|
Coumarin
Coumarin () or 2''H''-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain , forming a second six-membered heterocycle that shares two carbons with the benzene ring. It can be placed in the benzopyrone chemical class and considered as a lactone. Coumarin is a colorless crystalline solid with a sweet odor resembling the scent of vanilla and a bitter taste. It is found in many plants, where it may serve as a chemical defense against predators. By inhibiting synthesis of vitamin K, a related compound is used as the prescription drug warfarin – an anticoagulant – to inhibit formation of blood clots, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Etymology Coumarin is derived from ''coumarou'', the French word for the tonka bean. The word ''tonka'' for the tonka bean is taken from the Galibi (Carib) tongue spoken by natives of French Gui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent stroke in people who have atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, or artificial heart valves. Less commonly, it is used following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and orthopedic surgery. It is generally taken by mouth, but may also be used intravenously. The common side effect is bleeding. Less common side effects may include areas of tissue damage and purple toes syndrome. Use is not recommended during pregnancy. The effects of warfarin typically should be monitored by checking prothrombin time (INR) every one to four weeks. Many other medications and dietary factors can interact with warfarin, either increasing or decreasing its effectiveness. The effects of warfarin may be reversed with phytomenadione (vitamin K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
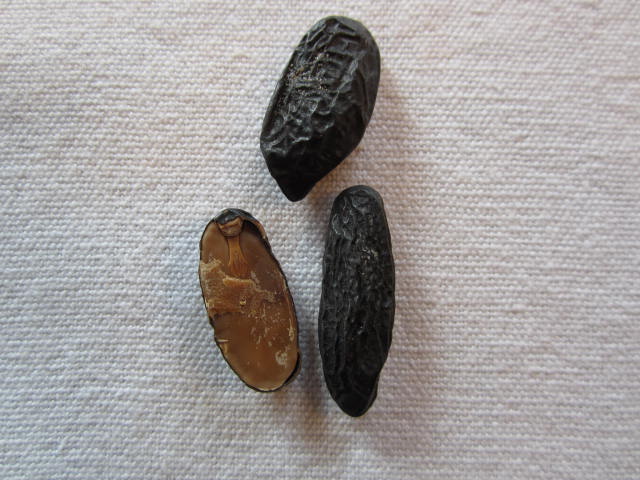
Tonka Beans
''Dipteryx odorata'' (commonly known as "cumaru", "kumaru", or "Brazilian teak") is a species of flowering tree in the pea family, Fabaceae. The tree is native to Central America and northern South America and is semi-deciduous. Its seeds are known as tonka beans (sometimes tonkin beans or tonquin beans). They are black and wrinkled and have a smooth, brown interior. They have a strong fragrance similar to sweet woodruff due to their high content of coumarin. The word ''tonka'' is taken from the Galibi (Carib) tongue spoken by natives of French Guiana; it also appears in Tupi, another language of the same region, as the name of the tree. The old genus name, ''Coumarouna'', was formed from another Tupi name for tree, ''kumarú''. Many anticoagulant prescription drugs, such as warfarin, are based on 4-hydroxycoumarin, a chemical derivative of coumarin initially isolated from this bean. Coumarin, however, does not have anticoagulant properties. Biology of the tree The tree gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonka Bean
''Dipteryx odorata'' (commonly known as "cumaru", "kumaru", or "Brazilian teak") is a species of flowering tree in the pea family, Fabaceae. The tree is native to Central America and northern South America South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ... and is semi-deciduous. Its seeds are known as tonka beans (sometimes tonkin beans or tonquin beans). They are black and wrinkled and have a smooth, brown interior. They have a strong fragrance similar to Galium odoratum, sweet woodruff due to their high content of coumarin. The word ''tonka'' is taken from the Galibi (Carib) tongue spoken by natives of French Guiana; it also appears in Tupi, another language of the same region, as the name of the tree. The old genus name, ''Coumarouna'', was formed from another Tupi name for tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation (K from ''Koagulation'', German for "coagulation") or for controlling binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. The complete synthesis involves final modification of these so-called "Gla proteins" by the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase that uses vitamin K as a cofactor. Vitamin K is used in the liver as the intermediate VKH2 to deprotonate a glutamate residue and then is reprocessed into vitamin K through a vitamin K oxide intermediate. The presence of uncarboxylated proteins indicates a vitamin K deficiency. Carboxylation allows them to bind ( chelate) calcium ions, which they cannot do otherwise. Without vitamin K, blood coagulation is seriously impaired, and uncontrolled bleeding occurs. Research suggests that deficiency o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where they help keep the bite area unclotted long enough for the animal to obtain some blood. As a class of medications, anticoagulants are used in therapy for thrombotic disorders. Oral anticoagulants (OACs) are taken by many people in pill or tablet form, and various intravenous anticoagulant dosage forms are used in hospitals. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as sample tubes, blood transfusion bags, heart–lung machines, and dialysis equipment. One of the first anticoagulants, warfarin, was initially approved as a rodenticide. Anticoagulants are closely related to antiplatelet drugs and thrombolytic drugs by manipulating the various pathways of blood coagulation. Specifically, antiplatelet drugs inhibit pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromone
Chromone (or 1,4-benzopyrone) is a derivative of benzopyran with a substituted keto group on the pyran ring. It is an isomer of coumarin. Derivatives of chromone are collectively known as ''chromones''. Most, though not all, chromones are also phenylpropanoids. Examples * 6,7-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydrochromone has been isolated from '' Sarcolobus globosus''. * Eucryphin, a chromone rhamnoside, can be isolated from the bark of '' Eucryphia cordifolia''. * Cromolyn (disodium cromoglicate) was found to inhibit antigen challenge as well as stress induced symptoms.HOWELL, J.B. & ALTOUNYAN, R.E. (1967). A double-blind trial of disodium cromoglycate in the treatment of allergic bronchial asthma. Lancet, 2, 539–542Abstract/ref> Cromoglicate is used as a mast cell stabilizer in allergic rhinitis, asthma and allergic conjunctivitis. * Nedocromil sodium was found to have a somewhat longer half-life than cromolyn; however, production was discontinued in the US in 2008. * Xanthone with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzopyrone
Benzopyrone may refer to either of two ketone derivatives of benzopyran which constitute the core skeleton of many flavonoid compounds: *Chromone (1-benzopyran-4-one) * Coumarin (1-benzopyran-2-one) Certain simple benzopyrones have clinical medical value as an edema modifiers. Coumarin and other benzopyrones, such as 5,6 benzopyrone, 1,2 benzopyrone, diosmin and others are known to stimulate macrophages to degrade extracellular albumin, allowing faster resorption of edematous fluids. Naturally occurring coumarin is also the basis for various 4-hydroxybenzopyrone-based molecules which occur naturally dicoumarol and are made synthetically warfarin Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent st ... and function as anticoagulants. References {{reflist Benzopyrans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
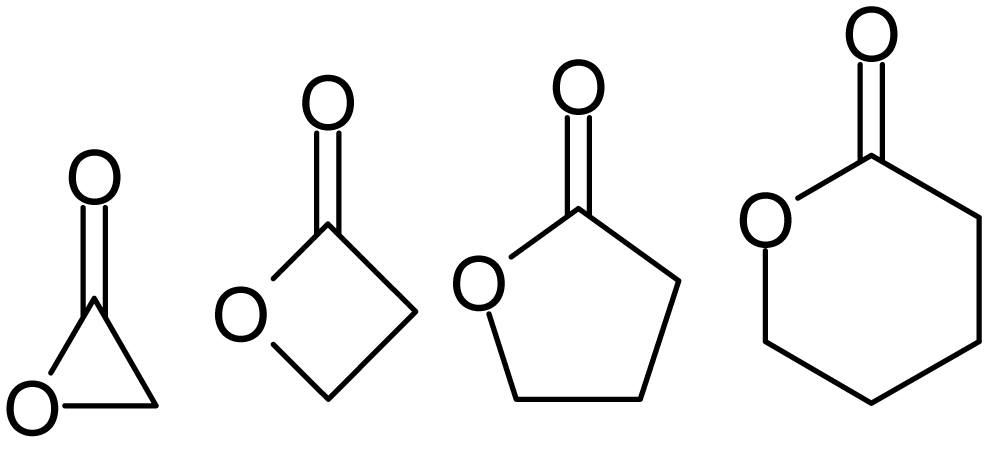
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia''). Pollination is required to make the plants produce the fruit from which the vanilla spice is obtained. In 1837, Belgian botanist Charles François Antoine Morren discovered this fact and pioneered a method of artificially pollinating the plant. The method proved financially unworkable and was not deployed commercially. In 1841, Edmond Albius, a 12-year-old enslaved child who lived on the French island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean, discovered that the plant could be hand-pollination, hand-pollinated. Hand-pollination allowed global cultivation of the plant. Noted French botanist and plant collector Jean Michel Claude Richard falsely claimed to have discovered the technique three or four years earlier. By the end of the 20th century, Albius was considered the true discoverer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Perkin
Sir William Henry Perkin (12 March 1838 – 14 July 1907) was a British chemist and entrepreneur best known for his serendipitous discovery of the first commercial synthetic organic dye, mauveine, made from aniline. Though he failed in trying to synthesise quinine for the treatment of malaria, he became successful in the field of dyes after his first discovery at the age of 18. Perkin set up a factory to produce the dye industrially. Lee Blaszczyk, professor of business history at the University of Leeds, states, "By laying the foundation for the synthetic organic chemicals industry, Perkin helped to revolutionize the world of fashion." Early years William Perkin was born in the East End of London, the youngest of the seven children of George Perkin, a successful carpenter. His mother, Sarah, was of Scottish descent and moved to East London as a child.UXL Encyclopedia of World Biography (2003). Accessed 18 March 2008. He was baptized in the Anglican parish church of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fougère
''Fougère'', , is one of the main olfactive families of perfumes. The name comes from the French language word for "fern". ''Fougère'' perfumes are made with a blend of fragrances: top-notes are sweet, with the scent of lavender flowers; as the more volatile components evaporate, the scents of oakmoss, derived from a species of lichen and described as woody, sharp and slightly sweet, and coumarin, similar to the scent of new-mown hay, become noticeable. Aromatic ''fougère'', a derivative of this class, contains additional notes of herbs, spice and/or wood. The name originated with Houbigant Parfum's ''Fougère Royale''. This perfume, created by Houbigant owner Paul Parquet, was later added to the scent archives known as the Osmothèque, in Versailles, France. Houbigant re-introduced this fragrance in 2010. Perfumes of this type are especially popular as fragrances for men. Many modern fougère perfumes have various citrus, herbaceous, green, floral and animalic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Académie Nationale De Médecine
Situated at 16 Rue Bonaparte in the 6th arrondissement of Paris, the Académie nationale de médecine (National Academy of Medicine) was created in 1820 by King Louis XVIII at the urging of baron Antoine Portal. At its inception, the institution was known as the Académie royale de médecine (or ''Royal Academy of Medicine''). This academy was endowed with the legal status of two institutions which preceded it—the Académie royale de chirurgie (or ''Royal Academy of Surgery''), which was created in 1731 and of the Société royale de médecine (or ''Royal Society of Medicine''), which was created in 1776. Background Academy members initially convened at the ''Paris Faculty of Medicine (or Faculté de Médecine de Paris)''. Four years later, the academy acquired its own headquarters, in the form of a mansion in the rue de Poitiers, where it was located until 1850. The office was then relocated to a vaulted hall of the Hospital of Charity on rue Saint Pierre. Their current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)

