|
Creationism
Creationism is the religious belief that nature, and aspects such as the universe, Earth, life, and humans, originated with supernatural acts of divine creation. Gunn 2004, p. 9, "The ''Concise Oxford Dictionary'' says that creationism is 'the belief that the universe and living organisms originated from specific acts of divine creation.'" In its broadest sense, creationism includes a continuum of religious views, Haarsma 2010, p. 168, "Some Christians, often called 'Young Earth creationists,' reject evolution in order to maintain a semi-literal interpretation of certain biblical passages. Other Christians, called 'progressive creationists,' accept the scientific evidence for some evolution over a long history of the earth, but also insist that God must have performed some miracles during that history to create new life-forms. Intelligent design, as it is promoted in North America is a form of progressive creation. Still other Christians, called theistic evolutionists' or 'e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Design
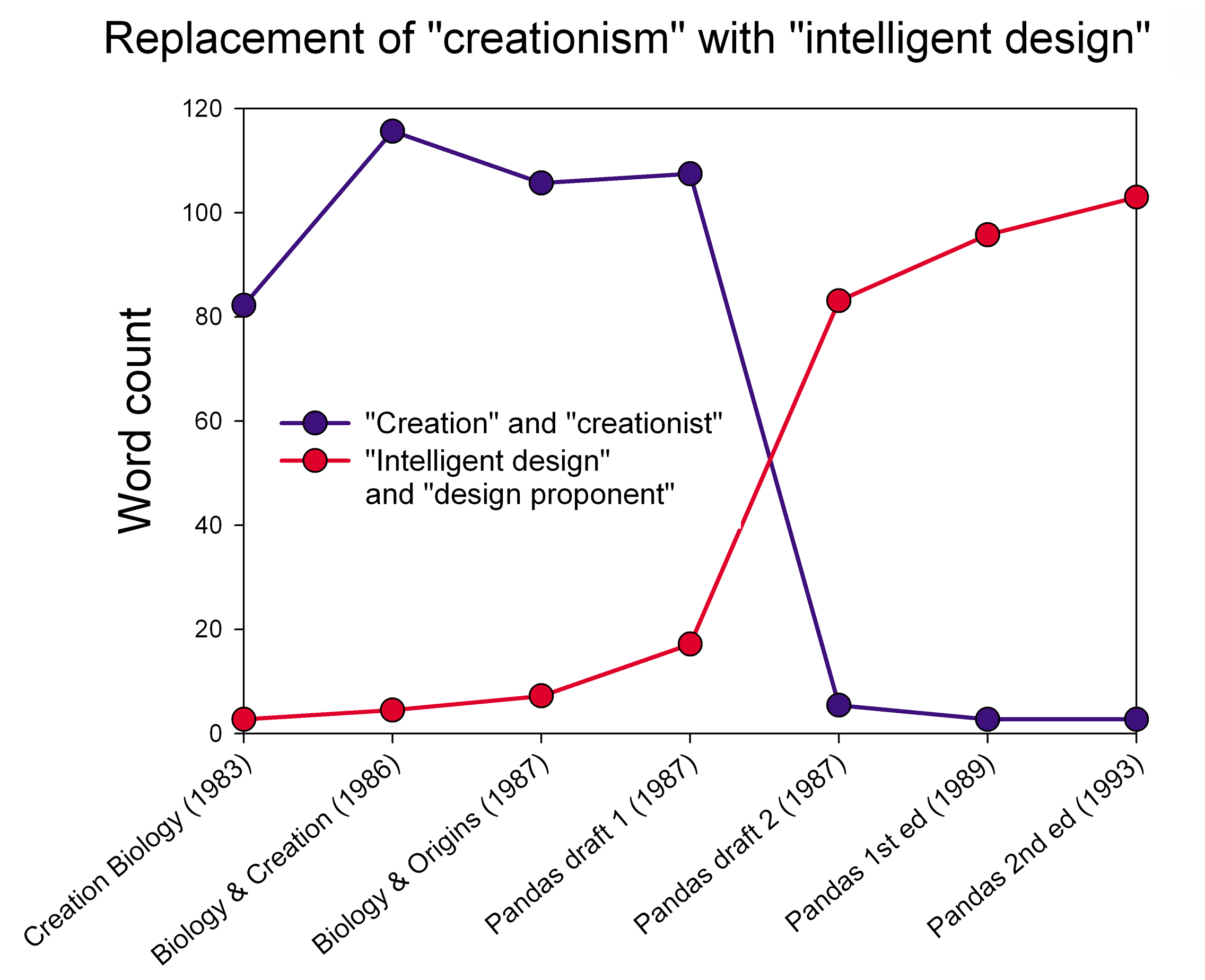
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins". Numbers 2006, p. 373; " Dcaptured headlines for its bold attempt to rewrite the basic rules of science and its claim to have found indisputable evidence of a God-like being. Proponents, however, insisted it was 'not a religious-based idea, but instead an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins – one that challenges strictly materialistic views of evolution.' Although the intellectual roots of the design argument go back centuries, its contemporary incarnation dates from the 1980s" Article available froUniversiteit Gent/ref> Proponents claim that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection." * * ID is a form of creationism that lacks empirical support and offers no testable or tenable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Earth Creationism
Young Earth creationism (YEC) is a form of creationism which holds as a central tenet that the Earth and its lifeforms were created by supernatural acts of the Abrahamic God between approximately 6,000 and 10,000 years ago. In its most widespread version, YEC is based on the religious belief in the inerrancy of certain literal interpretations of the Book of Genesis. Its primary adherents are Christians and Jews who believe that God created the Earth in six literal days, in contrast with old Earth creationism (OEC), which holds literal interpretations of Genesis that are compatible with the scientifically determined ages of the Earth and universe and theistic evolution, which posits that the scientific principles of evolution, the Big Bang, abiogenesis, solar nebular theory, age of the universe, and age of Earth are compatible with a metaphorical interpretation of Genesis. Since the mid-20th century, young Earth creationists—starting with Henry Morris (1918–2006)—h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Earth Creationism
Old Earth creationism (OEC) is an umbrella of theological views encompassing certain varieties of creationism which may or can include day-age creationism, gap creationism, progressive creationism, and sometimes theistic evolutionism. Broadly speaking, OEC usually occupies a middle ground between young Earth creationism (YEC) and theistic evolution (TE). In contrast to YEC, it is typically more compatible with the scientific consensus on the issues of physics, chemistry, geology, and the age of the Earth. However, like YEC and in contrast with TE, some forms of it reject macroevolution, claiming it is biologically untenable and not supported by the fossil record, and the concept of universal descent from a last universal common ancestor. For a long time Evangelical creationists generally subscribed to Old Earth Creationism until 1960 when John C. Whitcomb and Henry M. Morris published the book ''The Genesis Flood'', which caused the Young Earth creationist view to become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creation Science
Creation science or scientific creationism is a pseudoscientific form of Young Earth creationism which claims to offer scientific arguments for certain literalist and inerrantist interpretations of the Bible. It is often presented without overt faith-based language, but instead relies on reinterpreting scientific results to argue that various myths in the Book of Genesis and other select biblical passages are scientifically valid. The most commonly advanced ideas of creation science include special creation based on the Genesis creation narrative and flood geology based on the Genesis flood narrative. Creationists also claim they can disprove or reexplain a variety of scientific facts, theories and paradigms of geology, cosmology, biological evolution, archaeology, history, and linguistics using creation science. Creation science was foundational to intelligent design. The overwhelming consensus of the scientific community is that creation science fails to qualify as scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Creationism
Gap creationism (also known as ruin-restoration creationism, restoration creationism, or "the Gap Theory") is a form of old Earth creationism that posits that the six-'' yom'' creation period, as described in the Book of Genesis, involved six literal 24-hour days (light being "day" and dark "night" as God specified), but that there was a gap of time between two distinct creations in the first and the second verses of Genesis, which the theory states explains many scientific observations, including the age of the Earth. It differs from day-age creationism, which posits that the 'days' of creation were much longer periods (of thousands or millions of years), and from young Earth creationism, which although it agrees concerning the six literal 24-hour days of creation, does not posit any gap of time. History From 1814, Thomas Chalmers popularized gap creationism; he attributed the concept to the 17th-century Dutch Arminian theologian Simon Episcopius. Chalmers wrote: Chalmers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Geology
Flood geology (also creation geology or diluvial geology) is a pseudoscientific attempt to interpret and reconcile geological features of the Earth in accordance with a literal belief in the global flood described in Genesis 6–8. In the early 19th century, diluvial geologists hypothesized that specific surface features provided evidence of a worldwide flood which had followed earlier geological eras; after further investigation they agreed that these features resulted from local floods or from glaciers. In the 20th century, young-Earth creationists revived flood geology as an overarching concept in their opposition to evolution, assuming a recent six-day Creation and cataclysmic geological changes during the biblical flood, and incorporating creationist explanations of the sequences of rock strata. In the early stages of development of the science of geology, fossils were interpreted as evidence of past flooding. The "theories of the Earth" of the 17th century proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Creationism
Progressive creationism (see for comparison intelligent design) is the religious belief that God created new forms of life gradually over a period of hundreds of millions of years. As a form of old Earth creationism, it accepts mainstream geological and cosmological estimates for the age of the Earth, some tenets of biology such as microevolution as well as archaeology to make its case. In this view creation occurred in rapid bursts in which all "kinds" of plants and animals appear in stages lasting millions of years. The bursts are followed by periods of stasis or equilibrium to accommodate new arrivals. These bursts represent instances of God creating new types of organisms by divine intervention. As viewed from the archaeological record, progressive creationism holds that "species do not gradually appear by the steady transformation of its ancestors; utappear all at once and "fully formed." The view rejects macroevolution, claiming it is biologically untenable and no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Day-age Creationism
Day-age creationism, a type of old Earth creationism, is an interpretation of the creation accounts in Genesis. It holds that the six days referred to in the Genesis account of creation are not ordinary 24-hour days, but are much longer periods (from thousands to billions of years). The Genesis account is then reconciled with the age of the Earth. Proponents of the day-age theory can be found among both theistic evolutionists, who accept the scientific consensus on evolution, and progressive creationists, who reject it. The theories are said to be built on the understanding that the Hebrew word ''yom'' is also used to refer to a time period, with a beginning and an end and not necessarily that of a 24-hour day. The differences between the young Earth interpretation of Genesis and modern scientific theories believed by some day-age creationists such as the Big Bang, abiogenesis, and common descent are significant. The young Earth interpretation says that everything in the uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Creation
In creationism, special creation is a belief that the universe and all life in it originated in its present form by fiat or divine decree. Catholicism uses the phrase "special creation" in two different senses: * in the context of theistic evolution to refer to the "special creation of humans", a point of hominization where evolved near-human animals were given souls by God, and became fully human; this belief is also called special transformism by some scholars. * to refer to the doctrine of immediate or special creation of each human soul Creationism In creationism, "special creation" is a literal interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative, viewing it as an accurate description of the creation of the universe in essentially its present form over the course of six 24-hour days. Duane Gish of the Institute for Creation Research defined "special creation" as being creation using supernatural processes: Dennis Jensen of the American Scientific Affiliation states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creationism (soul)
Creationism is a doctrine held by some Christians that God creates a soul for each body that is generated. Alternative Christian views on the origin of souls are traducianism and also the idea of a pre-existence of the soul. The Scholastic philosophers held the theory of Creationism. Concept Creationism holds that the origin of the soul cannot be by spiritual generation from the souls of parents (as the German theologian Jakob Frohschammer (1821-1893) maintained) because human souls, being essentially and integrally simple and indivisible, can give forth no spiritual germs or reproductive elements. The creation of the soul by the First Cause, when second causes have posited the pertinent conditions, falls within the order of nature; it is a so-called "law of nature", not an interference therewith.Sieg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claims; reliance on confirmation bias rather than rigorous attempts at refutation; lack of openness to evaluation by other experts; absence of systematic practices when developing hypotheses; and continued adherence long after the pseudoscientific hypotheses have been experimentally discredited. The demarcation between science and pseudoscience has scientific, philosophical, and political implications. Philosophers debate the nature of science and the general criteria for drawing the line between scientific theories and pseudoscientific beliefs, but there is general agreement on examples such as ancient astronauts, climate change denial, dowsing, evolution denial, Holocaust denialism, astrology, alchemy, alternative medicine, occulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Fundamentalism
Christian fundamentalism, also known as fundamental Christianity or fundamentalist Christianity, is a religious movement emphasizing biblical literalism. In its modern form, it began in the late 19th and early 20th centuries among British and American ProtestantsMarsden (1980), pp. 55–62, 118–23. as a reaction to theological liberalism and cultural modernism. Fundamentalists argued that 19th-century modernist theologians had misinterpreted or rejected certain doctrines, especially biblical inerrancy, which they considered the fundamentals of the Christian faith.Sandeen (1970), p. 6 Fundamentalists are almost always described as upholding beliefs in biblical infallibility and biblical inerrancy. In keeping with traditional Christian doctrines concerning biblical interpretation, the role of Jesus in the Bible, and the role of the church in society. Fundamentalists usually believe in a core of Christian beliefs, typically called the "Five Fundamentals," this arose from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Theory.png)

.png)
