|
Endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not an offspring). It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of '' Bacillus marismortui'' in salt crystals approximately 250 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
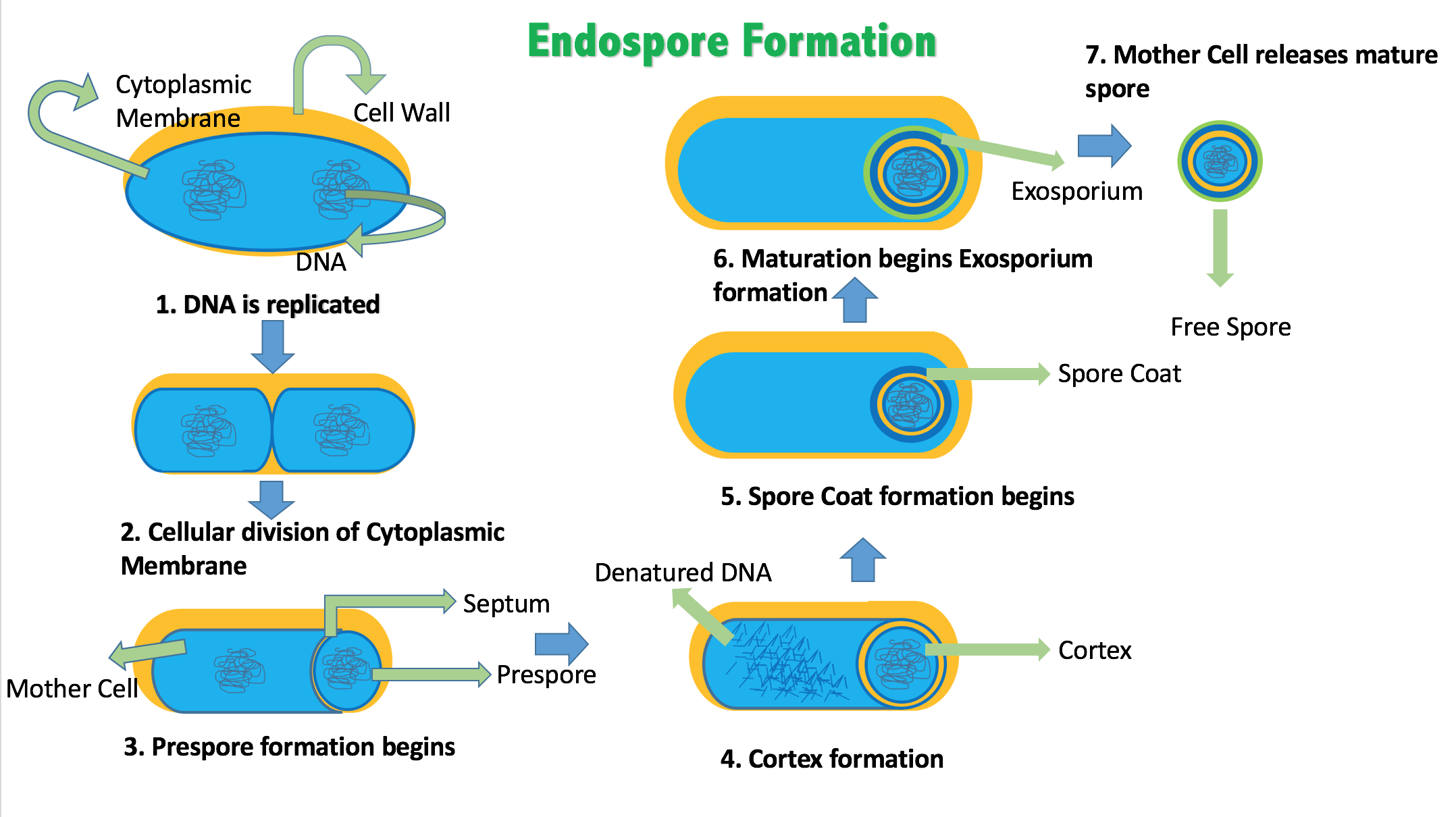
Endospore Formation
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not an offspring). It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of '' Bacillus marismortui'' in salt crystals approximately 250 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
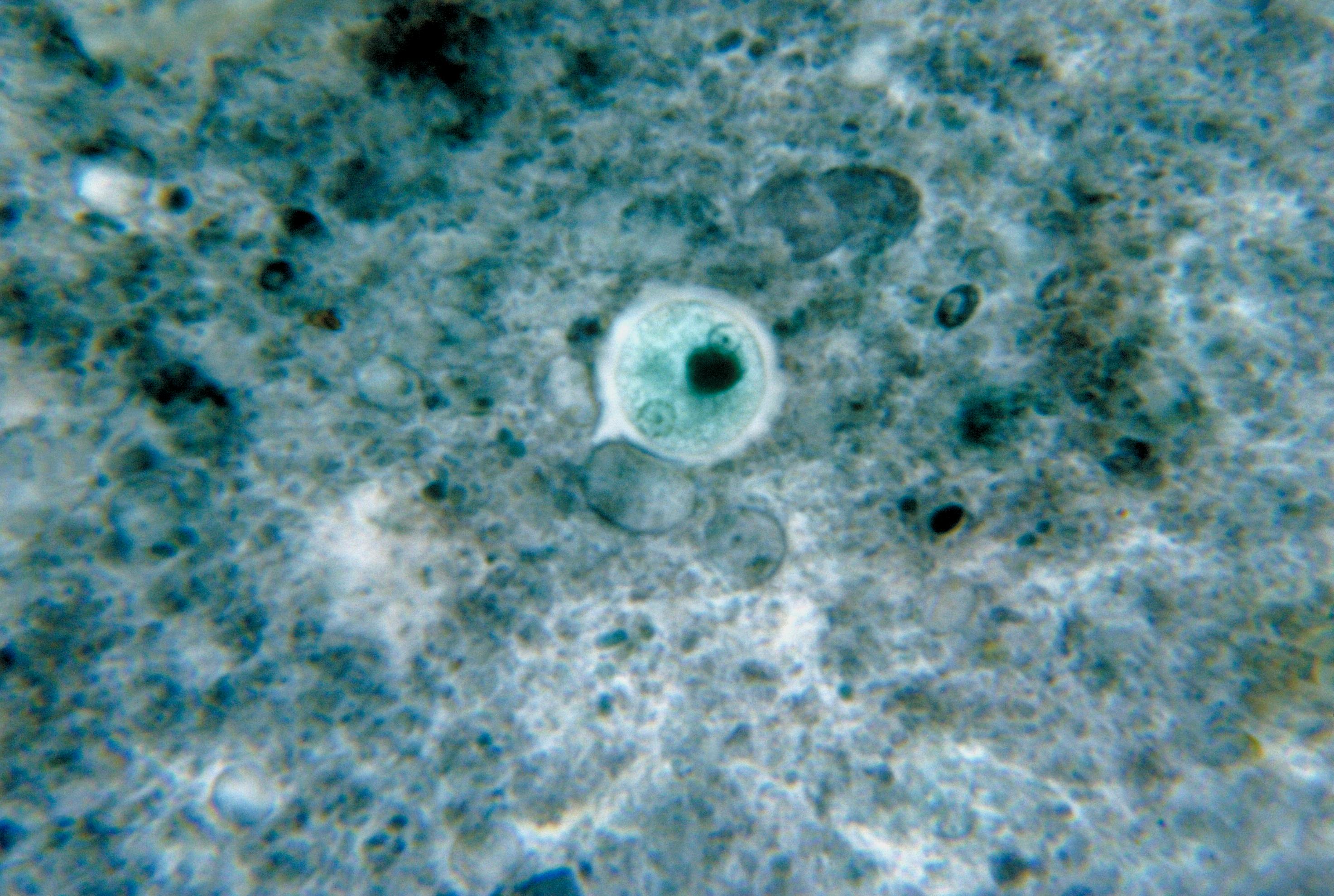
Bacillus Subtilis Spore
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum '' Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacilli'' is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. ''Bacillus'' species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured ''Bacillus'' species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present. ''Bacillus'' can reduce themselves to oval endospores and can remain in this dormant state for years. The endospore of one species from Morocco is reported to have survived being heated to 420 °C. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients: the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. They are not true spores (i.e., not an offspring). Endospore for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Cyst
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, usually a bacterium or a protist or rarely an invertebrate animal, that helps the organism to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. It can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Encystment, the formation of the cyst, also helps the microbe to disperse easily, from one host to another or to a more favorable environment. When the encysted microbe reaches an environment favorable to its growth and survival, the cyst wall breaks down by a process known as excystation. In excystment, the exact stimulus is unknown for most protists. Unfavorable environmental conditions such as lack of nutrients or oxygen, extreme temperatures, lack of moisture and presence of toxic chemicals, which are not conducive for the growth of the microbeEugene W. Nester, Denise G. Anderson, C. Evans Rober ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be anaerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' (referred to herein as ''B. cereus''), '' B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Cohn
Ferdinand Julius Cohn (24 January 1828 – 25 June 1898) was a German biologist. He is one of the founders of modern bacteriology and microbiology. Ferdinand J. Cohn was born in the Jewish quarter of Breslau in the Prussian Province of Silesia (which is now Wroclaw, Poland).Chung, King-ThomFerdinand Julius Cohn (1828-1898): Pioneer of Bacteriology Department of Microbiology and Molecular Cell Sciences, The University of Memphis. His father, Issak Cohn, was a successful merchant and manufacturer. At the age of 10 Ferdinand suffered hearing impairment (for an unknown reason). Starting at age 16 he studied botany under Heinrich Goppert at the University of Breslau. Due to Cohn's Jewish background he was prevented from taking the final degree examinations at Breslau. Biography.yourdictionary.com (2014-06-20). Retrieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steinn Sigurdsson
Steinn may refer to: *Andri Steinn (born 1979), Icelandic film editor *Guðmundur Steinn Gunnarsson (born 1982), Icelandic composer *Hallar-Steinn, Icelandic poet active around the year 1200 *Snorri Steinn Gudjonsson (born 1981), Icelandic handball player * Steinn O. Thompson (1893–1972), politician in Manitoba, Canada * Steinn Steinarr (1908–1958), Icelandic poet See also *Völu-Steinn, Icelandic skald of the mid-10th century *Stein (other) *Steina *Steine (other) Steine may refer to: Places * Steine, Vestland, a village in Kvam municipality, Vestland county, Norway *Steine, a district in Bø municipality in Nordland county, Norway * Steine, Nordland, a village in Vestvågøy municipality, Nordland county, ... * Steinnes {{given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetative Cells
Vegetative describes vegetation Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic charac .... Vegetative may also refer to: * Vegetative reproduction, a type of asexual reproduction for plants * Persistent vegetative state, a condition of people with severe brain damage * Plant community, sometimes called a vegetative community, a collection of plants in a geographic area * Vegetative (or somatic) cell, a non-reproductive cell {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptobiotic
Cryptobiosis or anabiosis is a metabolic state of life entered by an organism in response to adverse environmental conditions such as desiccation, freezing, and oxygen deficiency. In the cryptobiotic state, all measurable metabolic processes stop, preventing reproduction, development, and repair. When environmental conditions return to being hospitable, the organism will return to its metabolic state of life as it was prior to the cryptobiosis. Forms Anhydrobiosis Anhydrobiosis is the most studied form of cryptobiosis and occurs in situations of extreme desiccation. The term ''anhydrobiosis'' derives from the Greek for "life without water" and is most commonly used for the desiccation tolerance observed in certain invertebrate animals such as bdelloid rotifers, tardigrades, brine shrimp, nematodes, and at least one insect, a species of chironomid ('' Polypedilum vanderplanki''). However, other life forms exhibit desiccation tolerance. These include the resurrection plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. Industry Desiccation is widely employed in the oil and gas industry. These materials are obtained in a hydrated state, but the water content leads to corrosion or is incompatible with downstream processing. Removal of water is achieved by cryogenic condensation, absorption into glycols, and absorption onto desiccants such as silica gel. Laboratory A desiccator is a heavy glass or plastic container, now somewhat antiquated, used in practical chemistry for drying or keeping small amounts of materials very dry. The material is placed on a shelf, and a drying agent or ''desiccant'', such as dry silica gel or anhydrous sodium hydroxide, is placed below the shelf. Often some sort of humidity indicator is included in the desiccator to sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |