|
Donatism
Donatism was a Christian sect leading to a schism in the Church, in the region of the Church of Carthage, from the fourth to the sixth centuries. Donatists argued that Christian clergy must be faultless for their ministry to be effective and their prayers and sacraments to be valid. Donatism had its roots in the long-established Christian community of the Roman province Africa Proconsularis (present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the western coast of Libya), in the persecutions of Christians under Diocletian. Named after the Berber Christian bishop Donatus Magnus, Donatism flourished during the fourth and fifth centuries. Origin and controversy The Roman governor of North Africa, lenient to the large Christian minority under his rule throughout the Diocletianic Persecutions, was satisfied when Christians handed over their scriptures as a token repudiation of faith. When the persecution ended, Christians who did so were called '' traditores''—"those who handed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donatus Magnus
Donatus Magnus, also known as Donatus of Casae Nigrae, became leader of a schismatic sect known as the Donatists in North Africa, Algeria. He is believed to have died in exile around 355. Life Little is known of his early life because of the complete loss of his correspondence and written works. He first appears in Church records as Donatus of Casae Nigrae in October 313 when Pope Miltiades found him guilty of re-baptizing clergy who had lapsed and of forming a schism within the Church. Casae was a settlement located on the extreme southern edge of the plains of Numidia, south of Theveste, an area settled by people predominantly of Berber descent. The Schism During the wave of persecutions of Christians by the Roman Emperor Diocletian, in order to avoid torture, exile, or death, some Church leaders turned over their scriptures, liturgical books, and other church goods to the imperial authorities. Such people became known as ''traditors'' ("surrenderers"). The schism between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majorinus
Majorinus was the leader of a schismatic Christian sect in Roman North Africa known as the Donatists. Life Very little is known of his early life, as Donatist writings were mostly destroyed in the following years. What we can garner of his life and beliefs is accessed through what his enemies said against him. He had been a reader or a lector in the church at Carthage, during the time that Caecilianus, had been an archdeacon at Carthage and Mesurius was Bishop of Carthage. He seems to have also had some domestic office in the household of a Roman noblewoman Lucilla. In 311 he was chosen as Bishop of Carthage, by a council of 70 bishops in Cirta led by Secundus of Tigisis. Secundus of Tigisis was the primate of Numidia and as such was meant to be consulted prior to the appointment of Caecilianus. This appointment was intended to depose the existing recently appointed bishop Caecilianus. Caecilianus had been the understudy of the recently deceased bishop Mensurius con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
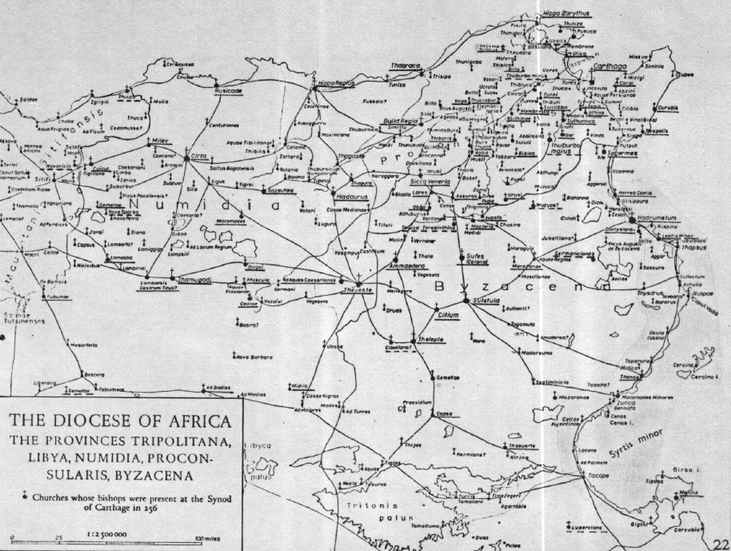
Church Of Carthage
The Archdiocese of Carthage, also known as the Church of Carthage, was a Latin Catholic diocese established in Carthage, Roman Empire, in the 2nd century. Agrippin was the first named bishop, around 230 AD. The temporal importance of the city of Carthage in the Roman Empire had previously been restored by Julius Caesar and Augustus. When Christianity became firmly established around the Roman province of Africa Proconsulare, Carthage became its natural ecclesiastical seat. Carthage subsequently exercised informal primacy as an archdiocese, being the most important center of Christianity in the whole of Roman Africa, corresponding to most of today's Mediterranean coast and inland of Northern Africa. As such, it enjoyed honorary title of patriarch as well as primate of Africa: Pope Leo I confirmed the primacy of the bishop of Carthage in 446: "Indeed, after the Roman Bishop, the leading Bishop and metropolitan for all Africa is the Bishop of Carthage."François Decret, ''Early C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Miltiades
Pope Miltiades ( grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης, ''Miltiádēs''), also known as Melchiades the African ( ''Melkhiádēs ho Aphrikanós''), was the bishop of Rome from 311 to his death on 10 or 11 January 314. It was during his pontificate that Emperor Constantine the Great issued the Edict of Milan (313), giving Christianity legal status within the Roman Empire. The pope also received the palace of Empress Fausta where the Lateran Palace, the papal seat and residence of the papal administration, would be built. At the Lateran Council, during the schism with the Church of Carthage, Miltiades condemned the rebaptism of apostatised bishops and priests, a teaching of Donatus Magnus. Background The year of Miltiades' birth is unknown but it is known that he was of North African descent and, according to the '' Liber Pontificalis'', compiled from the 5th century onwards, a Roman citizen. Miltiades and his successor, Sylvester I, were part of the clergy of Pope Marcellinus. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocletianic Persecution
The Diocletianic or Great Persecution was the last and most severe persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. In 303, the emperors Diocletian, Maximian, Galerius, and Constantius issued a series of edicts rescinding Christians' legal rights and demanding that they comply with traditional religious practices. Later edicts targeted the clergy and demanded universal sacrifice, ordering all inhabitants to sacrifice to the gods. The persecution varied in intensity across the empire—weakest in Gaul and Britain, where only the first edict was applied, and strongest in the Eastern provinces. Persecutory laws were nullified by different emperors (Galerius with the Edict of Serdica in 311) at different times, but Constantine and Licinius' Edict of Milan in 313 has traditionally marked the end of the persecution. Christians had been subject to intermittent local discrimination in the empire, but emperors prior to Diocletian were reluctant to issue general laws against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditors
Traditor, plural: ''traditores'' (Latin), is a term meaning "the one(s) who had handed over" and defined by Merriam-Webster as "one of the Christians giving up to the officers of the law the Scriptures, the sacred vessels, or the names of their brethren during the Roman persecutions". It refers to bishops and other Christians who turned over sacred scriptures or betrayed their fellow Christians to the Roman authorities under threat of persecution. During the Diocletianic Persecution between AD 303 and 305, many church leaders had gone as far as turning in Christians to the authorities and "handed over" sacred religious texts to authorities to be burned. Philip Schaff says about them: "In this, as in former persecutions, the number of apostates who preferred the earthly life to the heavenly, was very great. To these was now added also the new class of the ''traditores'', who delivered the holy Scriptures to the heathen authorities, to be burned". While many church members would ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. The city developed from a Canaanite Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. According to accounts by Timaeus of Tauromenium, she purchased from a local tribe the amount of land that could be covered by an oxhide. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule the colonies. The ancient city was destroyed in the nearly-three year siege of Carthage by the Roman Republic during the Third Punic War in 146 BC and then re-developed as Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecilianus
Caecilianus, or Caecilian, was archdeacon and then bishop of Carthage in 311 AD. His appointment as Bishop led to the Donatist Controversy of the Late Roman Empire. He was also one of only five Western bishops at the First Council of Nicea. Background to the controversy Caecilianus was an archdeacon of Carthage, who supported his bishop Mensurius in opposing the fanatical cult of martyrdom. Mensurius forbade any to be honoured as martyrs who had given themselves up of their own accord, or who had boasted that they possessed copies of the scriptures which they would not relinquish. Some of these he claimed were criminals and debtors to the state, who thought they might by this means rid themselves of a burdensome life, or wipe away the remembrance of their misdeeds, or at least gain money and enjoy in prison the luxuries supplied by the kindness of Christians. A deacon of Carthage, Felix, was accused of writing a defamatory letter against the emperor Maxentius. Mensurius was sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novatianism
Novatianism or Novationism was an early Christian sect devoted to the theologian Novatian ( 200–258) that held a strict view that refused readmission to communion of '' lapsi'' (those baptized Christians who had denied their faith or performed the formalities of a ritual sacrifice to the pagan gods under the pressures of the persecution sanctioned by Emperor Decius in AD 250). The Church of Rome declared the Novatianists heretical following the letters of Saint Cyprian of Carthage and Ambrose wrote against them. Novatianism survived until the 8th century. Novatian theology was heavily influenced by Tertullian, and made heavy use of his writings. Novatian After the martyrdom of Pope Fabian during the Decian persecution, a Roman priest, Novatian, opposed the election of Pope Cornelius in 251, on the grounds that Cornelius was too liberal in accepting lapsed Christians. Novatian held that lapsed Christians, who had not maintained their confession of faith under persecution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumcellions
The Circumcellions or Agonistici (as called by Donatists) were bands of Roman Christian radicals in North Africa in the early to mid-4th century.. They were considered heretical by the Catholic Church. They were initially concerned with remedying social grievances, but they became linked with the Donatist sect. They condemned poverty and slavery, and advocated canceling debt and freeing slaves. The term "Circumcellions" may have been coined or mocked by critics who referred to them as "circum cellas euntes", ''they go around larders'', because "they roved about among the peasants, living on those they sought to indoctrinate." Background The Circumcellions first appeared about 317, and were active primarily in Numidia, and Mauretania Sitifensis. They promoted ideas of social reform along with eschatological hopes. Optatus, Bishop of Milevis, says that around 340 they started an uprising directed at creditors and slave owners. They regarded as martyrs those among them killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad to the south, Niger to the southwest, Algeria to the west, and Tunisia to the northwest. Libya is made of three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica. With an area of almost 700,000 square miles (1.8 million km2), it is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the 16th-largest in the world. Libya has the 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. The largest city and capital, Tripoli, is located in western Libya and contains over three million of Libya's seven million people. Libya has been inhabited by Berbers since the late Bronze Age as descendants from Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures. In ancient times, the Phoenicians established city-states and tradin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Of Aptungi
Felix, Bishop of Aptunga, in proconsular Africa was a 4th-century churchman, at the center of the Donatist controversy. Felix was one of those who laid hands on Caecilian as Bishop of Carthage in 311AD. This act led to a major schism in Early North African Christianity. Biography Felix of Abthugni, the bishop of Aptunga had escaped arrest during the Diocletian Persecution in 303. He held an administrative office within the town council, and was on friendly relations with the local magistrate who was to implement the persecution. It is therefore probable he was warned of the coming persecution, and was away at the time. The cathedral and some documents were destroyed in his absence. Felix consecrated Caecilian as Bishop of Carthage in 311. The proto-Donatist in a Council at Cirta called this consecration invalid because of Felix's participation. However, Felix was considered to have been a '' traditor'' during the Diocletian Persecution and as such Caecilian's consecration w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_Foto_G._Dall'Orto_28-5-2006.jpg)

