|
Eanmund
Eanmund was a Swedish prince of the Scylfing dynasty, whose existence is alleged in ''Beowulf''.''Beowulf'', lines 2612-2615. Life according to ''Beowulf'' Unlike his relatives, Eanmund is only mentioned in Beowulf. Eanmund was the son of Ohthere, and was the brother of Eadgils. If he existed in real life, his real name was probably Proto-Norse *''Aiwamunduz'' (Old East Norse ''Ēmund'') or ''Āmunduz'' (Old East Norse ''Āmund''). Ohthere died, and Ohthere's younger brother Onela, usurped the Swedish throne. Since their uncle had seized power, Eanmund and Eadgils sought refuge among the Geats. This caused Onela to attack the Geats, an attack which was also motivated by the fact that the Geatish king Heardred's father had killed Onela's father Ongentheow. During the battle, Eanmund was killed by Onela's champion Weohstan and Heardred was killed as well. Eadgils, however, survived and according to the poem Beowulf later helped him avenge Eanmund and Ohthere by slaying Onela, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eadgils
Eadgils, ''Adils'', ''Aðils'', ''Adillus'', ''Aðísl at Uppsölum'', ''Athisl'', ''Athislus'' or ''Adhel'' was a semi-legendary king of Sweden, who is estimated to have lived during the 6th century. ''Beowulf'' and Old Norse sources present him as the son of Ohthere and as belonging to the ruling Yngling (Scylfing) dynasty. These sources also deal with his war against Onela, which he won with foreign assistance: in ''Beowulf'' he gained the throne of Sweden by defeating his uncle Onela with Geatish help, and in two Scandinavian sources ('' Skáldskaparmál'' and '' Skjöldunga saga''), he is also helped to defeat Onela in the Battle on the Ice of Lake Vänern, but with Danish help. However, Scandinavian sources mostly deal with his interaction with the legendary Danish king Hrólfr Kraki (Hroðulf), and Eadgils is mostly presented in a negative light as a rich and greedy king. Snorri Sturluson, who documented many of the Scandinavian traditions, reported that the Swedes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weohstan
Weohstan, Wēohstān or Wīhstān (Proto-Norse *'' Wīha stainaz'', meaning "sacred stone", non, Vésteinn and ''Wǣstēn'') is a legendary character who appears in the Anglo-Saxon epic poem ''Beowulf'' and scholars have pointed out that he also appears to be present in the Norse '' Kálfsvísa''. In both ''Beowulf'' and ''Kálfsvísa'', Weohstan (''Vésteinn'') fought for his king Onela (''Áli'') against Eadgils (''Aðils''). ''Beowulf'' According to ''Beowulf'', Weohstan is the father of Wiglaf, and he belongs to a clan called the '' Wægmundings''. Ecgþeow, the father of Beowulf, also belonged to this clan, so Weohstan is in some degree related to Beowulf. Thus he counts Weohstan's son Wiglaf as his kinsman. Weohstan is said to have died of old age before the action of the later part of the poem. Weohstan is first mentioned at line 2602. We learn that he had held a Geatland estate and rights in common land which Beowulf gave to him. When the Scylfing prince Eanmund re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onela
Onela was according to ''Beowulf'' a Swedish king, the son of Ongentheow and the brother of Ohthere. He usurped the Swedish throne, but was killed by his nephew Eadgils, who won by hiring foreign assistance. In Scandinavian sagas a Norwegian king by the same name exists, Áli (the Old Norse form of ''Onela'', also rendered as ''Ole'', ''Åle'' or ''Ale''), who had the cognomen ("from Oppland"). Etymology The name stems from the Proto-Norse *''Anula'' (diminutive with l-suffix to a name starting with *''Anu-'', or directly of an appellative , "ancestor").(Lexicon of nordic personal names before the 8th century) Beowulf In the Anglo-Saxon poem ''Beowulf'', Onela plays a central part in the Swedish-Geatish wars. Onela and his brother Ohthere were the sons of the Swedish king Ongenþeow. When the Geatish king Hreðel died, Onela and Ohthere saw the opportunity to pillage in Geatland starting the Swedish-Geatish wars: The war ended with Ongenþeow's death. It is implied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heardred
Heardred (Proto-Norse *''Harðurāðaz''), died c. 530, is the son of Hygelac, king of the Geats, and his queen Hygd, in ''Beowulf''. After Hygelac's death, in Frisia, Hygd wants to make Hygelac's nephew Beowulf, king of Geatland, as she fears that the young Heardred won't be able to defend his people. Beowulf, however, declares his trust in the young man and Heardred is proclaimed king. However, further north in Sweden (then restricted to Svealand), the Swedish king Ohthere dies and is succeeded by his younger brother Onela. Ohthere's sons Eadgils and Eanmund flee to the Geats and are received by Heardred. This makes Onela attack the Geats to neutralize his nephews, and to avenge his father Ongentheow, who had been killed by the Geats. During the battle Heardred is killed. Eanmund is slain by his kinsman Weohstan.''Beowulf'' lines 2370–2391 Heardred is succeeded by his cousin Beowulf, who avenges Eanmund by helping Eadgils Eadgils, ''Adils'', ''Aðils'', ''Adillus'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yngling
The Ynglings were a dynasty of kings, first in Sweden and later in Norway, primarily attested through the poem '' Ynglingatal''. The dynasty also appears as Scylfings ( Old Norse ''Skilfingar'') in ''Beowulf''. When ''Beowulf'' and ''Ynglingatal'' were composed sometime in the eighth to tenth centuries, the respective scop and skald (poet) expected his audience to have a great deal of background information about these kings, which is shown in the allusiveness of the references. According to sources such as ''Ynglingatal'' and ''Íslendingabók'', the Fairhair dynasty in Oppland, Norway was in fact a branch of the Ynglings. Saxo Grammaticus held that Eric the Victorious, whom modern regnal lists usually begin with, and his descendents were also Ynglings, but this does not tally with Icelandic sources. The dynasty claimed descent from the gods Freyr and Njörðr, and other kings were likely mythical as well, whereas others may have been real: especially Egil, Ottar, Ale and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohthere
Ohthere (also ''Ohtere''), Old Norse ''Óttarr vendilkráka'' (''Vendelcrow''; in Modern Swedish ''Ottar Vendelkråka'') was a semi-legendary king of Sweden of the house of Scylfings, who is said to have lived during the Germanic Heroic Age, possibly during the early 6th century (fl. c. 515 – c. 530"Ottar" Encyclopedia Nordisk familjebok). His name can be reconstructed as *''Ōhta-harjaz'' or *''Ōhtu-harjaz''. The '' harjaz'' element is common in and has a meaning of "warrior, army" (whence Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beowulf (character)
Beowulf (; ang, Bēowulf ) is a legendary Geatish hero in the eponymous epic poem, one of the oldest surviving pieces of English literature. Etymology and origins of the character A number of origins have been proposed for the name ''Beowulf''. Beowulf Henry Sweet, a philologist and linguist specializing in Germanic languages, proposed that the name ''Bēowulf'' literally means in Old English "bee-wolf" or "bee-hunter" and that it is a kenning for "bear".Sweet, Henry. (1884) ''Anglo-Saxon Reader in Prose and Verse'' The Clarendon Press, p. 202. Recorded instances of similar names mirror this etymology. The AD 1031 ''Liber Vitae'' records the name ''Biuuuwulf''. The name is attested to a monk from Durham and means ''bee wolf'' in the Old Northumbrian dialect.Chadwick, Hector Munro (1983) ''The Origin of the English Nation'', p. 294. The 11th century English ''Domesday Book'' contains a recorded instance of the name ''Beulf''. The scholar suggested that the name ''Beowulf'' de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
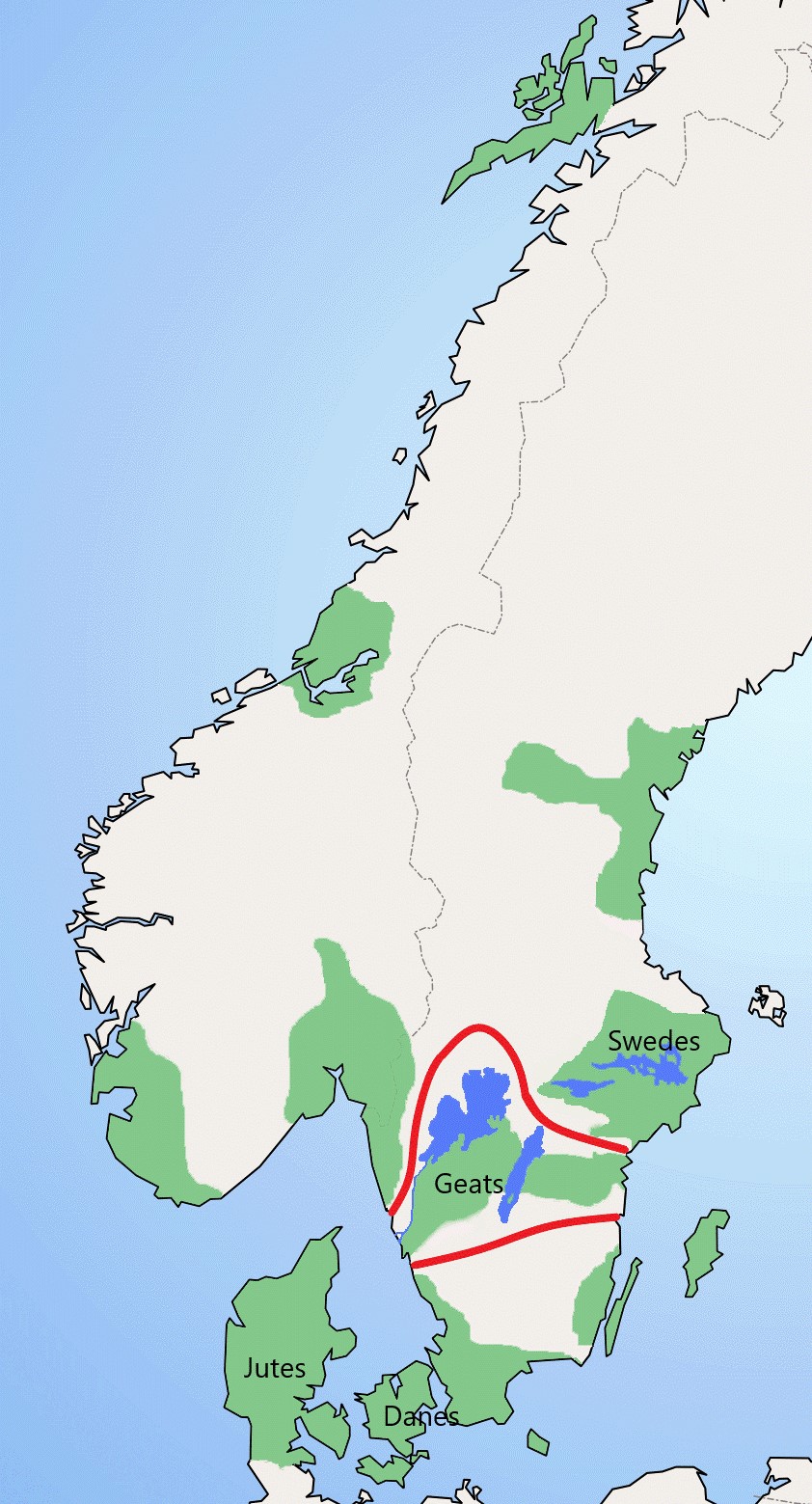
Geatish King
Geatish kings ( la, Rex Getarum/Gothorum; sv, Götakungar), ruling over the provinces of Götaland (Gautland/Geatland), appear in several sources for early Swedish history. Today, most of them are not considered historical. This list follows the generally accepted identification between the names Götar ( modern Swedish), Gautar (Old Norse) and Geatas (Old English), which is based both on tradition, literary sources and on etymology. However, unlike some translations it does not identify this tribe with the Goths. Both Old Norse and Old English records clearly separate the Geats from the Goths, while still depicting them as closely related to each other. From the Middle Ages until 1974, the king of Sweden claimed the title King of the Geats as "King of Sweden and Geats/Goths" or "Rex Sweorum et Gothorum". Danish monarchs used the similar title " King of the Goths" from 1362 until 1972. Legendary kings Some names appear in Norse mythology and in Germanic legend and in at l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as winged, horned, and capable of breathing fire. Dragons in eastern cultures are usually depicted as wingless, four-legged, serpentine creatures with above-average intelligence. Commonalities between dragons' traits are often a hybridization of feline, reptilian and avian features. Scholars believe huge extinct or migrating crocodiles bear the closest resemblance, especially when encountered in forested or swampy areas, and are most likely the template of modern Oriental dragon imagery. Etymology The word ''dragon'' entered the English language in the early 13th century from Old French ''dragon'', which in turn comes from la, draconem (nominative ) meaning "huge serpent, dragon", from Ancient Greek , (genitive , ) "serpent, giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ongentheow
Ongentheow (Old English: ''Ongenþeow'', ''Ongenþio'', ''Ongendþeow''; Old Norse: ''Angantýr'') (died ca. 515) was the name of a semi-legendary Swedish king of the house of Scylfings, who appears in Old English sources. He is generally identified with the Swedish king Egil Vendelcrow mentioned in ''Ynglingatal'', ''Historia Norwegiae'' and in ''Ynglinga saga''. The reason why they are thought to have been the same is that each has the same position in the line of Swedish kings and is described as the father of Ohthere and grandfather of Eadgils. The name Ongentheow contains as its second element '' þeōw'' "servant, slave". The first appears to be ''ongēan'' "against, opposite". Old English sources ''Beowulf'' In the Old English epic poem ''Beowulf'', Ongentheow is described as a fearsome warrior, and it took two Geatish warriors Eofor and Wulf Wonreding to take him down. The epic tells that the Geats under their new king Hæþcyn captured the Swedish queen, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
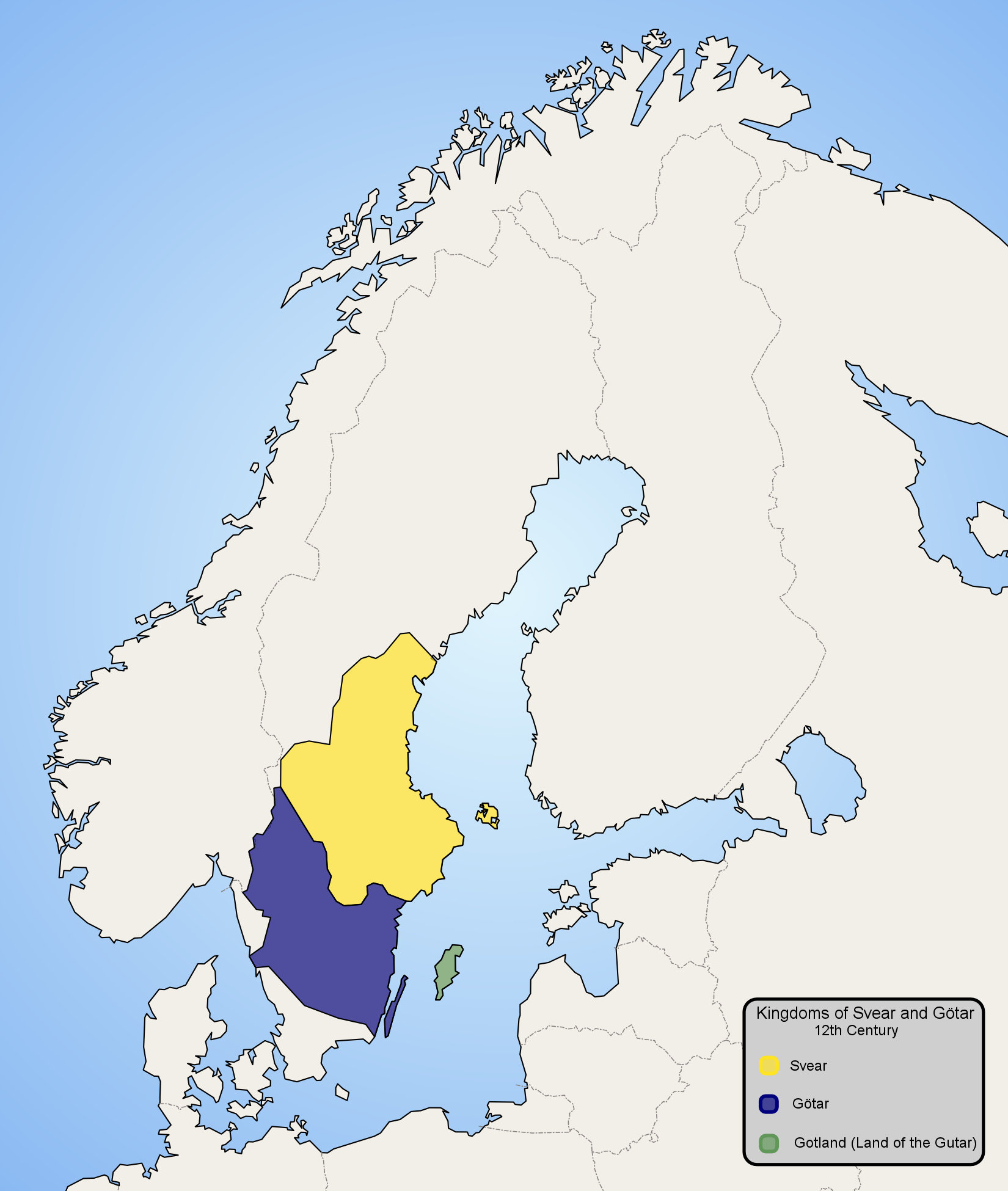
Suiones
The Swedes ( sv, svear; Old Norse: ''svíar'') (probably from the PIE reflexive pronominal root * s(w)e, "one's own ribesmen/kinsmen;Bandle, Oskar. 2002. The Nordic languages: an international handbook of the history of the North Germanic languages. 2002. P.391 ang, Swēon) were a North Germanic tribe who inhabited Svealand ("land of the Swedes") in central Sweden and one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Geats and Gutes. They had their tribal centre in Gamla Uppsala. The first author who wrote about the tribe is Tacitus, who in his ''Germania'' from 98 CE mentions the ''Suiones''. They are possibly first mentioned locally by the Kylver Stone in the 4th century. Jordanes, in the 6th century, mentions ''Suehans'' and ''Suetidi''. ''Beowulf'' mentions the Swedes around 1000 A.D. According to early sources such as the sagas, especially ''Heimskringla'', the Swedes were a powerful tribe whose kings claimed descendence from the god Freyr. During the Viking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geats
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of and , the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and '' Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |