|
Deutsches Institut Für Normung
' (DIN; in English, the German Institute for Standardisation Registered Association) is the German national organization for standardization and is the German ISO member body. DIN is a German Registered Association ('' e.V.'') headquartered in Berlin. There are currently around thirty thousand DIN Standards, covering nearly every field of technology. History Founded in 1917 as the ' (NADI, "Standardisation Committee of German Industry"), the NADI was renamed ' (DNA, "German Standardisation Committee") in 1926 to reflect that the organization now dealt with standardization issues in many fields; viz., not just for industrial products. In 1975 it was renamed again to ', or 'DIN' and is recognised by the German government as the official national-standards body, representing German interests at the international and European levels. The acronym, 'DIN' is often incorrectly expanded as ' ("German Industry Standard"). This is largely due to the historic origin of the DIN as "N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIN Connector
The DIN connector is an electrical connector that was standardized by the ' (DIN), the German Institute for Standards, in the early 1970s. The male DIN connectors (plugs) feature a 13.2 mm diameter metal shield with a notch that limits the orientation in which plug and socket can mate. The range of DIN connectors, different only in the configuration of the pins, have been standardized as DIN 41524 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 (3-pin at 90° and 5-pin at 45°); DIN 45322 (5-pin and 6-pin at 60°); DIN 45329 / IEC/DIN EN 60130–9 (7-pin at 45°); and DIN 45326 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 (8-pin at 45°). In consumer electronics, the term "DIN connector" identifies types of cylindrical connectors that the German Institute for Standards (DIN) had initially standardised for analog audio signals. Some DIN connectors have been used in analog video applications, for power connections, and for digital interfaces, such as the MIDI (DIN 41524), the IBM PC keyboard and the IBM AT keyboard connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIN 41612
DIN 41612 was a DIN standard for electrical connectors that are widely used in rack based electrical systems. Standardisation of the connectors is a pre-requisite for open systems, where users expect components from different suppliers to operate together. The most widely known use of DIN 41612 connectors is in the VMEbus and NuBus systems. The standard has withdrawn in favor of international standards IEC 60603-2 and EN 60603-2. DIN 41612 connectors are used in Pancon, STEbus, Futurebus, VMEbus, Multibus II, NuBus, VXI Bus, eurocard TRAM motherboards, and Europe Card Bus, all of which typically use male DIN 41612 connectors on Eurocards plugged into female DIN 41612 on the backplane in a 19-inch rack A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple electronic equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is wide. The 19 inch dimension includes the edges or "ears" that protrude from each side of the equ ... chassis. Mechanical d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also refers to spoken Arabic that approximates this written standard. MSA is the language used in literature, academia, print and mass media, law and legislation, though it is generally not spoken as a first language, similar to Contemporary Latin. It is a pluricentric standard language taught throughout the Arab world in formal education, differing significantly from many vernacular varieties of Arabic that are commonly spoken as mother tongues in the area; these are only partially mutually intelligible with both MSA and with each other depending on their proximity in the Arabic dialect continuum. Many linguists consider MSA to be distinct from Classical Arabic (CA; ) – the written language prior to the mid-19th century – althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Arabic
The romanization of Arabic is the systematic rendering of written and spoken Arabic in the Latin script. Romanized Arabic is used for various purposes, among them transcription of names and titles, cataloging Arabic language works, language education when used instead of or alongside the Arabic script, and representation of the language in scientific publications by linguists. These formal systems, which often make use of diacritics and non-standard Latin characters and are used in academic settings or for the benefit of non-speakers, contrast with informal means of written communication used by speakers such as the Latin-based Arabic chat alphabet. Different systems and strategies have been developed to address the inherent problems of rendering various Arabic varieties in the Latin script. Examples of such problems are the symbols for Arabic phonemes that do not exist in English or other European languages; the means of representing the Arabic definite article, which is alw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIN 31635
DIN 31635 is a Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) standard for the transliteration of the Arabic alphabet adopted in 1982. It is based on the rules of the Deutsche Morgenländische Gesellschaft (DMG) as modified by the International Orientalist Congress 1935 in Rome. The most important differences from English-based systems were doing away with '' j'', because it stood for in the English-speaking world and for in the German-speaking world and the entire absence of digraphs like ''th, dh, kh, gh, sh''. Its acceptance relies less on its official status than on its elegance (one sign for each Arabic letter) and the ''Geschichte der arabischen Literatur'' manuscript catalogue of Carl Brockelmann and the dictionary of Hans Wehr. Today it is used in most German-language publications of Arabic and Islamic studies. Table :The 28 letters: Rules The ' (', ' and ') are transliterated as ', ' and '. A ' results in a geminate (consonant written twice). The article is written with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Sign
Traffic signs or road signs are signs erected at the side of or above roads to give instructions or provide information to road users. The earliest signs were simple wooden or stone milestones. Later, signs with directional arms were introduced, for example the fingerposts in the United Kingdom and their wooden counterparts in Saxony. With traffic volumes increasing since the 1930s, many countries have adopted pictorial signs or otherwise simplified and standardized their signs to overcome language barriers, and enhance traffic safety. Such pictorial signs use symbols (often silhouettes) in place of words and are usually based on international protocols. Such signs were first developed in Europe, and have been adopted by most countries to varying degrees. International conventions Various international conventions have helped to achieve a degree of uniformity in Traffic Signing in various countries. Categories Traffic signs can be grouped into several types. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typeface
A typeface (or font family) is the design of lettering that can include variations in size, weight (e.g. bold), slope (e.g. italic), width (e.g. condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font. There are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly. The art and craft of designing typefaces is called ''type design''. Designers of typefaces are called ''type designers'' and are often employed by ''type foundries''. In desktop publishing, type designers are sometimes also called ''font developers'' or ''font designers''. Every typeface is a collection of glyphs, each of which represents an individual letter, number, punctuation mark, or other symbol. The same glyph may be used for characters from different scripts, e.g. Roman uppercase A looks the same as Cyrillic uppercase А and Greek uppercase alpha. There are typefaces tailored for special applications, such as cartography, astrology or mathematics. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIN 1451
DIN 1451 is a sans-serif typeface that is widely used for traffic, administrative and technical applications. It was defined by the German standards body DIN (, 'German Institute for Standardisation', pronounced like the English word ''din'') in the standard sheet ('typefaces') in 1931. Similar standards existed for stencilled letters. Originally designed for industrial uses, the first DIN-type fonts were a simplified design that could be applied with limited technical difficulty. Due to the design's legibility and uncomplicated, unadorned design, it has become popular for general purpose use in signage and display adaptations. Many adaptations and expansions of the original design have been released digitally. Overview The DIN 1451 typeface family includes both a medium () and a condensed () version; an older extended version () has not been used since the early 1980s, but may still be encountered on older road signs in Germany. DIN 1451 is the typeface used on road signage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC BY-SA 4
CC, cc, or C-C may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * C.C. (''Code Geass''), a character in the ''Code Geass'' anime series, pronounced "C-two" * C.C. Babcock, a character in the American sitcom ''The Nanny'' * Comedy Chimp, a character in ''Sonic Boom'', called "CC" by Doctor Eggman Gaming * ''Command & Conquer'' (''C&C''), a series of real-time strategy games and the first game in the series * Crowd control (video gaming), the ability to limit the number of mobs actively fighting during an encounter Other arts, music, entertainment, and media * Cannibal Corpse, an American death metal band. * CC Media Holdings, the former name of iHeartMedia * Closed captioning, a process of displaying text on a visual display, such as a TV screen * Comedy Central, an American television network (URL is cc.com) Brands and enterprises Food and drink * Canadian Club, a brand of whisky * CC's, a tortilla chip brand in Australia Other companies * Stylized interl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
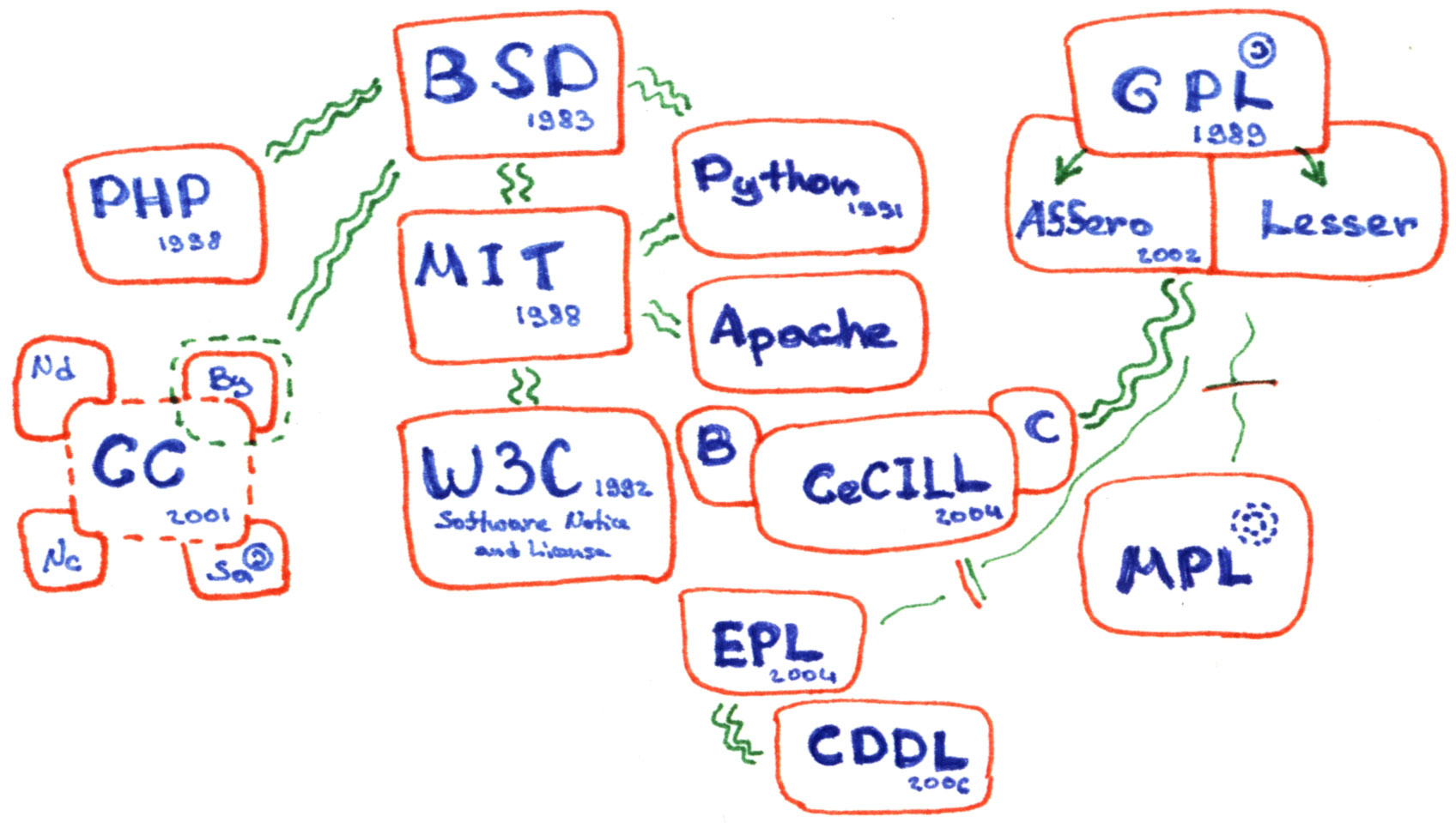
Open-license
A free license or open license is a license which allows others to reuse another creator’s work as they wish. Without a special license, these uses are normally prohibited by copyright, patent or commercial license. Most free licenses are worldwide, royalty-free, non-exclusive, and perpetual (see copyright durations). Free licenses are often the basis of crowdsourcing and crowdfunding projects. The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the hacker culture of the 1970s public domain software ecosystem, the social and political free software movement (since 1980) and the open source movement (since the 1990s). These rights were codified by different groups and organizations for different domains in Free Software Definition, Open Source Definition, Debian Free Software Guidelines, Definition of Free Cultural Works and The Open Definition. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |