|
Escharotomy
An escharotomy is a surgical procedure used to treat full-thickness (third-degree) circumferential burns. In full-thickness burns, both the epidermis and the dermis are destroyed along with sensory nerves in the dermis. The tough leathery tissue remaining after a full-thickness burn has been termed ''eschar''. Following a full-thickness burn, as the underlying tissues are rehydrated, they become constricted due to the eschar's loss of elasticity, leading to impaired circulation distal to the wound. An escharotomy can be performed as a prophylactic measure as well as to release pressure, facilitate circulation and combat burn-induced compartment syndrome. An escharotomy is performed by making an incision through the eschar to expose the fatty tissue below. Due to the residual pressure, the incision will often widen substantially. Overview Full-thickness circumferential and near-circumferential skin burns result in the formation of a tough, inelastic mass of burnt tissue (eschar) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burn (injury)
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainly in the home or the workplace. In the home, risks are associated with domestic kitchens, including stoves, flames, and hot liquids. In the workplace, risks are associated with fire and chemical and electric burns. Alcoholism and smoking are other risk factors. Burns can also occur as a result of self-harm or violence between people (assault). Burns that affect only the superficial skin layers are known as superficial or first-degree burns. They appear red without blisters and pain typically lasts around three days. When the injury extends into some of the underlying skin layer, it is a partial-thickness or second-degree burn. Blisters are frequently present and they are often very painful. Healing can require up to eight weeks and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a condition in which increased pressure within one of the body's anatomical compartments results in insufficient blood supply to tissue within that space. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Compartments of the leg or arm are most commonly involved. Symptoms of acute compartment syndrome (ACS) can include severe pain, poor pulses, decreased ability to move, numbness, or a pale color of the affected limb. It is most commonly due to physical trauma such as a bone fracture (up to 75% of cases) or crush injury, but it can also be caused by acute exertion during sport. It can also occur after blood flow returns following a period of poor blood flow. Diagnosis is generally based upon a person's symptoms and may be supported by measurement of intracompartmental pressure before, during, and after activity. Normal compartment pressure should be within 12-18 mmHg; anything greater than that is considered abnormal and would need treatment. Treatment is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
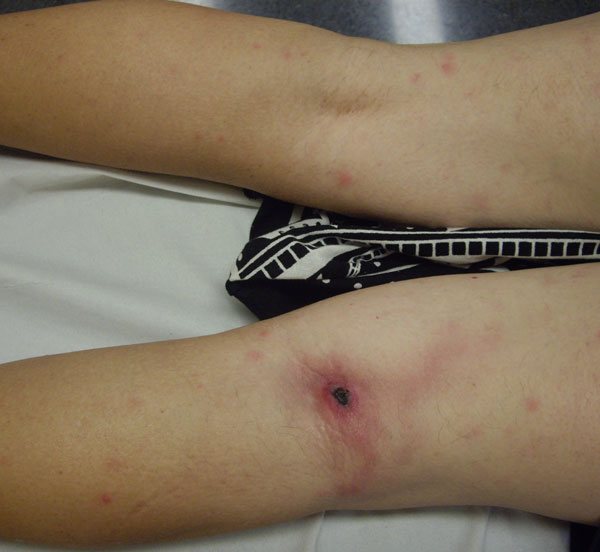
Eschar
An eschar (; Greek: ''ἐσχάρᾱ'', ''eskhara''; Latin: ''eschara'') is a slough or piece of dead tissue that is cast off from the surface of the skin, particularly after a burn injury, but also seen in gangrene, ulcer, fungal infections, necrotizing spider bite wounds, tick bites associated with spotted fevers and exposure to cutaneous anthrax. The term ‘eschar’ is not interchangeable with ‘scab’. An eschar contains necrotic tissue whereas a scab is composed of dried blood and exudate. Black eschars are most frequently attributed in medicine to cutaneous anthrax (infection by ''Bacillus anthracis''), which may be contracted through herd animal exposure and also from '' Pasteurella multocida'' exposure in cats and rabbits. A newly identified human rickettsial infection, ''R. parkeri'' rickettsiosis, can be differentiated from Rocky Mountain spotted fever by the presence of an eschar at the site of inoculation. Eschar is sometimes called a ''black wound'' becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Echocardiography
Doppler echocardiography is a procedure that uses Doppler ultrasonography to examine the heart. An echocardiogram uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of the heart while the use of Doppler technology allows determination of the speed and direction of blood flow by utilizing the Doppler effect. An echocardiogram can, within certain limits, produce accurate assessment of the direction of blood flow and the velocity of blood and cardiac tissue at any arbitrary point using the Doppler effect. One of the limitations is that the ultrasound beam should be as parallel to the blood flow as possible. Velocity measurements allow assessment of cardiac valve areas and function, any abnormal communications between the left and right side of the heart, any leaking of blood through the valves (valvular regurgitation), calculation of the cardiac output and calculation of E/A ratio [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciotomy
Fasciotomy or fasciectomy is a surgical procedure where the fascia is cut to relieve tension or pressure in order to treat the resulting loss of circulation to an area of tissue or muscle. Fasciotomy is a limb-saving procedure when used to treat acute compartment syndrome. It is also sometimes used to treat chronic compartment stress syndrome. The procedure has a very high rate of success, with the most common problem being accidental damage to a nearby nerve. Indications Compartment syndrome is one of the conditions where a fasciotomy may be indicated. People who are likely to have injuries needing a fasciotomy include the following: * Crush injuries * Athletes who have sustained one or more serious impact injuries * People with severe burns * People who are severely overweight * Snakebite victims, but very rarely Complications A delay in performing the procedure can lead to neurovascular complications or lead to the need for amputation of a limb. Complications can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |