|
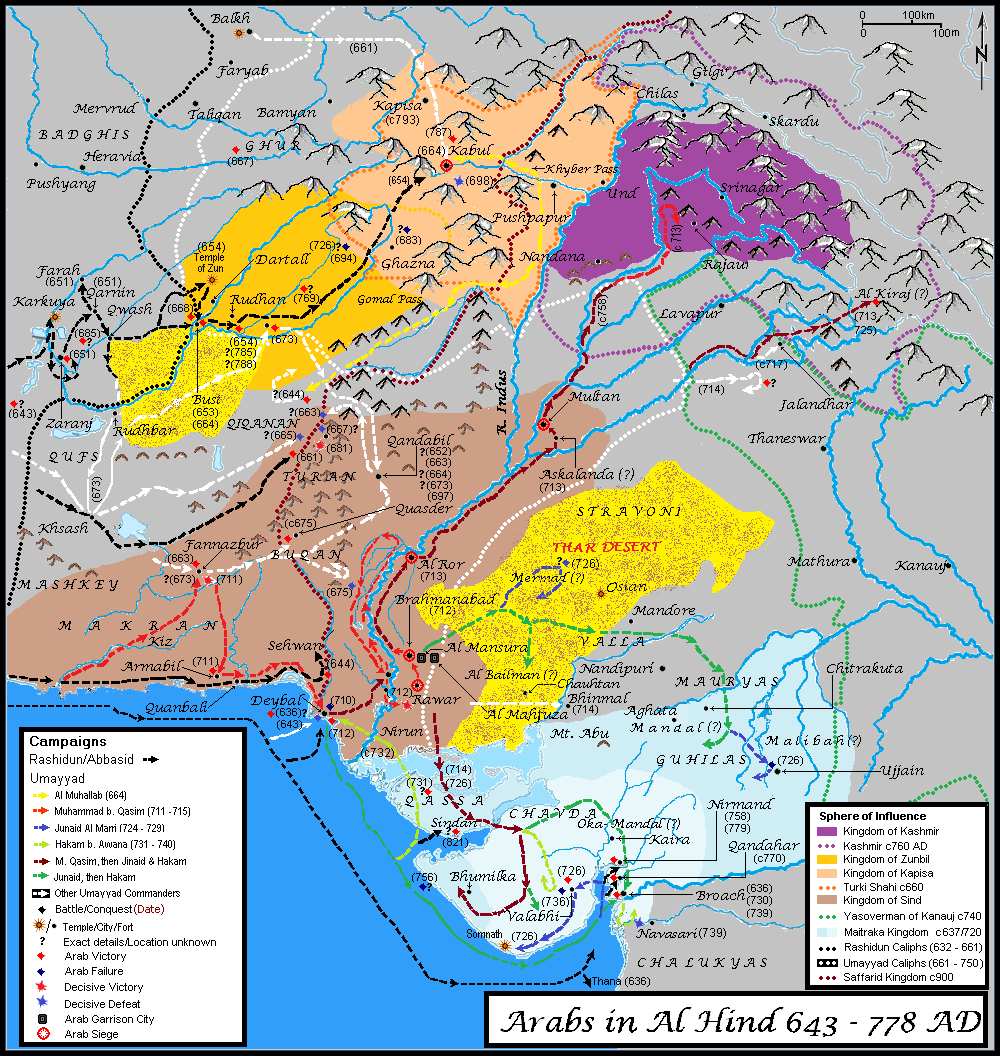
Debal
Debal (Urdu, Arabic, sd, ) was an ancient port located near modern Karachi, Pakistan. It is adjacent to the nearby Manora Island and was administered by Mansura, and later Thatta. Etymology In Arabic history books, most notably in the early eighth century accounts of the arrival of Islam in the Indian subcontinent, it was documented as Daybul (Dīwal ~ Dībal ). One view is that the name was derived from Devalaya, meaning abode of God in Sanskrit. According to the '' Chach Nama'', the name ''Dēbal'' is derived from ''Dēwal'', meaning 'temple'. The reason, it says, is because it was the site of a renowned temple. History According to modern archaeologists, Debal was founded in the first century CE, and soon became the most important trading city in Sindh. The port city was home to thousands of Sindhi sailors including the Bawarij. Ibn Hawqal, a tenth-century writer, geographer and chronicler, mentions huts of the city and the dry arid land surrounding the city that suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Conquests On The Indian Subcontinent
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place from the 13th to 17th centuries. Earlier Muslim conquests include the invasions into what is now modern-day Pakistan and the Umayyad campaigns in India in eighth century and resistance of Rajputs to them. Mahmud of Ghazni, who was the first Sultan, and preserved an ideological link to the suzerainty of the Abbasid Caliphate, invaded and plundered vast parts of Punjab and Gujarat, starting from the Indus River during the 11th century. After the capture of Lahore and the end of the Ghaznavids, the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor laid the foundation of Muslim rule in India. In 1206, Bakhtiyar Khalji led the Muslim conquest of Bengal, marking the easternmost expansion of Islam at the time. The Ghurid Empire soon evolved into the Delhi Sultanate, ruled by Qutb ud-Din Aibak, the founder of the Mamluk dynasty. With the Delhi Sultanate established, Islam was spread across most parts of the Indian subcontinent. In the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahari Bandar
Lahari Bandar, also called Lahori Bandar or Lari Bandar, was a historical port city in southern Sindh. From the early 1300s until the late 1600s, it was the main port in Sindh and one of the main ports in western India. Names According to Haig (1894), ''Lāhaṟī'' was the indigenous name used within Sindh, after the Lāhaṟ tribe that lived in that part of the delta, while ''Lāhorī'' was the name used outside Sindh, after its role as the port of Lahore. He connects it to the ''Lohāwar'' that al-Biruni uses for Lahore and says that it could have been Lohāwarānī, which would have been produced Lohārānī (the form used by al-Biruni) in common speech. Meanwhile, Elliot (1867) says that the original name was ''Lárí Bandar'', after the name ''Lár'' used for the southern part of Sindh. The city was also called ''Larrybunder'' by English merchants in the early modern period. The Portuguese called it ''Diul'', after the older port city of Debal, and the English also someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province by population after Punjab. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab to the north. It shares International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of the province. The economy of Sindh is the second-largest in Pakistan after the province of Punjab; its provincial capital of Karachi is the most populous city in the country as well as its main financial hub. Sindh is home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansura, Sindh
Mansura ( ar, المنصورة, al-manṣūra, the triumphant ity}), referred to as Brahmanabad ( ur, برہمن آباد ; sd, برهمڻ آباد, barhamaṇabād) in later centuries, was the historic capital of the Muslim Caliphate in Sindh, during the eighth century under the Umayyad Caliphate and then Abbasid Caliphate from the year 750 AD to 1006 AD. The city was founded as a central garrison by the Umayyad Forces in Sindh, the city transformed into a very vibrant metropolis during the Abbasid Era surpassing the wealth of Multan in the north and Debal in the south. Mansura was the first capital established by the Muslims in the Indian subcontinent after Muhammad bin Qasim seized the Brahmanabad territory. Mansura was built on the shores of the Indus River, it was surrounded by fertile farmland, Ibn Hauqal mentioned the wealthy local merchants who wore ''Baghdad Costume'' and were of Sindhi-Arab origins, houses were made of clay, baked bricks and plaster. Mansura e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernão Mendes Pinto
Fernão Mendes Pinto (; c.1509 – 8 July 1583) was a Portuguese explorer and writer. His voyages are recorded in ''Pilgrimage'' ( pt, Peregrinação) (1614), his autobiographical memoir. The historical accuracy of the work is debatable due to the many events that seem far-fetched or at least exaggerated, earning him the nickname "Fernão Mentes Minto" (wordplay with the Portuguese verb ''mentir'' 'lie', meaning "Fernão, are you lying? I am lying."). Many aspects of the work can be verified, particularly through records of Pinto's service to the Portuguese crown and by his association with Jesuit missionaries. Early life Pinto was born in about 1509, in Montemor-o-Velho, Portugal to a poor rural family (or perhaps to a family of minor nobility who had fallen on hard times). Pinto had two brothers and two sisters (and possibly other siblings). In 1551, a brother, Álvaro, was recorded in Portuguese Malacca. Letters also record that a brother died a martyr in Malacca. In 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
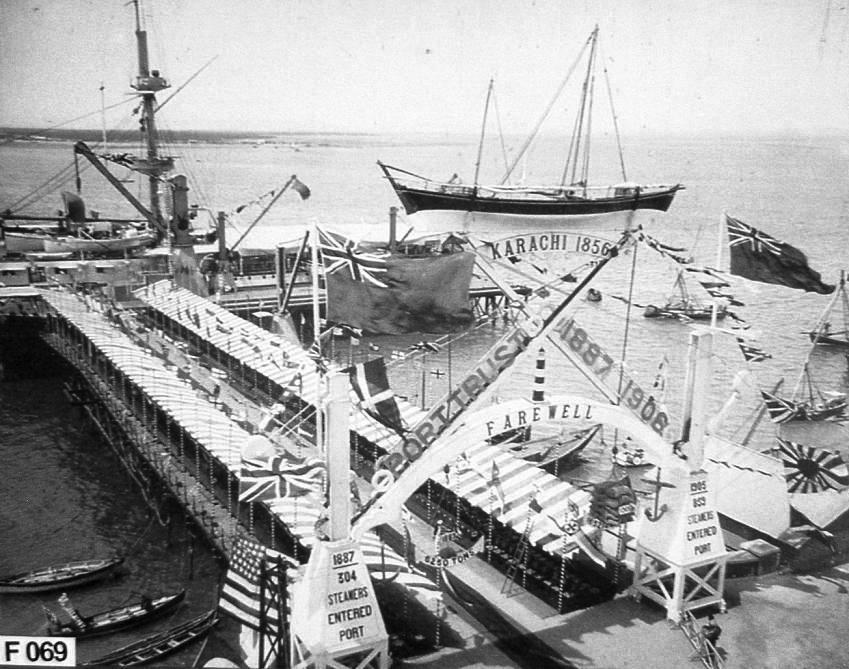
Port Of Karachi
The Port of Karachi ( ur, , ''Bandar gāh Karāchī'') is one of South Asia's largest and busiest deep-water seaports, handling about 60% of the nation's cargo (25 million tons per annum) located in Karachi, Pakistan. It is located on the Karachi Harbour, between Kiamari azra langri, Manora, and Kakapir, and close to Karachi's main business district and several industrial areas. The geographic position of the port places it in close proximity to major shipping routes such as the Strait of Hormuz. The administration of the port is carried out by the Karachi Port Trust, which was established in 1857. History The history of the port is intertwined with that of the city of Karachi. Several ancient ports have been attributed in the area including "Krokola", "Morontobara" (Woman's Harbour) (mentioned by Nearchus), Barbarikon (the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, and Debal (a city captured by the Arab general Muhammad bin Qasim in 712 CE). There is a reference to the early exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former capital of Pakistan and capital of the province of Sindh. Ranked as a beta-global city, it is Pakistan's premier industrial and financial centre, with an estimated GDP of over $200 billion ( PPP) . Karachi paid $9billion (25% of whole country) as tax during fiscal year July 2021 to May 2022 according to FBR report. Karachi is Pakistan's most cosmopolitan city, linguistically, ethnically, and religiously diverse, as well as one of Pakistan's most secular and socially liberal cities. Karachi serves as a transport hub, and contains Pakistan’s two largest seaports, the Port of Karachi and Port Qasim, as well as Pakistan's busiest airport, Jinnah International Airport. Karachi is also a media center, home to news channels, film and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manora, Karachi
Manora ( sd, منهوڙو, ur, ) is a small peninsula that forms a protective barrier between Karachi Harbour to the north and the Arabian Sea to the south. Manora, having a total population of 4,273 local residents (as per 2017 census), was formerly an island, but due to silting is now connected to the mainland by a 12 kilometer long natural sandbridge known as Sandspit Beach, Sandspit. The entrance to Karachi was once guarded against pirate raids by the Manora Fort, Karachi, Manora Fort built in the 1790s, which was later upgraded by the British, and then the Pakistan Navy. Geography Manora and neighboring islands form a protective barrier between Karachi Harbour to the north and the Arabian Sea to the south. The western bay of the harbor contains mangrove forests which border the Sandspit Beach, Sandspit and Manora island. The coastline is also home to the ''Peelu'' tree (Salvadora persica) that protects Manora's coast from erosion. History The area of Karachi was know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thatta
Thatta ( sd, ٺٽو; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh. Thatta was the medieval capital of Sindh, and served as the seat of power for three successive dynasties. Thatta's historic significance has yielded several monuments in and around the city. Thatta's Makli Necropolis, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is site of one of the world's largest cemeteries and has numerous monumental tombs built between the 14th and 18th centuries designed in a syncretic funerary style characteristic of lower Sindh. The city's 17th century Shah Jahan Mosque is richly embellished with decorative tiles, and is considered to have the most elaborate display of tile work in the South Asia. Etymology Thatta name refer to riverside settlements "/> Villagers in the rural areas of lower Sindh often refer to the city as ''Thatta Nagar'', or simply ''Nagar''. History Early Thatta may be the site of ancient Patala, the main port on the Indus in the time of Alexander the Great, though the site of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seydi Ali Reis
Seydi Ali Reis (1498–1563), formerly also written Sidi Ali Reis and Sidi Ali Ben Hossein, was an Ottoman admiral and navigator. Known also as Katib-i Rumi, Galatalı or Sidi Ali Çelebi,Danışan, Gaye. 2019. “A Sixteenth-Century Ottoman Compendium of Astronomical Instruments: Seydi Ali’s Mirʾat-ı Kâinat.” In ''Scientific Instruments between East and West'', edited by Neil Brown ''et al.'', 1–15. Leiden: Brill. he commanded the left wing of the Ottoman fleet at the naval Battle of Preveza in 1538. He was later promoted to the rank of fleet admiral of the Ottoman fleet in the Indian Ocean, and as such, encountered the Portuguese forces based in the Indian city of Goa on several occasions in 1554. Seydi was able to unite several Muslim countries on the coast of the Arabian Sea (such as the Makran Kingdom, Gujarat Sultanate and Adal Sultanate) against the Portuguese. He is famous today for his books of travel such as the '' Mir'ât ül Memâlik'' (The Mirror ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirat Ul Memalik
''Mirat ul Memalik'' (The Mirror of Countries) is a historical book written in 1557 by Ottoman admiral Seydi Ali Reis about his travels in South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East. This book, which is now considered one of the earliest travel books of Turkish literature, was written in the Ottoman Turkish and Chagatai language ( seyahatname) both of which are now extinct Turkic languages. Background Seydi Ali Reis was an Ottoman admiral sent by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent to counter the Portuguese piracy and attacks on Muslim pilgrim ships in the Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, Red Sea, and Persian Gulf. But after two marine battles against the Portuguese fleet and a great storm named the ''elephant typhoon'' (''tufan’ı fil'') by the locals, his remaining six galleys drifted to India. The fleet was unserviceable, resulting in his return home overland with 50 men. The book Seydi Ali Reis then arrived at the royal court of the Mughal Emperor Humayun in Delhi, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |