|
Cray
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world. Cray manufactures its products in part in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin, where its founder, Seymour Cray, was born and raised. The company also has offices in Bloomington, Minnesota (which have been converted to Hewlett Packard Enterprise offices), and numerous other sales, service, engineering, and R&D locations around the world. The company's predecessor, Cray Research, Inc. (CRI), was founded in 1972 by computer designer Seymour Cray. Seymour Cray later formed Cray Computer Corporation (CCC) in 1989, which went bankrupt in 1995. Cray Research was acquired by Silicon Graphics (SGI) in 1996. Cray Inc. was formed in 2000 when Tera Computer Company purchased the Cray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray2
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world. Cray manufactures its products in part in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin, where its founder, Seymour Cray, was born and raised. The company also has offices in Bloomington, Minnesota (which have been converted to Hewlett Packard Enterprise offices), and numerous other sales, service, engineering, and R&D locations around the world. The company's predecessor, Cray Research, Inc. (CRI), was founded in 1972 by computer designer Seymour Cray. Seymour Cray later formed Cray Computer Corporation (CCC) in 1989, which went bankrupt in 1995. Cray Research was acquired by Silicon Graphics (SGI) in 1996. Cray Inc. was formed in 2000 when Tera Computer Company purchased the Cray R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
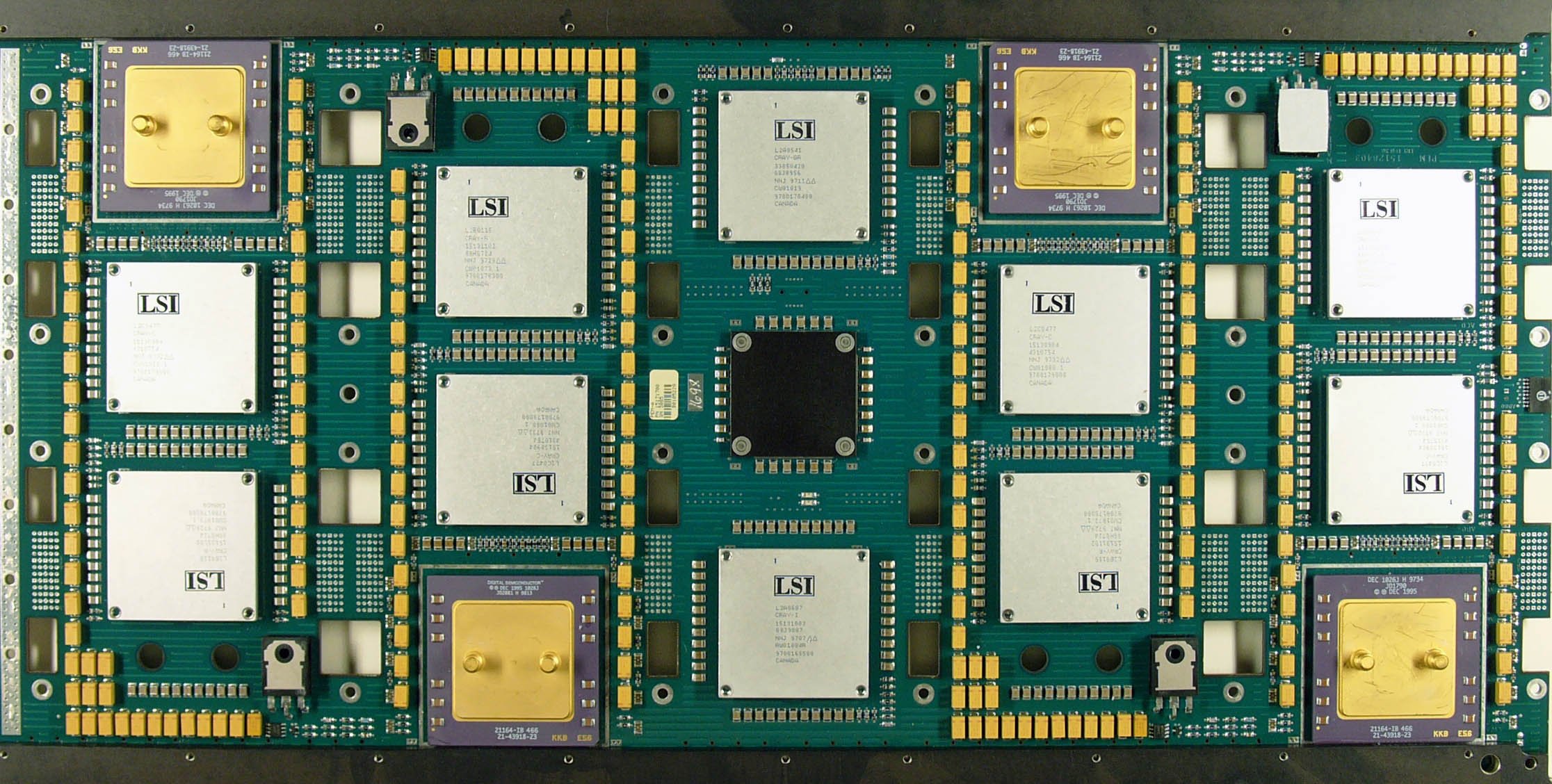
Cray-1
The Cray-1 was a supercomputer designed, manufactured and marketed by Cray Research. Announced in 1975, the first Cray-1 system was installed at Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1976. Eventually, over 100 Cray-1s were sold, making it one of the most successful supercomputers in history. It is perhaps best known for its unique shape, a relatively small C-shaped cabinet with a ring of benches around the outside covering the power supplies and the cooling system. The Cray-1 was the first supercomputer to successfully implement the vector processor design. These systems improve the performance of math operations by arranging memory and registers to quickly perform a single operation on a large set of data. Previous systems like the CDC STAR-100 and ASC had implemented these concepts but did so in a way that seriously limited their performance. The Cray-1 addressed these problems and produced a machine that ran several times faster than any similar design. The Cray-1's architect wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymour Cray
Seymour Roger Cray (September 28, 1925 – October 5, 1996 ) was an American and architect who designed a series of computers that were the fastest in the world for decades, and founded which built many of these machines. Called "the father of supercomputing", Cray has been credited with creating the supercomputer industry. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray-3
The Cray-3 was a vector supercomputer, Seymour Cray's designated successor to the Cray-2. The system was one of the first major applications of gallium arsenide (GaAs) semiconductors in computing, using hundreds of custom built ICs packed into a CPU. The design goal was performance around 16 GFLOPS, about 12 times that of the Cray-2. Work started on the Cray-3 in 1988 at Cray Research's (CRI) development labs in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin. Other teams at the lab were working on designs with similar performance. To focus the teams, the Cray-3 effort was moved to a new lab in Colorado Springs, Colorado later that year. Shortly thereafter, the corporate headquarters in Minneapolis decided to end work on the Cray-3 in favor of another design, the Cray C90. In 1989 the Cray-3 effort was spun off to a newly formed company, Cray Computer Corporation (CCC). The launch customer, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, cancelled their order in 1991 and a number of company executives le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray-2
The Cray-2 is a supercomputer with four vector processors made by Cray Research starting in 1985. At 1.9 GFLOPS peak performance, it was the fastest machine in the world when it was released, replacing the Cray X-MP in that spot. It was, in turn, replaced in that spot by the Cray Y-MP in 1988. The Cray-2 was the first of Seymour Cray's designs to successfully use multiple CPUs. This had been attempted in the CDC 8600 in the early 1970s, but the emitter-coupled logic (ECL) transistors of the era were too difficult to package into a working machine. The Cray-2 addressed this through the use of ECL integrated circuits, packing them in a novel 3D wiring that greatly increased circuit density. The dense packaging and resulting heat loads were a major problem for the Cray-2. This was solved in a unique fashion by forcing the electrically inert Fluorinert liquid through the circuitry under pressure and then cooling it outside the processor box. The unique "waterfall" cooler sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray X-MP
The Cray X-MP was a supercomputer designed, built and sold by Cray Research. It was announced in 1982 as the "cleaned up" successor to the 1975 Cray-1, and was the world's fastest computer from 1983 to 1985 with a quad-processor system performance of 800 MFLOPS. The principal designer was Steve Chen. Description The X-MP's main improvement over the Cray-1 was that it was a shared-memory parallel vector processor, the first such computer from Cray Research. It housed up to four CPUs in a mainframe that was nearly identical in outside appearance to the Cray-1. The X-MP CPU had a faster 9.5 nanosecond clock cycle (105 MHz), compared to 12.5 ns for the Cray-1A. It was built from bipolar gate-array integrated circuits containing 16 emitter-coupled logic gates each. The CPU was very similar to the Cray-1 CPU in architecture, but had better memory bandwidth (with two read ports and one write port to the main memory instead of only one read/write port) and improved ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second ( FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second ( FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Data Corporation
Control Data Corporation (CDC) was a mainframe and supercomputer firm. CDC was one of the nine major United States computer companies through most of the 1960s; the others were IBM, Burroughs Corporation, DEC, NCR, General Electric, Honeywell, RCA, and UNIVAC. CDC was well-known and highly regarded throughout the industry at the time. For most of the 1960s, Seymour Cray worked at CDC and developed a series of machines that were the fastest computers in the world by far, until Cray left the company to found Cray Research (CRI) in the 1970s. After several years of losses in the early 1980s, in 1988 CDC started to leave the computer manufacturing business and sell the related parts of the company, a process that was completed in 1992 with the creation of Control Data Systems, Inc. The remaining businesses of CDC currently operate as Ceridian. Background and origins: World War II–1957 During World War II the U.S. Navy had built up a classified team of engineers to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
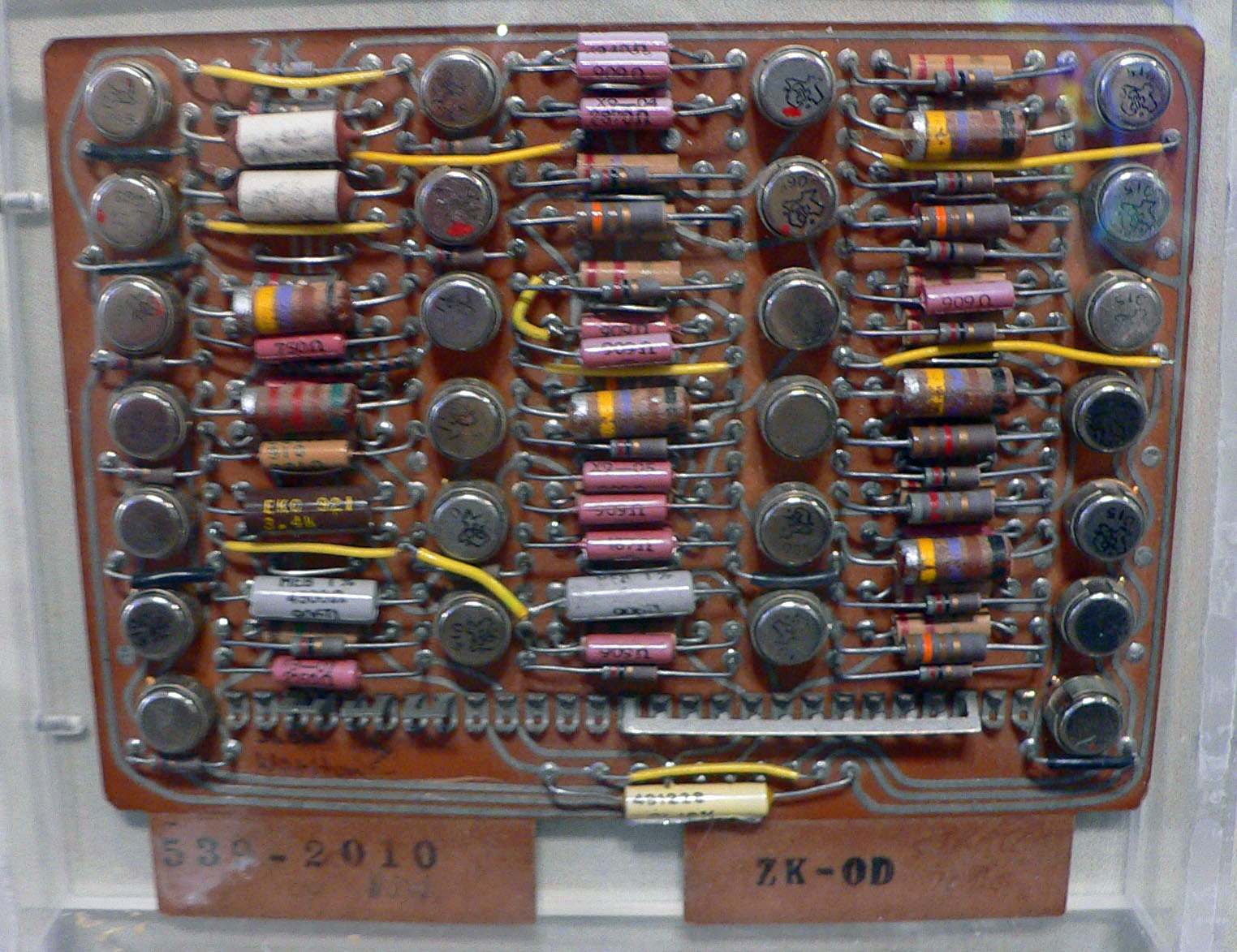
CDC 8600
The CDC 8600 was the last of Seymour Cray's supercomputer designs while he worked for Control Data Corporation. As the natural successor to the CDC 6600 and CDC 7600, the 8600 was intended to be about 10 times as fast as the 7600, already the fastest computer on the market. The design was essentially four 7600's, packed into a very small chassis so they could run at higher clock speeds. Development started in 1968, shortly after the release of the 7600, but the project soon started to bog down. The dense packaging of the system led to serious reliability problems and difficulty cooling the individual components. By 1971, CDC was having cash-flow problems and the design was still not coming together, prompting Cray to leave the company in 1972. The 8600 design effort was eventually canceled in 1974, and Control Data moved on to the CDC STAR-100 series instead. Cray revisited the 8600's basic design in his Cray-2 of the early 1980s. The introduction of integrated circuits solve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDC 6600
The CDC 6600 was the flagship of the 6000 series of mainframe computer systems manufactured by Control Data Corporation. Generally considered to be the first successful supercomputer, it outperformed the industry's prior recordholder, the IBM 7030 Stretch, by a factor of three."Designed by Seymour Cray, the CDC 6600 was almost three times faster than the next fastest machine of its day, the IBM 7030 Stretch." With performance of up to three megaFLOPS, the CDC 6600 was the world's fastest computer from 1964 to 1969, when it relinquished that status to its successor, the CDC 7600."The 7600 design lasted longer than any other supercomputer design. It had the highest performance of any computer from its introduction in 1969 till the introduction of the Cray 1 in 1976." The first CDC 6600s were delivered in 1965 to Livermore and Los Alamos. They quickly became a must-have system in high-end scientific and mathematical computing, with systems being delivered to Courant Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOP500
The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non- distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for distributed-memory computers. The 60th TOP500 was published in November 2022. Since June 2022, USA's Frontier is the most powerful supercomputer on TOP500, reaching 1102 petaFlops (1.102 exaFlops) on the LINPACK benchmarks. The United States has by far the highest share of total computing power on the list (nearly 50%), while China currently leads the list in number of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |