|
Contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only became available in the 20th century. Planning, making available, and using birth control is called family planning. Some cultures limit or discourage access to birth control because they consider it to be morally, religiously, or politically undesirable. The World Health Organization and United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provide guidance on the safety of birth control methods among women with specific medical conditions. The most effective methods of birth control are sterilization by means of vasectomy in males and tubal ligation in females, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and implantable birth control. This is followed by a number of hormone-based methods including oral pills, patches, vaginal ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Contraceptive
Emergency contraception (EC) is a birth control measure, used after sexual intercourse to prevent pregnancy. There are different forms of EC. Emergency contraceptive pills (ECPs), sometimes simply referred to as emergency contraceptives (ECs), or the morning-after pill, are medications intended to disrupt or delay ovulation or fertilization, which are necessary for pregnancy. p. 121: Intrauterine devices (IUDs)usually used as a primary contraceptive methodare sometimes used as the most effective form of emergency contraception. However, the use of IUDs for emergency contraception is relatively rare. Definition Emergency contraception is a birth control measure taken to reduce the risk of pregnancy following unprotected sexual intercourse or when other regular contraceptive measures have not worked properly or have not been used correctly. It is intended to be used occasionally and is not the same as medical abortion. Emergency contraception is offered to women who do not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrier Contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only became available in the 20th century. Planning, making available, and using birth control is called family planning. Some cultures limit or discourage access to birth control because they consider it to be morally, religiously, or politically undesirable. The World Health Organization and United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provide guidance on the safety of birth control methods among women with specific medical conditions. The most effective methods of birth control are sterilization by means of vasectomy in males and tubal ligation in females, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and implantable birth control. This is followed by a number of hormone-based methods including oral pills, patches, vaginal rings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
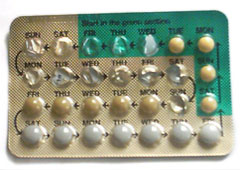
Combined Oral Contraceptive Pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: progestin (a synthetic form of the hormone progestogen/progesterone) and estrogen (usually ethinylestradiol and 17β estradiol). When taken correctly, it alters the menstrual cycle to eliminate ovulation and prevent pregnancy. COCPs were first approved for contraceptive use in the United States in 1960, and are a very popular form of birth control. They are used by more than 100 million women worldwide and by about 9 million women in the United States. From 2015 to 2017, 12.6% of women aged 15–49 in the US reported using COCPs, making it the second most common method of contraception in this age range (female sterilization is the most common method). Use of COCPs, however, varies widely by country, age, education, and marital status. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marital situation, career or work considerations, financial situations. If sexually active, family planning may involve the use of contraception and other techniques to control the timing of reproduction. Family planning has been of practice since the 16th century by the people of Djenné in West Africa, when physicians advised women to space their births at three-year intervals. Others aspects of family planning aside from contraception include sex education, prevention and management of sexually transmitted infections, pre-conception counseling and management, and infertility management.World Health Organization. (n.d.)Sexual and Reproductive Health Retrieved on 30 October 2019. Family planning, as defined by the United Nations and the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormonal Contraceptive
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original hormonal method—the combined oral contraceptive pill—was first marketed as a contraceptive in 1960. In the ensuing decades many other delivery methods have been developed, although the oral and injectable methods are by far the most popular. Hormonal contraception is highly effective: when taken on the prescribed schedule, users of steroid hormone methods experience pregnancy rates of less than 1% per year. Perfect-use pregnancy rates for most hormonal contraceptives are usually around the 0.3% rate or less. Currently available methods can only be used by women; the development of a male hormonal contraceptive is an active research area. There are two main types of hormonal contraceptive formulations: ''combined methods'' which co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Device
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversible birth control (LARC). One study found that female family planning providers choose LARC methods more often (41.7%) than the general public (12.1%). Among birth control methods, IUDs, along with other contraceptive implants, result in the greatest satisfaction among users. IUDs are safe and effective in adolescents as well as those who have not previously had children. Once an IUD is removed, even after long-term use, fertility returns to normal rapidly. Copper devices have a failure rate of about 0.8% while hormonal ( levonorgestrel) devices fail about 0.2% of the time within the first year of use. In comparison, male sterilization and male condoms have a failure rate of about 0.15% and 15%, respectively. Copper IUDs can also be u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-acting Reversible Birth Control
Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARC) are methods of birth control that provide effective contraception for an extended period without requiring user action. They include injections, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and subdermal contraceptive implants. They are the most effective reversible methods of contraception because their efficacy is not reliant on patient compliance. The typical use failure rates of IUDs and implants, less than 1% per year, are about the same as perfect use failure rates. LARCS are convenient, enjoyable and cost effective. Typically, users save thousands of dollars over a five-year period compared to those who buy condoms and birth control pills. About 15.5% of women worldwide use IUDs, and 3.4% use subdermal implants. LARCS are recommended to adolescents to decrease the teen pregnancy rate. They work in women of any age and number of births. Women may consider family planning advice beforehand. Methods LARC methods include IUDs and the subderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Education
Sex education, also known as sexual education, sexuality education or sex ed, is the instruction of issues relating to human sexuality, including emotional relations and responsibilities, human sexual anatomy, sexual activity, sexual reproduction, age of consent, reproductive health, reproductive rights, sexual health, safe sex and birth control. Sex education which includes all of these issues is known as comprehensive sex education, and is often opposed to abstinence-only sex education, which only focuses on sexual abstinence. Sex education may be provided by parents or caregivers or as part at school programs and public health campaigns. In some countries it is known as Relationships and Sexual health education. History In many cultures, the discussion of all sexual issues has traditionally been considered taboo, and adolescents were not given any information on sexual matters. Such instruction, as was given, was traditionally left to a child's parents, and oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (contraceptive)
The diaphragm is a barrier method of birth control. It is moderately effective, with a one-year failure rate of around 12% with typical use. It is placed over the cervix with spermicide before sex and left in place for at least six hours after sex. Fitting by a healthcare provider is generally required. Side effects are usually very few. Use may increase the risk of bacterial vaginosis and urinary tract infections. If left in the vagina for more than 24 hours toxic shock syndrome may occur. While use may decrease the risk of sexually transmitted infections, it is not very effective at doing so. There are a number of types of diaphragms with different rim and spring designs. They may be made from latex, silicone, or natural rubber. They work by blocking access to and holding spermicide near the cervix. The diaphragm came into use around 1882. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical use Before inserting or removing a diaphragm, one's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
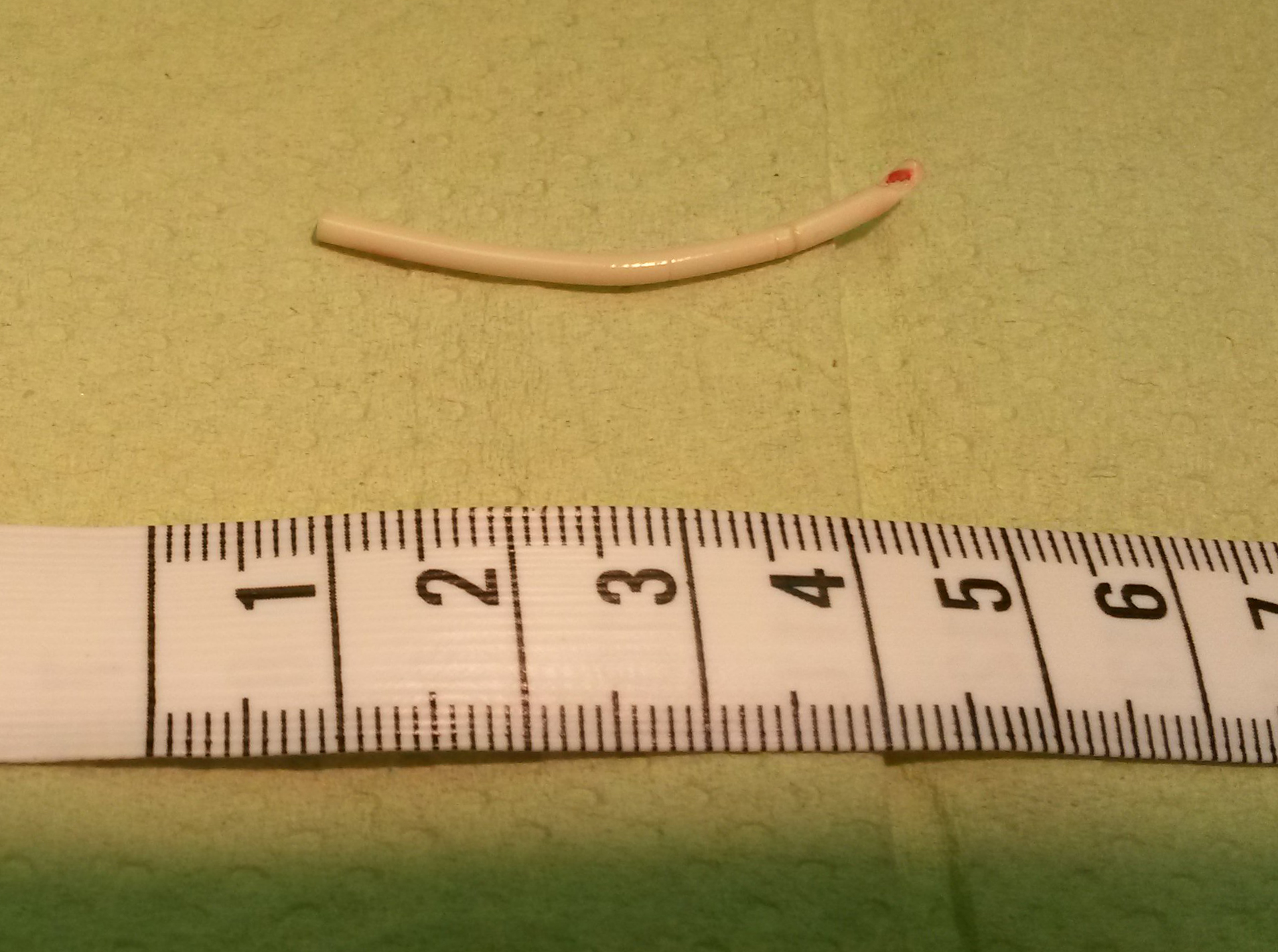
Contraceptive Implant
A contraceptive implant is an implantable medical device used for the purpose of birth control. The implant may depend on the timed release of hormones to hinder ovulation or sperm development, the ability of copper to act as a natural spermicide within the uterus, or it may work using a non-hormonal, physical blocking mechanism. As with other contraceptives, a contraceptive implant is designed to prevent pregnancy, but it does not protect against sexually transmitted infections. Women Implant The contraceptive implant is hormone-based and highly effective, approved in more than 60 countries and used by millions of women around the world. The typical implant is a small flexible tube measuring about 40mm in length. It is most commonly inserted subdermally in the inner portion of the upper, non-dominant arm by a trained and certified health care provider. After insertion, it prevents pregnancy by releasing progestin which inhibits ovulation. The two most common versions are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teenage Pregnancy
Teenage pregnancy, also known as adolescent pregnancy, is pregnancy in a female adolescent or young adult under the age of 20. This includes those who are legally considered adults in their country. The WHO defines adolescence as the period between the ages of 10 and 19 years. Pregnancy can occur with sexual intercourse after the start of ovulation, which can be before the first menstrual period (menarche) but usually occurs after the onset of periods. In well-nourished girls, the first period usually takes place around the age of 12 or 13. Pregnant teenagers face many of the same pregnancy related issues as other women. There are additional concerns for those under the age of 15 as they are less likely to be physically developed to sustain a healthy pregnancy or to give birth. For girls aged 15–19, risks are associated more with socioeconomic factors than with the biological effects of age. Risks of low birth weight, premature labor, anemia, and pre-eclampsia are not c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teenage Pregnancies
Teenage pregnancy, also known as adolescent pregnancy, is pregnancy in a female adolescent or young adult under the age of 20. This includes those who are legally considered adults in their country. The WHO defines adolescence as the period between the ages of 10 and 19 years. Pregnancy can occur with sexual intercourse after the start of ovulation, which can be before the first menstrual period (menarche) but usually occurs after the onset of periods. In well-nourished girls, the first period usually takes place around the age of 12 or 13. Pregnant teenagers face many of the same pregnancy related issues as other women. There are additional concerns for those under the age of 15 as they are less likely to be physically developed to sustain a healthy pregnancy or to give birth. For girls aged 15–19, risks are associated more with socioeconomic factors than with the biological effects of age. Risks of low birth weight, premature labor, anemia, and pre-eclampsia are not c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |