|
Extensor
In anatomy, extension is a movement of a joint that increases the angle between two bones or body surfaces at a joint. Extension usually results in straightening of the bones or body surfaces involved. For example, extension is produced by extending the flexed (bent) elbow. Straightening of the arm would require extension at the elbow joint. If the head is tilted all the way back, the neck is said to be extended. Muscles of extension Upper limb *of arm at shoulder **Axilla and Shoulder ***Latissimus Dorsi *** Posterior Fibres of Deltoid *** Teres Major *of forearm at elbow ** Posterior compartment of the arm ***Triceps Brachii *** Anconeus *of hand at wrist ** Posterior compartment of the forearm ***Extensor carpi radialis longus *** Extensor carpi radialis brevis *** Extensor carpi ulnaris *** Extensor digitorum *of phalanges, at all joints ** Posterior compartment of the forearm *** Extensor digitorum *** Extensor digiti minimi (little finger only) ***Extensor indicis (index fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Indicis
In human anatomy, the extensor indicis roprius'' is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it extends. Structure It arises from the distal third of the dorsal part of the body of ulna and from the interosseous membrane. It runs through the fourth tendon compartment together with the extensor digitorum, from where it projects into the dorsal aponeurosis of the index finger. Opposite the head of the second metacarpal bone, it joins the ulnar side of the tendon of the extensor digitorum which belongs to the index finger. Like the extensor digiti minimi (i.e. the extensor of the little finger), the tendon of the extensor indicis runs and inserts on the ulnar side of the tendon of the common extensor digitorum. The extensor indicis lacks the juncturae tendinum interlinking the tendons of the extensor digitorum on the dorsal side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Compartment Of The Forearm
The posterior compartment of the forearm (or extensor compartment) contains twelve muscles which primarily extend the wrist and digits. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna. Structure Muscles There are generally twelve muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm, which can be further divided into superficial, intermediate, and deep. Most of the muscles in the superficial and the intermediate layers share a common origin which is the outer part of the elbow, the lateral epicondyle of humerus. The deep muscles arise from the distal part of the ulna and the surrounding interosseous membrane. The brachioradialis, flexor of the elbow, is unusual in that it is located in the posterior compartment, but it is actually a muscle of flexor / anterior compartment of the forearm. The anconeus, assisting in extension of the elbow joint, is by some considered part of the posterior compartment of the arm. The majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Digitorum
The extensor digitorum muscle (also known as extensor digitorum communis) is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. Extensor digitorum is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the radial nerve. Structure The extensor digitorum muscle arises from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, by the common tendon; from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles, and from the antebrachial fascia. It divides below into four tendons, which pass, together with that of the extensor indicis proprius, through a separate compartment of the dorsal carpal ligament, within a mucous sheath. The tendons then diverge on the back of the hand, and are inserted into the middle and distal phalanges of the fingers in the following manner.''Gray's anatomy'' (1918), see infobox Opposite the metacarpophalangeal articulation each tendon is bound by fasciculi to the collateral ligaments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "hand" and fingerprints extremely similar to human fingerprints) are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking. Some evolutionary anatomists use the term ''hand'' to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb more generally—for example, in the context of whether the three digits of the bird hand involved the same homologous loss of two digits as in the dinosaur hand. The human hand usually has five digits: four fingers plus one thumb; these are often referred to collectively as five fingers, however, whereby the thumb is included as one of the fingers. It has 27 bones, not including the sesamoid bone, the numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "hand" and fingerprints extremely similar to human fingerprints) are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking. Some evolutionary anatomists use the term ''hand'' to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb more generally—for example, in the context of whether the three digits of the bird hand involved the same homologous loss of two digits as in the dinosaur hand. The human hand usually has five digits: four fingers plus one thumb; these are often referred to collectively as five fingers, however, whereby the thumb is included as one of the fingers. It has 27 bones, not including the sesamoid bone, the nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Pollicis Brevis
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) belongs to the deep group of the posterior fascial compartment of the forearm. It is a part of the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox. Structure The extensor pollicis brevis arises from the ulna distal to the abductor pollicis longus, from the interosseous membrane, and from the dorsal surface of the radius. Its direction is similar to that of the abductor pollicis longus, its tendon passing the same groove on the lateral side of the lower end of the radius, to be inserted into the base of the first phalanx of the thumb. Variation Absence; fusion of tendon with that of the extensor pollicis longus or abductor pollicis longus muscle. Function In a close relationship to the abductor pollicis longus, the extensor pollicis brevis both exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Pollicis Longus
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle. Structure The extensor pollicis longus arises from the dorsal surface of the ulna and from the interosseous membrane, next to the origins of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis. Passing through the third tendon compartment, lying in a narrow, oblique groove on the back of the lower end of the radius,'' Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox it crosses the wrist close to the dorsal midline before turning towards the thumb using Lister's tubercle on the distal end of the radius as a pulley. It obliquely crosses the tendons of the extensores carpi radialis longus and brevis, and is separated from the extensor pollicis brevis by a triangular interval, the anatomical snuff box in which the radial artery is fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
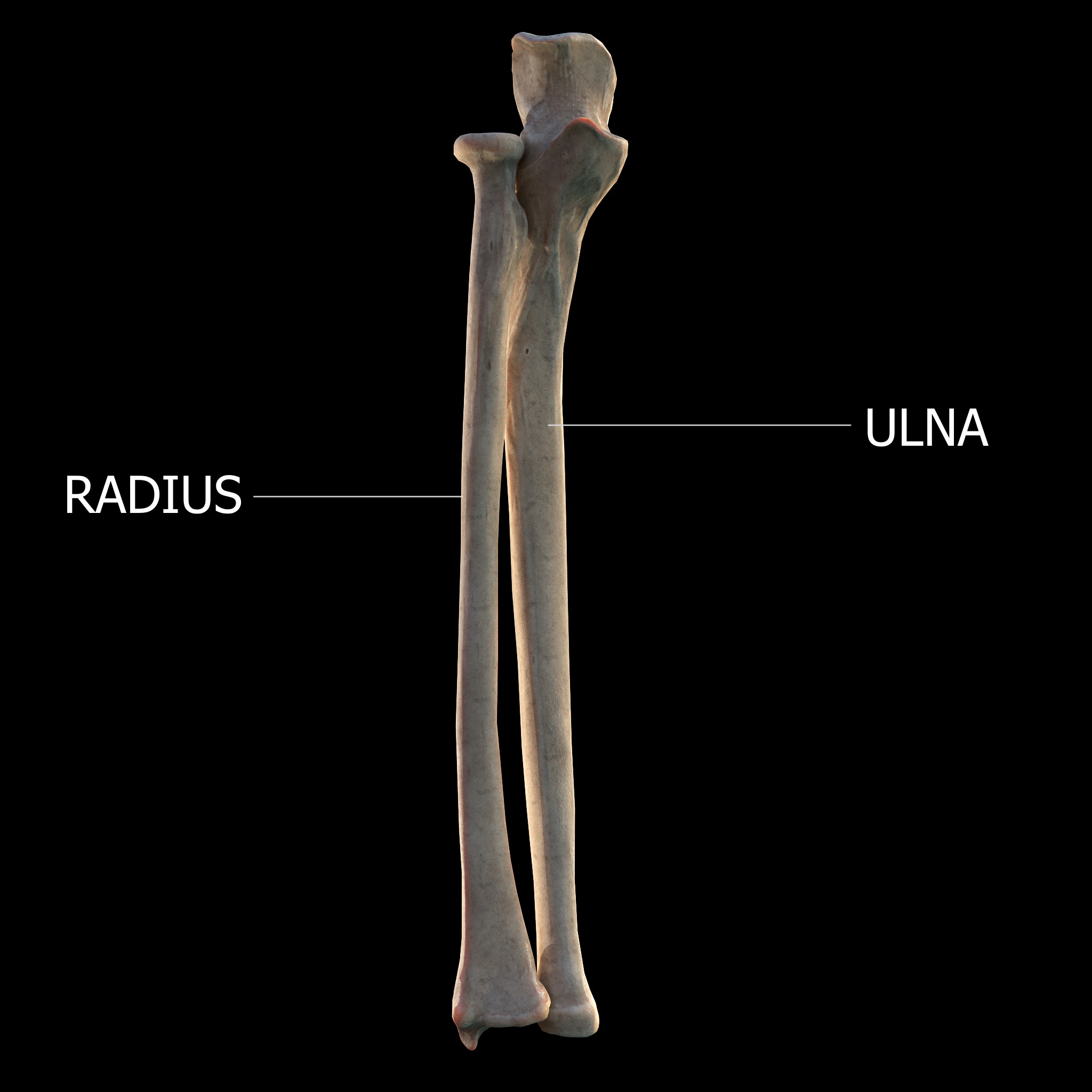
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
In human anatomy, the extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal muscle located on the ulnar side of the forearm. The extensor carpi ulnaris acts to extend and adduct at the carpus/wrist from anatomical position. Being an extensor muscle, extensor carpi ulnaris is located on the posterior side of the forearm. Origin and insertion It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the posterior border of the ulna, and crosses the forearm to the ulnar (medial) side to insert at the base of the 5th metacarpal. Action The extensor carpi ulnaris extends the wrist, but when acting alone inclines the hand toward the ulnar side; by its continued action it extends the elbow-joint. The muscle is a minor extensor of the carpus in carnivores, but has become a flexor in ungulates. In this case it would be described as ''ulnaris lateralis''. Innervation Despite its name, the extensor carpi ulnaris is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve (C7 and C8), the continuation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the extensor carpi radialis brevis. Origin and insertion It arises from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, by the common extensor tendon; from the radial collateral ligament of the elbow-joint; from a strong aponeurosis which covers its surface; and from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles.''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox The fibres end approximately at the middle of the forearm in the form of a flat tendon, which is closely connected with that of the extensor carpi radialis longus, and accompanies it to the wrist; it passes beneath the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, beneath the extensor retinaculum, and inserts into the lateral dorsal surface of the base of the third metacarpal bone, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Digiti Minimi
The extensor digiti minimi (extensor digiti quinti proprius) is a slender muscle of the forearm, placed on the ulnar side of the extensor digitorum communis, with which it is generally connected. It arises from the common extensor tendon by a thin tendinous slip and frequently from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles. Its tendon passes through a compartment of the extensor retinaculum, posterior to distal radio-ulnar joint, then divides into two as it crosses the dorsum of the hand, and finally joins the extensor digitorum tendon. All three tendons attach to the dorsal digital expansion of the fifth digit (little finger). There may be a slip of tendon to the fourth digit. Variations An additional fibrous slip from the lateral epicondyle; the tendon of insertion may not divide or may send a slip to the ring finger. Absence of muscle rare; fusion of the belly with the extensor digitorum communis The extensor digitorum muscle (also known as extensor dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |