|
Climatology
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "place, zone"; and , '' -logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. This modern field of study is regarded as a branch of the atmospheric sciences and a subfield of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology now includes aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry. The main methods employed by climatologists are the analysis of observations and modelling of the physical processes that determine the climate. The main topics of research are the study of climate variability, mechanisms of climate changes and modern climate change. Basic knowledge of climate can be used within shorter term weather forecasting, for instance about climatic cycles such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO), the North Atlantic oscillation (NAO), the Arctic oscillation (AO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude/ longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme was the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Variability
Climate variability includes all the variations in the climate that last longer than individual weather events, whereas the term climate change only refers to those variations that persist for a longer period of time, typically decades or more. ''Climate change'' may refer to any time in Earth's history, but the term is now commonly used to describe contemporary climate change. Since the Industrial Revolution, the climate has increasingly been affected by human activities. The climate system receives nearly all of its energy from the sun and radiates energy to outer space. The balance of incoming and outgoing energy and the passage of the energy through the climate system is Earth's energy budget. When the incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy, Earth's energy budget is positive and the climate system is warming. If more energy goes out, the energy budget is negative and Earth experiences cooling. The energy moving through Earth's climate system finds expression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Geography
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. This focus is in contrast with the branch of human geography, which focuses on the built environment, and technical geography, which focuses on using, studying, and creating tools to obtain,analyze, interpret, and understand spatial information. The three branches have significant overlap, however. Sub-branches Physical geography can be divided into several branches or related fields, as follows: * Geomorphology is concerned with understanding the surface of the Earth and the processes by which it is shaped, both at the present as well as in the past. Geomorphology as a field has several sub-fields that deal with the specific landforms of various environments e.g. desert geomorphology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Sciences
Atmospheric science is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study of atmospheric changes (both long and short-term) that define average climates and their change over time, due to both natural and anthropogenic climate variability. Aeronomy is the study of the upper layers of the atmosphere, where dissociation and ionization are important. Atmospheric science has been extended to the field of planetary science and the study of the atmospheres of the planets and natural satellites of the Solar System. Experimental instruments used in atmospheric science include satellites, rocketsondes, radiosondes, weather balloons, radars, and lasers. The term aerology (from Greek ἀήρ, ''aēr'', " air"; and -λογία, '' -logia'') is sometimes used as an alternative term for the study of Earth's atmosph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres, namely biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. Earth science encompasses four main branches of study, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields. There are both reductionist and holistic approaches to Earth sciences. It is also the study of Earth and its neighbors in space. Some Earth scientists use their knowledge of the planet to locate and develop energy and mineral resources. Others study the impact of human activity on Earth's environment, and design methods to protect the planet. Some use their knowledge about Earth proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Model
Numerical climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the important drivers of climate, including atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate. Climate models may also be qualitative (i.e. not numerical) models and also narratives, largely descriptive, of possible futures. Quantitative climate models take account of incoming energy from the sun as short wave electromagnetic radiation, chiefly visible and short-wave (near) infrared, as well as outgoing long wave (far) infrared electromagnetic. An imbalance results in a change in temperature. Quantitative models vary in complexity. For example, a simple radiant heat transfer model treats the earth as a single point and averages outgoing energy. This can be expanded vertically (radiative-convective models) and/or horizontally. Coupled atmosphere–ocean–sea ice global climate model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and the geology of the sea floor; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers utilize to glean further knowledge of the world ocean, including astronomy, biology, chemistry, climatology, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past. An oceanographer is a person who studies many matters concerned with oceans, including marine geology, physics, chemistry and biology. History Early history Humans first acquired knowledge of the waves and currents of the seas and oceans in pre-historic times. Observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Model
Numerical climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the important drivers of climate, including atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate. Climate models may also be qualitative (i.e. not numerical) models and also narratives, largely descriptive, of possible futures. Quantitative climate models take account of incoming energy from the sun as short wave electromagnetic radiation, chiefly visible and short-wave (near) infrared, as well as outgoing long wave (far) infrared electromagnetic. An imbalance results in a change in temperature. Quantitative models vary in complexity. For example, a simple radiant heat transfer model treats the earth as a single point and averages outgoing energy. This can be expanded vertically (radiative-convective models) and/or horizontally. Coupled atmosphere–ocean–sea ice global climate model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is an irregular periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics. The warming phase of the sea temperature is known as ''El Niño'' and the cooling phase as '' La Niña''. The ''Southern Oscillation'' is the accompanying atmospheric component, coupled with the sea temperature change: ''El Niño'' is accompanied by high air surface pressure in the tropical western Pacific and ''La Niña'' with low air surface pressure there. The two periods last several months each and typically occur every few years with varying intensity per period. The two phases relate to the Walker circulation, which was discovered by Gilbert Walker during the early twentieth century. The Walker circulation is caused by the pressure gradient force that results from a high-pressure area over the eastern Pacific Ocean, and a low-pressure system over Indonesia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land, and ocean and using meteorology to project how the atmosphere will change at a given place. Once calculated manually based mainly upon changes in barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky condition or cloud cover, weather forecasting now relies on computer-based models that take many atmospheric factors into account. Human input is still required to pick the best possible forecast model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and knowledge of model biases. The inaccuracy of forecasting is due to the chaotic nature of the atmosphere, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
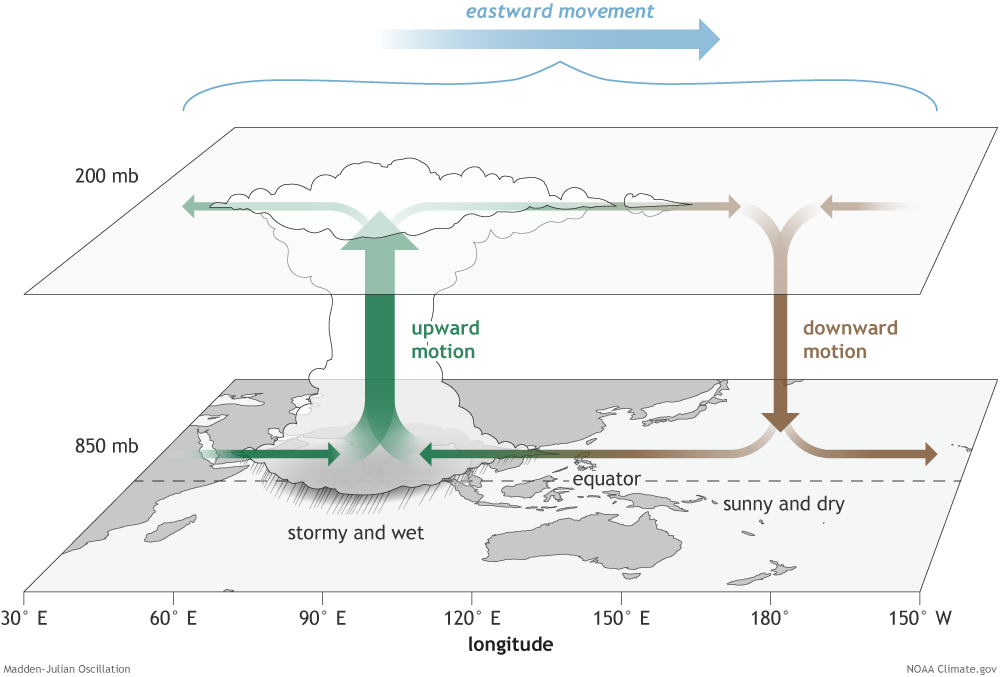
Madden–Julian Oscillation
The Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO) is the largest element of the intraseasonal (30- to 90-day) variability in the tropical atmosphere. It was discovered in 1971 by Roland Madden and Paul Julian of the American National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is a large-scale coupling between atmospheric circulation and tropical deep atmospheric convection. Unlike a standing pattern like the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Madden–Julian oscillation is a traveling pattern that propagates eastward, at approximately , through the atmosphere above the warm parts of the Indian and Pacific oceans. This overall circulation pattern manifests itself most clearly as anomalous rainfall. The Madden–Julian oscillation is characterized by an eastward progression of large regions of both enhanced and suppressed tropical rainfall, observed mainly over the Indian and Pacific Ocean. The anomalous rainfall is usually first evident over the western Indian Ocean, and remains ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo (; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁),Yao (2003), 544. was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman of the Song dynasty (960–1279). Shen was a master in many fields of study including mathematics, optics, and horology. In his career as a civil servant, he became a finance minister, governmental state inspector, head official for the Bureau of Astronomy in the Song court, Assistant Minister of Imperial Hospitality, and also served as an academic chancellor.Needham (1986), Volume 4, Part 2, 33. At court his political allegiance was to the Reformist faction known as the New Policies Group, headed by Chancellor Wang Anshi (1021–1085). In his ''Dream Pool Essays'' or ''Dream Torrent Essays'' (; ''Mengxi Bitan'') of 1088, Shen was the first to describe the magnetic needle compass, which would be used for navigation (first described in Europe by Alexander Neckam in 1187).Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)