinary research in the fields of energy, information, and bioeconomy. It operates research infrastructures with a focus on supercomputers. Current research priorities include the structural change in the Rhineland lignite-mining region, hydrogen, and quantum technologies. As a member of the Helmholtz Association with roughly 6,800 employees in ten institutes and 80 subinstitutes, Jülich is one of the largest research institutions in Europe. Forschungszentrum Jülich’s headquarters are located between the cities of Aachen, Cologne, and Düsseldorf on the outskirts of the North Rhine-Westphalian town of Jülich. FZJ has 15 branch offices in Germany and abroad, including eight sites at European and international neutron and synchrotron radiation sources, two joint institutes with the University of Münster, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), and He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Marquardt
Wolfgang is a German male given name traditionally popular in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. The name is a combination of the Old High German words ''wolf'', meaning "wolf", and ''gang'', meaning "path", "journey", "travel". Besides the regular "wolf", the first element also occurs in Old High German as the combining form "-olf". The earliest reference of the name being used was in the 8th century. The name was also attested as "Vulfgang" in the Reichenauer Verbrüderungsbuch in the 9th century. The earliest recorded famous bearer of the name was a tenth-century Saint Wolfgang of Regensburg. Due to the lack of conflict with the pagan reference in the name with Catholicism, it is likely a much more ancient name whose meaning had already been lost by the tenth century. Grimm (''Teutonic Mythology'' p. 1093) interpreted the name as that of a hero in front of whom walks the "wolf of victory". A Latin gloss by Arnold of St Emmeram interprets the name as ''Lupambulus''.E. F� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second ( FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FH Aachen
The FH Aachen – Aachen University of Applied Sciences is one of the biggest Fachhochschulen in Germany with roughly 15,000 students, 250 professors, 470 contract lecturers, and 340 assistants. It is specialized in certain topical areas (e.g. technology, engineering, business, design). The FH Aachen ranks as the first best among the Universities of Applied Sciences in Germany in the fields of Electrical, Mechanical engineering and Informatics. Ten Faculties offer 53 Bachelor's, 22 Master's and three cooperative degree programmes. The FH Aachen is situated in Aachen and in Jülich. History The FH Aachen was established in 1971 as a result of the amalgamation of several universities of applied sciences and vocational training centres. Thus, it can look back on a practice-oriented educational tradition going back more than 100 years. The Federal Framework Law for Education in 1976 raised the legal status of all Fachhochschulen to a position equal to that of traditional universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knut Urban
Knut W. Urban (born 25 June 1941 in Stuttgart) is a German physicist. He has been the Director of the Institute of Microstructure Research at Forschungszentrum Jülich from 1987 to 2010. Knut Urban's research focuses on the field of aberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy (both regarding the further development of instruments and the control software), the examination of structural defects in oxides and the physical properties of complex metallic alloys. He also works on Josephson effects in high-temperature superconductors and the application of these effects in SQUID systems and magnetometers as well as on the application of Hilbert transform spectroscopy in examining the excitation of solids, liquids and gases on the gigahertz and terahertz scale. Besides his activities at Forschungszentrum Jülich he was also professor for experimental physics at RWTH Aachen University before retirement. Biography Urban studied physics at the University of Stuttgart an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in multilayers composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR. The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on spin orientation. The main application of GMR is in magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physics
) , image = Nobel Prize.png , alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "MDCCCXXXIII" above, followed by (smaller) "OB•" then "MDCCCXCVI" below. , awarded_for = Outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of Physics , presenter = Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences , location = Stockholm, Sweden , date = , reward = 9 million Swedish kronor (2017) , year = 1901 , holder_label = Most recently awarded to , holder = Alain Aspect, John Clauser, and Anton Zeilinger , most_awards = John Bardeen (2) , website nobelprize.org, previous = 2021 , year2=2022, main=2022, next= 2023 The Nobel Prize in Physics is a yearly award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of physics. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Grünberg
Peter Andreas Grünberg (; 18 May 1939 – 7 April 2018) was a German physicist, and Nobel Prize in Physics laureate for his discovery with Albert Fert of giant magnetoresistance which brought about a breakthrough in gigabyte hard disk drives. Life and career Grünberg was born in Pilsen, Bohemia—which at the time was in the German-occupied Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (now the Czech Republic)—to the Sudeten German family of Anna and Feodor A. Grünberg which first lived in Dysina (Dýšina) to the east of Pilsen. Grünberg was a Catholic. After the war, the family was interned; the parents were brought to a camp. His father, a Russia-born engineer who since 1928 had worked for Škoda, died on 27 November 1945 in Czech imprisonment and is buried in a mass grave in Pilsen which is also inscribed with ''Grünberg Theodor † 27. November 1945''. His mother Anna (who died in 2002 aged 100) had to work in agriculture and stayed with her parents in the Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
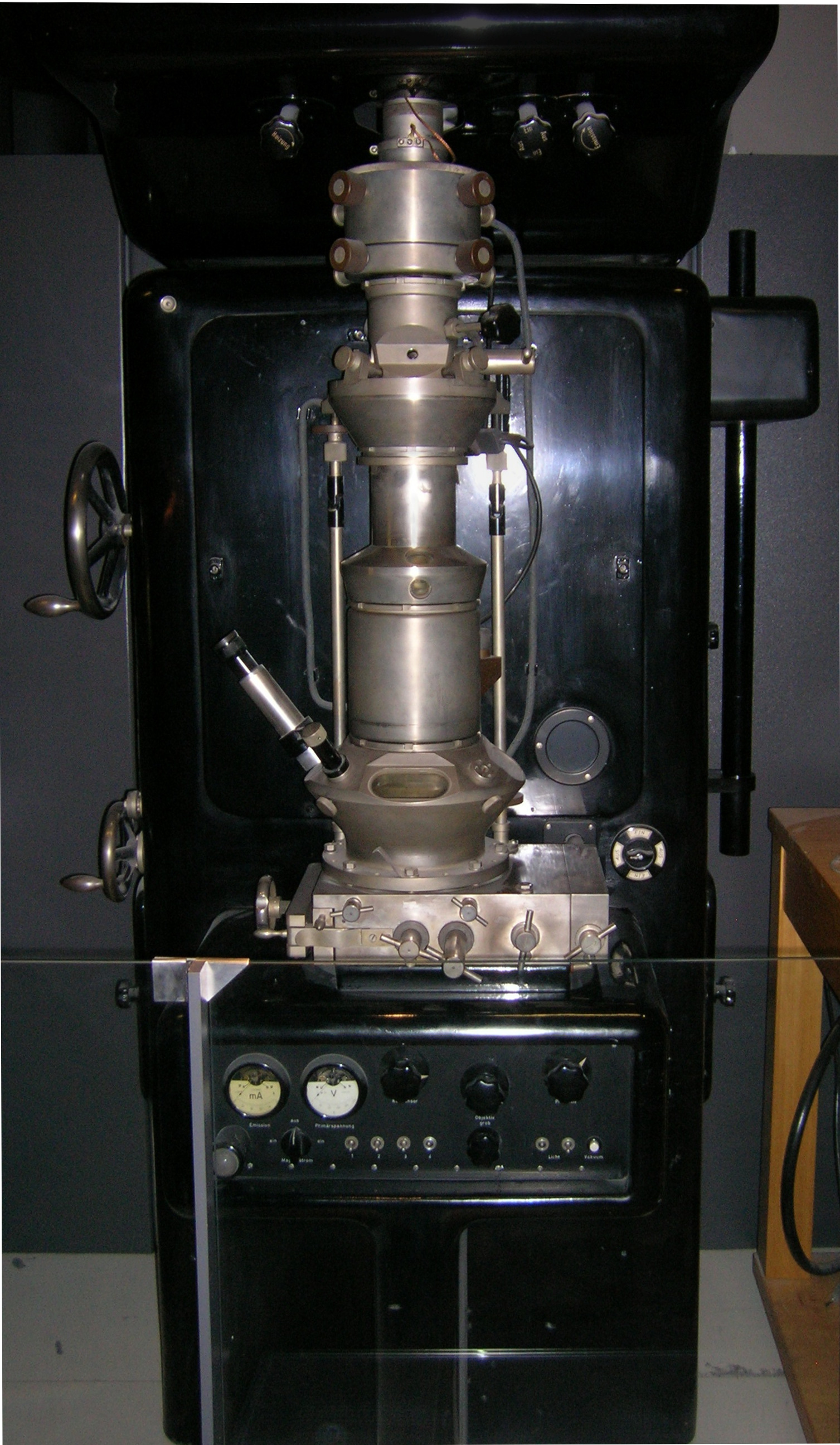
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a sensor such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy is a major analytical method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Ruska-Centre
The Ernst Ruska-Centre for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons (ER-C) is an institute located on the campus of Forschungszentrum Jülich belonging to the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres. It comprises three divisionsER-C-1“''Physics of Nanoscale systems''”,�ER-C-2“''Materials Science and Technology''” anER-C-3“''Structural Biology''”. Within the framework of a competence platform governed jointly by Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University, the ER-C operates a national and international user facility that provides access to state-of-the-art instruments, methods and expertise to universities, research institutions and industry. The ER-C's main purposes are fundamental research in electron microscopy, focusing on method development and applications of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and scanning-transmission electron microscopy (STEM) in physics, chemistry and biology. History As a competence platform, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
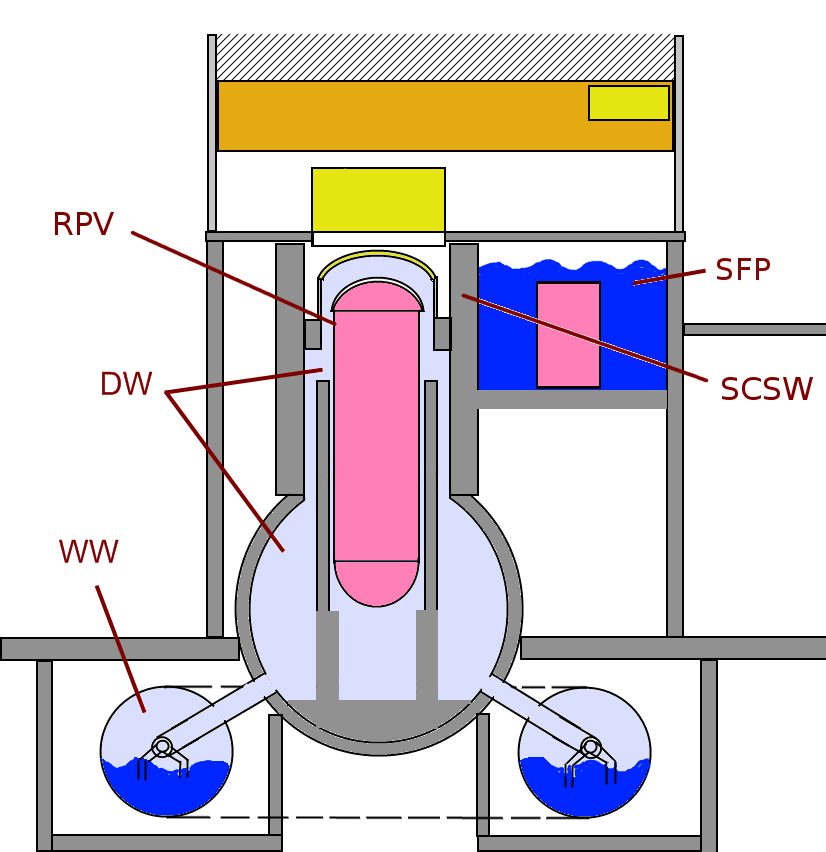
Fukushima Nuclear Disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and remains the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan. The earthquake triggered a powerful tsunami, with 13–14-meter-high waves damaging the nuclear power plant's emergency diesel generators, leading to a loss of electric power. The result was the most severe nuclear accident since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, classified as level seven on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) after initially being classified as level five, and thus joining Chernobyl as the only other accident to receive such classification. While the 1957 explosion at the Mayak facility was the second worst by radioactivity released, the INES ranks incidents by impact on population, so Chernobyl (335,000 people evacuated) and Fukushima (154,000 evacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainer Moormann
Rainer Moormann (born 1950) is a German chemist and nuclear whistleblower. He grew up in Osnabrück. After finishing highschool he studied physical chemistry in Braunschweig and received a doctor's degree with Raman spectroscopic and theoretical investigations on hydrogen bonds in liquids. Since 1976 he had been working at the Forschungszentrum Jülich, doing research on safety problems with pebble bed reactors (especially with the AVR reactor), fusion power and spallation neutron sources. Papers In 2008 Moormann published a critical paper on the safety of pebble bed reactors, which raised attention among specialists in the field, and managed to distribute it via the media, facing considerable opposition. In 2020, Moormann co-authored a paper that argued in favor of keeping the by then six German nuclear power plants running in order to reduce CO2 emissions. Whistleblower award For doing this despite the occupational disadvantages he had to accept as a consequence, Moo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)