|
Euparkeria
''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to the ancestry of Archosauria, the group that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, birds and crocodilians. ''Euparkeria'' had hind limbs that were slightly longer than its forelimbs, which has been taken as evidence that it may have been able to rear up on its hind legs as a facultative biped. Although ''Euparkeria'' is close to the ancestry of fully bipedal archosaurs such as early dinosaurs, it probably developed bipedalism independently. ''Euparkeria'' was not as well adapted to bipedal locomotion as dinosaurs and its normal movement was probably more analogous to a crocodilian high walk. Palaeobiology Locomotion The hind limbs of ''Euparkeria'' are somewhat longer than its forelimbs, which has led many researchers to conclude that it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euparkeria Skull Ezcurra 2016
''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to the ancestry of Archosauria, the group that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, birds and crocodilians. ''Euparkeria'' had hind limbs that were slightly longer than its forelimbs, which has been taken as evidence that it may have been able to rear up on its hind legs as a facultative biped. Although ''Euparkeria'' is close to the ancestry of fully bipedal archosaurs such as early dinosaurs, it probably developed bipedalism independently. ''Euparkeria'' was not as well adapted to bipedal locomotion as dinosaurs and its normal movement was probably more analogous to a crocodilian high walk. Palaeobiology Locomotion The hind limbs of ''Euparkeria'' are somewhat longer than its forelimbs, which has led many researchers to conclude that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
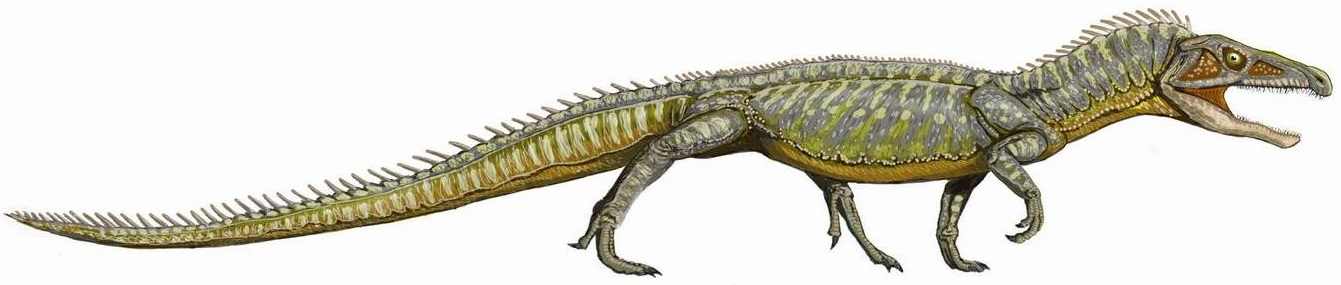
Euparkeria NT Small
''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to the ancestry of Archosauria, the group that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, birds and crocodilians. ''Euparkeria'' had hind limbs that were slightly longer than its forelimbs, which has been taken as evidence that it may have been able to rear up on its hind legs as a facultative biped. Although ''Euparkeria'' is close to the ancestry of fully bipedal archosaurs such as early dinosaurs, it probably developed bipedalism independently. ''Euparkeria'' was not as well adapted to bipedal locomotion as dinosaurs and its normal movement was probably more analogous to a crocodilian high walk. Palaeobiology Locomotion The hind limbs of ''Euparkeria'' are somewhat longer than its forelimbs, which has led many researchers to conclude that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euparkeria
''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to the ancestry of Archosauria, the group that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, birds and crocodilians. ''Euparkeria'' had hind limbs that were slightly longer than its forelimbs, which has been taken as evidence that it may have been able to rear up on its hind legs as a facultative biped. Although ''Euparkeria'' is close to the ancestry of fully bipedal archosaurs such as early dinosaurs, it probably developed bipedalism independently. ''Euparkeria'' was not as well adapted to bipedal locomotion as dinosaurs and its normal movement was probably more analogous to a crocodilian high walk. Palaeobiology Locomotion The hind limbs of ''Euparkeria'' are somewhat longer than its forelimbs, which has led many researchers to conclude that it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriform
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs bird.html"_;"title="ncluding_bird">ncluding_birds;_Phil_Senter.html" ;"title="bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were originally superficiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs". Prior to 2011, the clade Pseudosuchia was often called Crurotarsi in reference to the crurotarsal ankle found in almost all members of the group, which traditionally included phytosaurs, ornithosuchids, and suchians. However, a major 2011 study of Triassic archosaur relations proposed that phytosaurs were not closely related to other traditional "crurotarsans", at least compared to "bird-line archosaurs" (Avemetatarsalians) such as pterosaurs and dinosaurs. As a result, the possession of a crurotarsal ankle was considered a plesiomorphic ("primitive") feature retained by pseudosuchians. Crurotarsi now refers to a broader group of reptiles including Pseudosuchia, Phytosauria, and Avemetatarsalia. Despite Pseudosuchia meaning "false crocodiles", the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halazhaisuchus
''Halazhaisuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Early Triassic of China. It is known from a single species, ''Halazhaisuchus qiaoensis'', which was named in 1982 from the lower Ermaying Formation in Shaanxi. It was assigned to the family Euparkeriidae as a close relative of the genus ''Euparkeria'' from South Africa. ''Halazhaisuchus'' is known from a single holotype specimen called V6027, which was discovered in 1977 and includes a portion of the vertebral column, some ribs, two scapulae and two humeri, the right radius and ulna, and a left coracoid. Two rows of plate-like bones called osteoderms run along the length of the vertebrae. When it was first described in 1982, ''Halazhaisuchus'' was considered a close relative of ''Euparkeria'' because it has primitive features like small intercentra bones between the vertebrae and a large coracoid, not seen in later archosaurs. However, these features are common to many early archosauriforms and are not unique to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poposauroid
Poposauroidea is a clade of advanced pseudosuchians (archosaurs closer to crocodilians than to dinosaurs). It includes poposaurids, shuvosaurids, ctenosauriscids, and other unusual pseudosuchians such as ''Qianosuchus'' and ''Lotosaurus''. However, it excludes most large predatory quadrupedal "rauisuchians" such as rauisuchids and " prestosuchids". Those reptiles are now allied with crocodylomorphs (crocodile ancestors) in a clade known as Loricata, which is the sister taxon to the poposauroids in the clade Paracrocodylomorpha. Although it was first formally defined in 2007, the name "Poposauroidea" has been used for many years. The group has been referred to as Poposauridae by some authors, although this name is often used more narrowly to refer to the family that includes ''Poposaurus'' and its close relatives. Poposauroids went extinct at the end of the Triassic period along with other non-crocodylomorph pseudosuchians. However, they were among the most diverse and long-la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmolskina
left, 210px, Fossil elements. ''Osmolskina'' is a genus of archosauriform reptile which lived during the Early Triassic in what is now Poland. The type species, ''Osmolskina czatkowicensis'', was described by Magdalena Borsuk−Białynicka and Susan Evans in 2003. The generic name honors the late female Polish paleontologist Halszka Osmólska. ''Osmolskina'' closely resembles the well-known genus ''Euparkeria''. The authors of the 2003 paper considered classifying ''Osmolskina'' within the family Euparkeriidae, noting the animal's close resemblance to ''Euparkeria ''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to ...'', but concluded that "Euparkeriidae remains monotypic because no other genus can be assigned to it with confidence." References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4189167 Preh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is also not precisely defined. The Karoo is partly defined by its topography, geology and climate, and above all, its low rainfall, arid air, cloudless skies, and extremes of heat and cold.Potgieter, D.J. & du Plessis, T.C. (1972) ''Standard Encyclopaedia of Southern Africa''. Vol. 6. pp. 306–307. Nasou, Cape Town.''Reader’s Digest Illustrated Guide to Southern Africa''. (5th Ed. 1993). pp. 78–89. Reader’s Digest Association of South Africa Pty. Ltd., Cape Town. The Karoo also hosted a well-preserved ecosystem hundreds of million years ago which is now represented by many fossils. The ǃ’Aukarob formed an almost impenetrable barrier to the interior from Cape Town, and the early adventurers, explorers, hunters, and travelers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger. There were two major types of pterosaurs. Basal pterosaurs (also called 'non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs' or 'rhamphorhynchoids') were smaller animals with fully toothed jaws and, typically, long tails. Their wide wing membranes probably included and connected the hind legs. On the ground, they would have had an awkward sprawling posture, but the anatomy of their joints and strong claws would have made them effective climbers, and some may have even lived in trees. Basal pterosaurs were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerotic Ring
Sclerotic rings are rings of bone found in the eyes of many animals in several groups of vertebrates, except for mammals and crocodilians. They can be made up of single bones or multiple segments and take their name from the sclera. They are believed to have a role in supporting the eye, especially in animals whose eyes are not spherical, or which live underwater. Fossil sclerotic rings are known for a variety of extinct animals, including ichthyosaurs, pterosaurs, and dinosaurs, but are often not preserved. File:Tawny Frogmouth Skull.jpg, A skull of an extant tawny frogmouth, showing large sclerotic rings. File:Uroplatus_phantasticus_skull1.jpg, A skull of an extant satanic leaf-tailed gecko, showing large sclerotic rings. File:Viatkogorgon skull.png, Skull and sclerotic ring of the gorgonopsian '' Viatkogorgon''. File:Prosaurolophus maximus3.JPG, Sclerotic ring of the hadrosaur ''Prosaurolophus ''Prosaurolophus'' (; meaning "before ''Saurolophus''", in comparison to the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |