|
Durophagy
Durophagy is the eating behavior of animals that consume hard-shelled or exoskeleton bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled mollusks, or crabs. It is mostly used to describe fish, but is also used when describing reptiles, including fossil turtles, placodonts and invertebrates, as well as "bone-crushing" mammalian carnivores such as hyenas. Durophagy requires special adaptions, such as blunt, strong teeth and a heavy jaw. Bite force is necessary to overcome the physical constraints of consuming more durable prey and gain a competitive advantage over other organisms by gaining access to more diverse or exclusive food resources earlier in life. Those with greater bite forces require less time to consume certain prey items as a greater bite force can increase the net rate of energy intake when foraging and enhance fitness in durophagous species. In the order Carnivora there are two dietary categories of durophagy; bonecrackers and bamboo eaters. Bonecrackers are exemplified by hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyena
Hyenas, or hyaenas (from Ancient Greek , ), are feliform carnivoran mammals of the family Hyaenidae . With only four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the Carnivora and one of the smallest in the class Mammalia. Despite their low diversity, hyenas are unique and vital components of most African ecosystems. Although phylogenetically closer to felines and viverrids, as part of suborder Feliformia, hyenas are behaviourally and morphologically similar to canids in several elements due to convergent evolution; both hyenas and canines are non- arboreal, cursorial hunters that catch prey with their teeth rather than claws. Both eat food quickly and may store it, and their calloused feet with large, blunt, nonretractable claws are adapted for running and making sharp turns. However, hyenas' grooming, scent marking, defecation habits, mating and parental behavior are consistent with the behavior of other feliforms. Hyenas feature promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
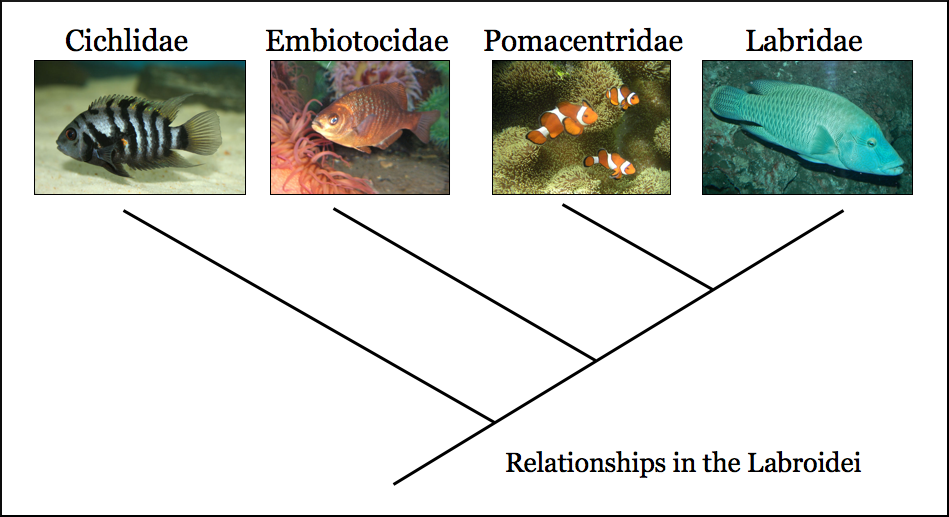
Cichlids
Cichlids are fish from the family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes. Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses ( Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have contradicted this grouping. The closest living relative of cichlids is probably the convict blenny, and both families are classified in the 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' as the two families in the Cichliformes, part of the subseries Ovalentaria. This family is both large and diverse. At least 1,650 species have been scientifically described, making it one of the largest vertebrate families. New species are discovered annually, and many species remain undescribed. The actual number of species is therefore unknown, with estimates varying between 2,000 and 3,000. Many cichlids, particularly tilapia, are important food fishes, while others, such as the ''Cichla'' species, are valued game fish. The family also includes many popular freshwater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangabey
Mangabeys are West-African Old World monkeys, with species in three of the six genera of tribe Papionini. The more typical representatives of ''Cercocebus'', also known as the white-eyelid mangabeys, are characterized by their bare, upper eye-lids which are lighter than their facial skin colouring, and the uniformly coloured hairs of the fur. Members of ''Lophocebus'', the crested mangabeys, tend to have dark skin, eyelids that match their facial skin, and crests of hair on their heads. A new species, the highland mangabey, was discovered in 2003 and was initially placed in ''Lophocebus''. The genus ''Rungwecebus'' was later created for this species. ''Lophocebus'' and ''Cercocebus'' were once thought to be very closely related, so much so that all the species were in one genus. However, the species within genus ''Lophocebus'' are now thought to be more closely related to the baboons in genus ''Papio'', while the species within genus ''Cercocebus'' are more closely related to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
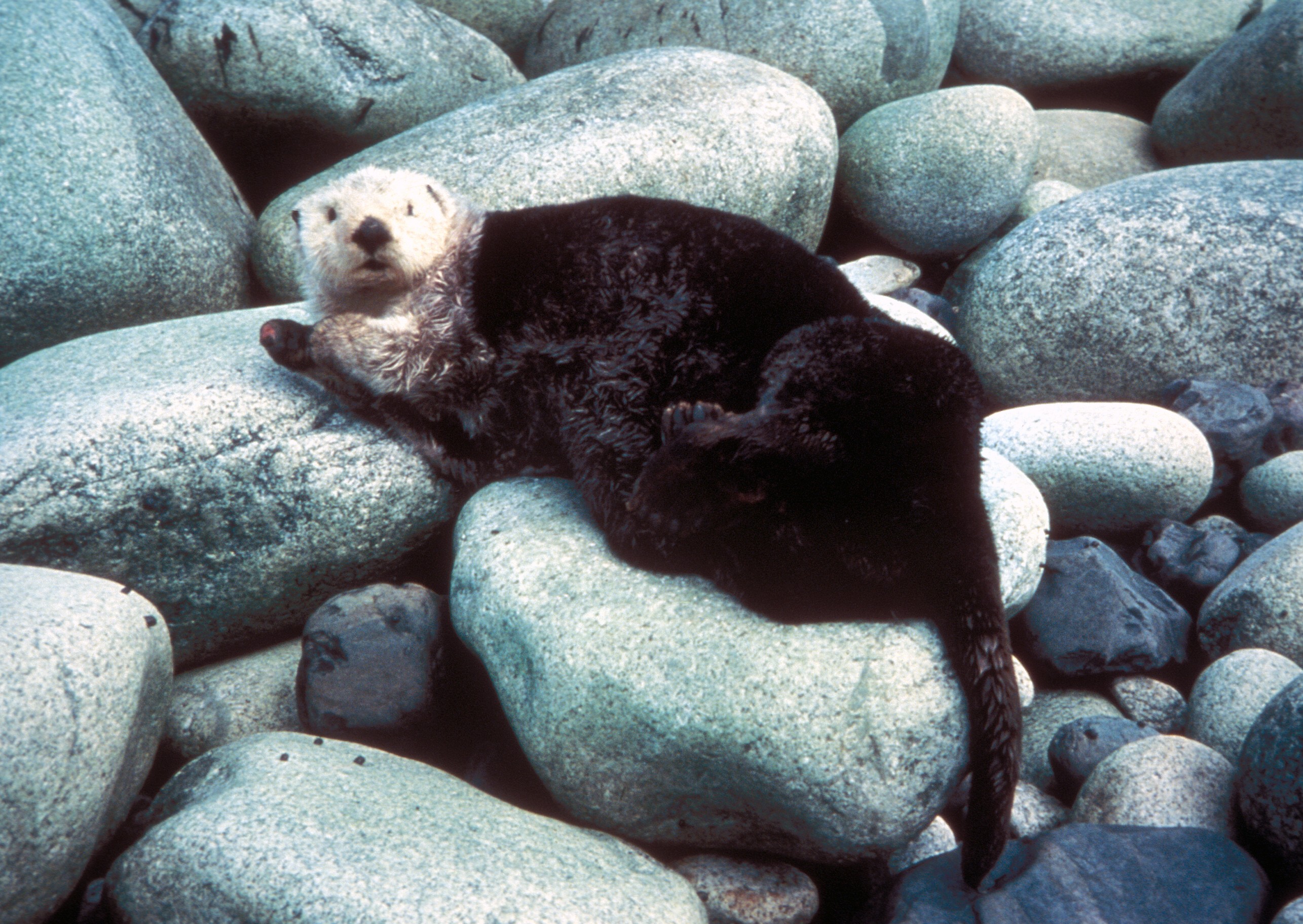
Sea Otters
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smallest marine mammals. Unlike most marine mammals, the sea otter's primary form of insulation is an exceptionally thick coat of fur, the densest in the animal kingdom. Although it can walk on land, the sea otter is capable of living exclusively in the ocean. The sea otter inhabits nearshore environments, where it dives to the sea floor to forage. It preys mostly on marine invertebrates such as sea urchins, various mollusks and crustaceans, and some species of fish. Its foraging and eating habits are noteworthy in several respects. Its use of rocks to dislodge prey and to open shells makes it one of the few mammal species to use tools. In most of its range, it is a keystone species, controlling sea urchin populations which would otherwise inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wader
245px, A flock of Dunlins and Red knots">Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflats in order to foraging, forage for food crawling or burrowing in the mud and sand, usually small arthropods such as aquatic insects or crustaceans. The term "wader" is used in Europe, while "shorebird" is used in North America, where "wader" may be used instead to refer to long-legged wading birds such as storks and herons. There are about 210 species of wader, most of which live in wetland or coastal environments. Many species of Arctic and temperate regions are strongly migratory, but tropical birds are often resident, or move only in response to rainfall patterns. Some of the Arctic species, such as the little stint, are amongst the longest distance migrants, spending the non-breeding season in the southern hemisphere. Many of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bat Ray
The bat ray (''Myliobatis californica'')Gill, T.N. (1865). "Note on the family of myliobatoids, and on a new species of ''Aetobatis''". ''Ann. Lyc. Nat. Hist. N. Y.'' 8, 135–138. is an eagle ray found in muddy or sandy sloughs, estuaries and bays, kelp beds and rocky-bottomed shoreline in the eastern Pacific Ocean, between the Oregon coast and the Gulf of California. It is also found in the area around the Galápagos Islands.Florida Museum of Natural HistoryBat Ray Biological Profile Retrieved 2006-01-16. The largest specimens can grow to a wingspan of and a mass of .Monterey Bay Aquarium Online Field GuideBat Ray Retrieved 2012-06-14. They more typically range from . The size of the bat ray is dependent on many factors, such as habitat alterations, different oceanographic and environmental conditions. Bat rays have one to three venomous barbed spines at the base of its tail. Some bat rays are solitary while others form schools numbering in the thousands. The sexual maturit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetobatus
''Aetobatus'' is a genus of eagle rays native to the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. It was formerly placed in Myliobatidae, but is now placed in its own family Aetobatidae based on salient differences from myliobatids, especially the pectoral fins joining the head at the level of the eyes.White, W. T. & Naylor, G. J. P. (2016). Resurrection of the family Aetobatidae (Myliobatiformes) for the pelagic eagle rays, genus Aetobatus. Zootaxa 4139, 435–438. 10.11646/zootaxa.4139.3.10 Species There are currently either 3 or 5 recognized extant species in this genus depending on the status of ''A. narinari'': There are also 6 extinct species (only known from fossil A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ... remains) placed in this genus: *†'' Aetobatus arcuatus'' *� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myliobatis
''Myliobatis'' is a genus of eagle rays in the family Myliobatidae. Description ''Myliobatis'' species can reach a width up to about . Their bodies consist of a rhomboidal disc, wider than long, with one dorsal fin. The head is broad and short, with eyes and spiracles on the sides. The tail is slender, with one or two large spines at the base, without tail fin. The teeth are arranged in the lower and upper jaws in flat tooth plates called pavement teeth, each consisting of about seven series of plates, which are used to crush clam shells and crustaceans. Biology ''Myliobatis'' species are ovoviviparous. Their gestation last about 6 months and a female produces four to seven embryos. ''Myliobatis'' species mainly feed on molluscs, bottom-living crustaceans, and small fishes. Habitat ''Mylobatis'' species live in warm, shallow waters. Adults prefer sandy shores, while juveniles can usually be encountered offshore. Species Extant species Currently, 11 species in this genus are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinoptera Javanica
''Rhinoptera'' is a genus of ray commonly known as the cownose rays. This genus is the only member of the family Rhinopteridae. Species There are currently 8 recognized extant (living) species in this genus: * '' Rhinoptera adspersa'' J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841 (Rough cownose ray) * '' Rhinoptera bonasus'' ( Mitchill, 1815) (Cownose ray) * '' Rhinoptera brasiliensis'' J. P. Müller, 1836 (Brazilian cownose ray) * '' Rhinoptera javanica'' J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841 (Flapnose ray) * '' Rhinoptera jayakari'' Boulenger, 1895 (Oman cownose ray) * '' Rhinoptera marginata'' ( É. Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817) (Lusitanian cownose ray) * '' Rhinoptera neglecta'' J. D. Ogilby, 1912 (Australian cownose ray) * '' Rhinoptera steindachneri'' Evermann & O. P. Jenkins, 1891 (Pacific cownose ray) There are several other extinct species that only are known from fossil remains: * †'' Rhinoptera prisca'' Woodward, 1907 * †'' Rhinoptera rasilis'' Böhm, 1926 * †'' Rhinoptera raeburn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetobatus Narinari
The spotted eagle ray (''Aetobatus narinari'') is a cartilaginous fish of the eagle ray family, Myliobatidae. As traditionally recognized, it is found globally in tropical regions, including the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Recent authorities have restricted it to the Atlantic (including the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico) with other populations recognized as the ocellated eagle ray (''A. ocellatus'') and Pacific white-spotted eagle ray (''A. laticeps''). Spotted eagle rays are most commonly seen alone, but occasionally swim in groups. They are ovoviviparous, the female retaining the eggs then releasing the young as miniature versions of the parent. This ray can be identified by its dark dorsal surface covered in white spots or rings. Near the base of the ray's relatively long tail, just behind the pelvic fins, are several venomous, barbed stingers. Spotted eagle rays commonly feed on small fish and crustaceans, and will sometimes dig with their snouts to look for foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |