|
FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the first fabless manufacturing model.Jonathan Cassell, iSuppli.A Forgettable Year for Memory Chip Makers: iSuppli releases preliminary 2008 semiconductor rankings." December 1, 2008. Retrieved January 15, 2009.John Edwards, EDN." June 1, 2006. Retrieved January 15, 2009. Xilinx was co-founded by Ross Freeman, Bernard Vonderschmitt, and James V Barnett II in 1984 and the company went public on the NASDAQ in 1990. AMD announced its acquisition of Xilinx in October 2020 and the deal was completed on February 14, 2022 through an all-stock transaction worth an estimated $50 billion. Company overview Xilinx was founded in Silicon Valley in 1984 and headquartered in San Jose, USA, with additional offices in Longmont, USA; Dublin, Ireland; Sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconfigurable Computing
Reconfigurable computing is a computer architecture combining some of the flexibility of software with the high performance of hardware by processing with very flexible high speed computing fabrics like field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). The principal difference when compared to using ordinary microprocessors is the ability to make substantial changes to the datapath itself in addition to the control flow. On the other hand, the main difference from custom hardware, i.e. application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) is the possibility to adapt the hardware during runtime by "loading" a new circuit on the reconfigurable fabric. History The concept of reconfigurable computing has existed since the 1960s, when Gerald Estrin's paper proposed the concept of a computer made of a standard processor and an array of "reconfigurable" hardware. The main processor would control the behavior of the reconfigurable hardware. The latter would then be tailored to perform a specific task ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altera StratixIVGX FPGA
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015. The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-range Arria series, and lower-cost Cyclone series system on a chip field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs); the MAX series complex programmable logic device and non-volatile FPGAs; Quartus design software; and Enpirion PowerSoC DC-DC power solutions. The company was founded in 1983 by semiconductor veterans Rodney Smith, Robert Hartmann, James Sansbury, and Paul Newhagen with $500,000 in seed money. The name of the company was a play on "alterable", the type of chips the company created. In 1984, the company formed a long-running design partnership with Intel, and 1988, became a public company via an initial public offering. In 1994, Altera acquired the PLD business of Intel for $50 million. On December 28, 2015, the company was acquired b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015. The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-range Arria series, and lower-cost Cyclone series system on a chip field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs); the MAX series complex programmable logic device and non-volatile FPGAs; Quartus design software; and Enpirion PowerSoC DC-DC power solutions. The company was founded in 1983 by semiconductor veterans Rodney Smith, Robert Hartmann, James Sansbury, and Paul Newhagen with $500,000 in seed money. The name of the company was a play on "alterable", the type of chips the company created. In 1984, the company formed a long-running design partnership with Intel, and 1988, became a public company via an initial public offering. In 1994, Altera acquired the PLD business of Intel for $50 million. On December 28, 2015, the company was acquired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
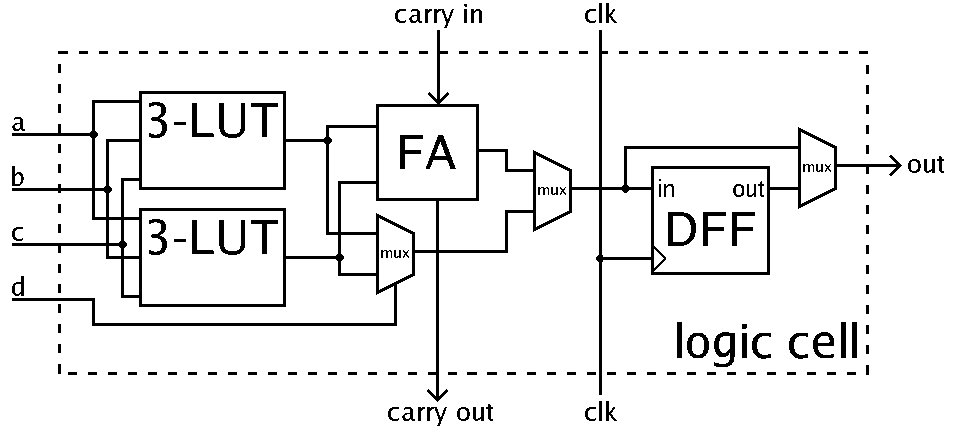
Logic Block
In computing, a logic block or configurable logic block (CLB) is a fundamental building block of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) technology. Logic blocks can be configured by the engineer to provide reconfigurable logic gates. Logic blocks are the most common FPGA architecture, and are usually laid out within a logic block array. Logic blocks require I/O pads (to interface with external signals), and routing channels (to interconnect logic blocks). Programmable logic blocks were invented by David W. Page and LuVerne R. Peterson, and defined within their 1985 patents.Google Patent Search,Re-programmable PLA. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted April 2, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009.Google Patent Search,Dynamic data re-programmable PLA. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted June 18, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009. Applications An application circuit must be mapped into an FPGA with adequate resources. While the number of logic blocks and I/Os required is easily determined from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsemi
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets. In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-based Microchip Technology was acquiring the company for over US$10 billion, pending regulatory approval. In May 2018, it was announced that Microchip had completed its acquisition of Microsemi. In August 2018, Microchip discovered that Microsemi shipped large orders to distributors on discount before the closing of the acquisition and had a culture of excessive extravagance, casting some doubt on the future prospect of the acquisition. History 1959 to 1970: Early years Microsemi was founded in February 1959 in Culver City, California as MicroSemiconductor. It incorporated in Delaware on September 27, 1960. A trade catalog and price lists from this early period can be found at the Smithsonian Institution. In March 1963, A. Feldon repre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manufacture. Before the PLD can be used in a circuit it must be programmed to implement the desired function. Compared to fixed logic devices, programmable logic devices simplify the design of complex logic and may offer superior performance. Unlike for microprocessors, programming a PLD changes the connections made between the gates in the device. PLDs can broadly be categorised into, in increasing order of complexity, Simple Programmable Logic Devices (SPLDs), comprising programmable array logic, programmable logic array and generic array logic; Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs) and Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). History In 1969, Motorola offered the XC157, a mask-programmed gate array with 12 gates and 30 uncommitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Devices
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manufacture. Before the PLD can be used in a circuit it must be programmed to implement the desired function. Compared to fixed logic devices, programmable logic devices simplify the design of complex logic and may offer superior performance. Unlike for microprocessors, programming a PLD changes the connections made between the gates in the device. PLDs can broadly be categorised into, in increasing order of complexity, Simple Programmable Logic Devices (SPLDs), comprising programmable array logic, programmable logic array and generic array logic; Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs) and Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). History In 1969, Motorola offered the XC157, a mask-programmed gate array with 12 gates and 30 uncommitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application-Specific Integrated Circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec. Application-specific standard product (ASSP) chips are intermediate between ASICs and industry standard integrated circuits like the 7400 series or the 4000 series. ASIC chips are typically fabricated using metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) technology, as MOS integrated circuit chips. As feature sizes have shrunk and design tools improved over the years, the maximum complexity (and hence functionality) possible in an ASIC has grown from 5,000 logic gates to over 100 million. Modern ASICs often include entire microprocessors, memory blocks including ROM, RAM, EEPROM, flash memory and other large building blocks. Such an ASIC is often termed a SoC (system-on-chip). Designers of digital ASICs often use a hardware descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardware Description Language
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, and most commonly, digital logic circuits. A hardware description language enables a precise, formal description of an electronic circuit that allows for the automated analysis and simulation of an electronic circuit. It also allows for the synthesis of an HDL description into a netlist (a specification of physical electronic components and how they are connected together), which can then be placed and routed to produce the set of masks used to create an integrated circuit. A hardware description language looks much like a programming language such as C or ALGOL; it is a textual description consisting of expressions, statements and control structures. One important difference between most programming languages and HDLs is that HDLs explicitly include the notion of time. HDLs form an integral part of electroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Array
A gate array is an approach to the design and manufacture of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) using a prefabricated chip with components that are later interconnected into logic devices (e.g. NAND gates, flip-flops, etc.) according to a custom order by adding metal interconnect layers in the factory. It was popular during upheaval in semiconductor industry in 80s and its usage declined by end of 90s. Similar technologies have also been employed to design and manufacture analog, analog-digital, and structured arrays, but, in general, these are not called gate arrays. Gate arrays have also been known as ''uncommitted logic arrays'' (''ULAs''), which also offered linear circuit functions, and ''semi-custom chips''. History Development Gate arrays had several concurrent development paths. Ferranti in the UK pioneered commercializing bipolar ULA technology, offering circuits of "100 to 10,000 gates and above" by 1983. The company's early lead in semi-custom chips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded System
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today. , it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e. microprocessors with integrated memory and peripheral interfaces), but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Cyclone_III_(cropped).jpg)