|
Eshnunna
Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Although situated in the Diyala Valley north-west of Sumer proper, the city nonetheless belonged securely within the Sumerian cultural milieu. It is sometimes, in archaeological papers, called Ashnunnak or Tuplias,. The tutelary deity of the city was Tishpak (Tišpak) (having replaced Ninazu) though other gods, including Sin, Adad, and Inanna of Kititum were also worshiped there. The personal goddess of the rulers were Belet-Šuḫnir and Belet-Terraban. History Early Bronze Inhabited since the Jemdet Nasr period, around 3000 BC, Eshnunna was a major city during the Early Dynastic period of Mesopotamia. It is known, from cuneiform records and excavations, that the city was occupied in the Akkadian period though its extent was noticeably less than it reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tishpak
Tishpak (Tišpak) was a Mesopotamian god associated with the ancient city Eshnunna and its sphere of influence, located in the Diyala area of Iraq. He was primarily a war deity, but he was also associated with snakes, including the mythical mushussu and bashmu, and with kingship. Tishpak was of neither Sumerian nor Akkadian origin and displaced Eshnunna's original tutelary god, Ninazu. Their iconography and character were similar, though they were not formally regarded as identical in most Mesopotamian sources. Origin It is commonly assumed that initially the tutelary deity of Eshnunna was Ninazu, worshiped in the temple Esikil. From the Sargonic period onward, Tishpak competed with Ninazu in that location, and the latter finally ceased to be mentioned in documents from it after Hammurabi's conquest. While similar in character, Ninazu and Tishpak were not fully conflated, and unlike Inanna and Ishtar or Enki and Ea were kept apart in god lists. It is generally agreed by sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
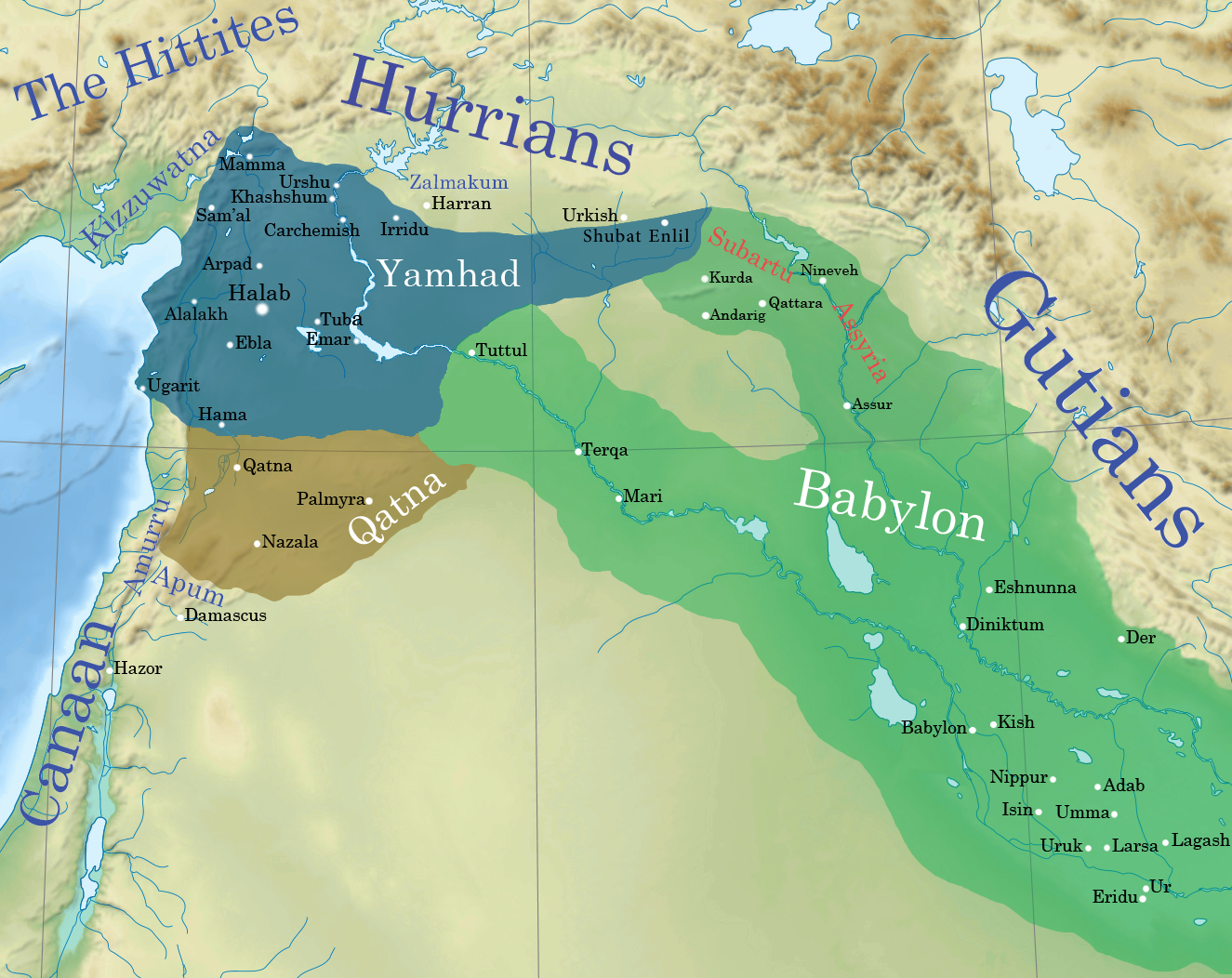
Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad ( akk, Šamši-Adad; Amorite: ''Shamshi-Addu''), ruled 1808–1776 BC, was an Amorite warlord and conqueror who had conquered lands across much of Syria, Anatolia, and Upper Mesopotamia.Some of the Mari letters addressed to Shamsi-Adad by his son can be found in the Mari Letters section of Rise Shamshi-Adad I inherited the throne in Ekallatum from Ila-kabkabu (fl. c. 1836 BC – c. 1833 BC). Ila-kabkabu is mentioned as the father of Shamshi-Adad I in the "Assyrian King List" (AKL); a similar name (not necessarily the same figure) is listed in the preceding section of the AKL among the “kings whose fathers are known”. However, Shamshi-Adad I did not inherit the Assyrian throne from his father but was instead a conqueror. Ila-kabkabu had been an Amorite king not of Assur (Aššur) (in Assyria) but of Ekallatum. According to the '' Mari Eponyms Chronicle'', Ila-kabkabu seized Shuprum (c. 1790 BC), then Shamshi-Adad I “entered his father's house” (Shamshi-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belet-Šuḫnir And Belet-Terraban
Belet-Šuḫnir and Belet-Terraban were a pair of Mesopotamian goddesses best known from the archives of the Third Dynasty of Ur, but presumed to originate further north, possibility in the proximity of modern Kirkuk and ancient Eshnunna. Their names are usually assumed to be derived from cities where they were originally worshiped. Both in ancient sources, such as ritual texts, seal inscriptions and god lists, and in modern scholarship, they are typically treated as a pair. In addition to Ur and Eshnunna, both of them are also attested in texts from Susa in Elam. Their character remains poorly understood due to scarcity of sources, though it has been noted that the tone of many festivals dedicated to them was "lugubrious," which might point at an association with the Ancient Mesopotamian underworld, underworld. Names and character The names of Belet-Šuḫnir and Belet-Terraban, written conventionally as ''dingir, dBe-la-at-Šuḫ-nir'' and ''dBe-la-at-Dar-ra-ba-an'', can be tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammurabi
Hammurabi (Akkadian: ; ) was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from to BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered Elam and the city-states of Larsa, Eshnunna, and Mari. He ousted Ishme-Dagan I, the king of Assyria, and forced his son Mut-Ashkur to pay tribute, bringing almost all of Mesopotamia under Babylonian rule. Hammurabi is best known for having issued the Code of Hammurabi, which he claimed to have received from Shamash, the Babylonian god of justice. Unlike earlier Sumerian law codes, such as the Code of Ur-Nammu, which had focused on compensating the victim of the crime, the Law of Hammurabi was one of the first law codes to place greater emphasis on the physical punishment of the perpetrator. It prescribed specific penalties for each crime and is among the first codes to establish the presumption of innocence. Although its penalties are extremely harsh by modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Ishchali
Tell Ishchali (also Iščāli or Šaǧālī) an archaeological site in Diyala Province (Iraq). It is thought to be ancient Nerebtum or Kiti and was part of the city-state of Eshnunna. It was occupied during the Old Babylonian period. Ancient name At first, the site of Ishchali was thought to be Khafajah. Upon discovery there of a date formula that read "year that king Ishme-Bali built the great wall of Nerebtum", that designation became popular. Currently, scholarly opinion is split between Nerebtum and Kiti as the result of many tablets from the temple of Inanna of Kiti being analyzed. The name of Sadlas has also been proposed. A number of bricks of Ipiq-Adad II were found in the Kitium temple inscribed with: History of archaeological research Items from illegal excavations at Ishchali began appearing on the open market in the 1920s, including many clay tablets. To pre-empt this activity, the Iraq expedition of the Oriental Institute of Chicago conducted two seasons of excavati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naram-Suen Of Eshnunna
Naram-Suen (also transcribed Narām-Sîn, Naram-Sin) was a king who ruled over Eshnunna for at least nine years during the later 19th century BCE, during its brief time of political power. He is known to be the son of Ipiq-Adad II, king of Eshnunna, and a contemporary of Shamshi-Adad I, king of the Kingdom of Upper Mesopotamia. An inscription praying for the king's peace was found in Kythira. References See also *Naram-Sin of Akkad Naram-Sin, also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen ( akk, : '' DNa-ra-am D Sîn'', meaning "Beloved of the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" being a silent honorific for "Divine"), was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned c. 2254–2218 BC ... * Naram-Sin of Assyria Kings of Eshnunna {{AncientNearEast-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Agrab
Tell Agrab (or Aqrab) is a tell or settlement mound southeast of Eshnunna in the Diyala region of Iraq. History Tell Agrab was occupied during the Jemdet Nasr and Early Dynastic periods through the Akkadian and Larsa periods. It was during the Early Dynastic period that monumental building occurred, including the Shara Temple. There is no evidence that it was occupied after the end of the third millennium BC. Archaeology The site of Tell Agrab is encompassed by a rectangle with a height of around . Though it had been subject to illegal digging earlier, the site was officially excavated in 1936 and 1937 by a team from the Oriental Institute of Chicago which was also working at Eshnunna, Khafajah and Tell Ishchali during that time. The dig was led by Seton Lloyd. The primary excavation effort was on the large Early Dynastic temple, which was formerly believed to be dedicated to Shara based on a bowl inscription. However, subsequent research revealed that it belonged to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia)
The Early Dynastic period (abbreviated ED period or ED) is an archaeological culture in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) that is generally dated to c. 2900–2350 BC and was preceded by the Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods. It saw the development of writing and the formation of the first cities and states. The ED itself was characterized by the existence of multiple city-states: small states with a relatively simple structure that developed and solidified over time. This development ultimately led to the unification of much of Mesopotamia under the rule of Sargon, the first monarch of the Akkadian Empire. Despite this political fragmentation, the ED city-states shared a relatively homogeneous material culture. Sumerian cities such as Uruk, Ur, Lagash, Umma, and Nippur located in Lower Mesopotamia were very powerful and influential. To the north and west stretched states centered on cities such as Kish, Mari, Nagar, and Ebla. The study of Central and Lower Mesopotamia has long be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin (mythology)
Nanna, Sīn or Suen ( akk, ), and in Aramaic ''syn'', ''syn’'', or even ''shr'' 'moon', or Nannar ( sux, ) was the god of the moon in the Mesopotamian religions of Sumer, Akkad, Assyria, Babylonia and Aram. He was also associated with cattle, perhaps due to the perceived similarity between bull horns and the crescent moon. He was always described as a major deity, though only a few sources, mostly these from the reign of Nabonidus, consider him to be the head of the Mesopotamian pantheon. The two chief seats of his worship were Ur in the south of Mesopotamia and Harran in the north, though he was also worshiped in numerous other cities, especially in the proximity of Ur and in the Diyala area. In Ur, he was connected to royal power, and many Mesopotamian kings visited his temple in this city. According to Mesopotamian mythology, his parents were Enlil and Ninlil, while his wife was Ningal, worshiped with him in his major cult centers. Their children included maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Dynasty Of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC ( middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider to have been a nascent empire. The Third Dynasty of Ur is commonly abbreviated as Ur III by historians studying the period. It is numbered in reference to previous dynasties, such as the First Dynasty of Ur (26-25th century BC), but it seems the once supposed Second Dynasty of Ur was never recorded. The Third Dynasty of Ur was the last Sumerian dynasty which came to preeminent power in Mesopotamia. It began after several centuries of control by Akkadian and Gutian kings. It controlled the cities of Isin, Larsa, and Eshnunna and extended as far north as Upper Mesopotamia. History The Third Dynasty of Ur arose some time after the fall of the Akkad Dynasty. The period between the last powerful king of the Akkad Dynasty, Shar-Kali-Shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of civilization in the world, along with ancient Egypt, Elam, the Caral-Supe civilization, Mesoamerica, the Indus Valley civilisation, and ancient China. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumerian farmers grew an abundance of grain and other crops, the surplus from which enabled them to form urban settlements. Proto-writing dates back before 3000 BC. The earliest texts come from the cities of Uruk and Jemdet Nasr, and date to between c. 3500 and c. 3000 BC. Name The term "Sumer" ( Sumerian: or , Akkadian: ) is the name given to the language spoken by the "Sumerians", the ancient non- Semitic-speaking inhabitants of southern Mesopotamia, by their successors the East Semitic-speaking Akkadians. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diyala River
The Diyala River (Arabic: ; ku, Sîrwan; Farsi: , ) is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of Sirwan river and Tanjaro river in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total distance of . Course It rises near Hamadan, in the Zagros Mountains of Iran. It then descends through the mountains, where for some 32 km it forms the border between the two countries. It finally feeds into the Tigris below Baghdad. Navigation of the upper reaches of the Diyala is not possible because of its narrow defiles, but the river's valley provides an important trade route between Iran and Iraq. The river flows southwest of the Hamrin Mountains. Name Its Aramaic origin is "Diyalas" and in Kurdish it is called "Sirwan", meaning 'roaring sea' or 'shouting river'. In early Islamic period, the lower course of the river formed part of the Nahrawan Canal. The Diyala Governorate in Iraq is named after the river. History Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
