|
Chlamydomonas
''Chlamydomonas'' is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 speciesSmith, G.M. 1955 ''Cryptogamic Botany Volume 1. Algae and Fungi'' McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". ''Chlamydomonas'' is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of ''Chlamydomonas'' is that it contains ion channels ( channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of ''Chlamydomonas'' are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains. Molecular phylogeny studies indicated that the traditional genus ''Chlamydomonas'' as defined using morphological data was polyphyletic within Volvocales. Many species were subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
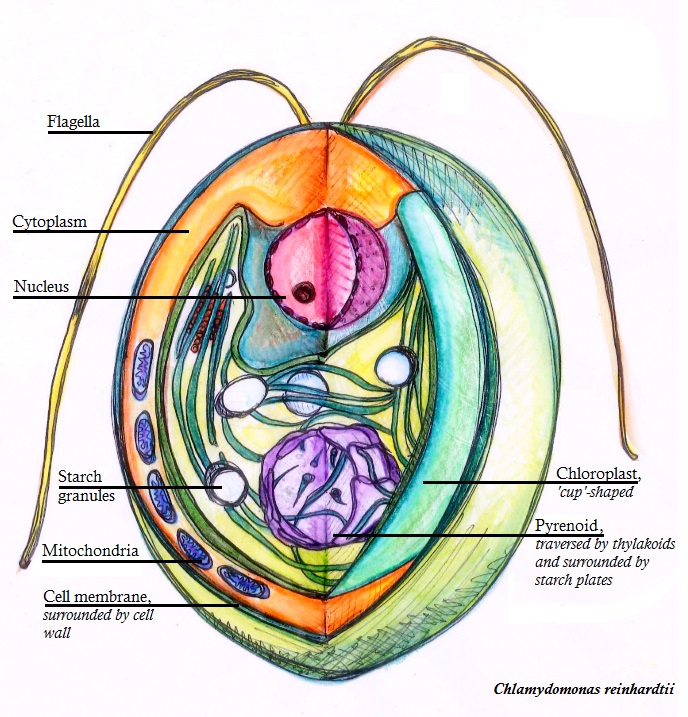
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot that senses light. ''Chlamydomonas'' species are widely distributed worldwide in soil and fresh water. ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is an especially well studied biological model organism, partly due to its ease of culturing and the ability to manipulate its genetics. When illuminated, ''C. reinhardtii'' can grow photoautotrophically, but it can also grow in the dark if supplied with organic carbon. Commercially, ''C. reinhardtii'' is of interest for producing biopharmaceuticals and biofuel, as well being a valuable research tool in making hydrogen. History The ''C. reinhardtii'' wild-type laboratory strain c137 (mt+) originates from an isolate collected near Amherst, Massachusetts, in 1945 by Gilbert M. Smith. The species' name ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas Caudata
''Chlamydomonas'' is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 speciesSmith, G.M. 1955 ''Cryptogamic Botany Volume 1. Algae and Fungi'' McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". ''Chlamydomonas'' is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of ''Chlamydomonas'' is that it contains ion channels ( channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of ''Chlamydomonas'' are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains. Molecular phylogeny studies indicated that the traditional genus ''Chlamydomonas'' as defined using morphological data was polyphyletic within Volvocales. Many species were subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Vector Scheme
''Chlamydomonas'' is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 speciesSmith, G.M. 1955 ''Cryptogamic Botany Volume 1. Algae and Fungi'' McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". ''Chlamydomonas'' is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of ''Chlamydomonas'' is that it contains ion channels ( channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of ''Chlamydomonas'' are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains. Molecular phylogeny studies indicated that the traditional genus ''Chlamydomonas'' as defined using morphological data was polyphyletic within Volvocales. Many species were subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas EPA
''Chlamydomonas'' is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 speciesSmith, G.M. 1955 ''Cryptogamic Botany Volume 1. Algae and Fungi'' McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". ''Chlamydomonas'' is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of ''Chlamydomonas'' is that it contains ion channels ( channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of ''Chlamydomonas'' are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains. Molecular phylogeny studies indicated that the traditional genus ''Chlamydomonas'' as defined using morphological data was polyphyletic within Volvocales. Many species were subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas Globosa - 400x (13263097835)
''Chlamydomonas'' is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 speciesSmith, G.M. 1955 ''Cryptogamic Botany Volume 1. Algae and Fungi'' McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". ''Chlamydomonas'' is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of ''Chlamydomonas'' is that it contains ion channels ( channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of ''Chlamydomonas'' are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains. Molecular phylogeny studies indicated that the traditional genus ''Chlamydomonas'' as defined using morphological data was polyphyletic within Volvocales. Many species were subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas Nivalis
''Chlamydomonas nivalis'', also referred to as ''Chloromonas typhlos'', is a unicellular red-coloured photosynthetic green alga that is found in the snowfields of the alps and polar regions all over the world. They are one of the main algae responsible for causing the phenomenon of watermelon snow (also ''blood snow'', ''raspberry snow''), where patches of snow appear red or pink. The first account of microbial communities that form red snow was made by Aristotle. Researchers have been active in studying this organism for over 100 years. Although ''C. nivalis'' is closely related to ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'', the environmental conditions each species inhabits are very different. ''C. nivalis'' can be found in mountains, snowfields, and polar regions around the world. The habitat of ''C. nivalis'' subjects the cells to environmental extremes including limited nutrients, low temperatures, and intense sunlight. In comparison with the mesophilic ''C. reinhardtii'', ''C. nivalis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channelrhodopsins
Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes (see optogenetics). Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants that are sensitive to different colors of light or selective for specific ions (ACRs, KCRs) have been cloned from other species of algae and protists. History Phototaxis and photoorientation of microalgae have been studied over more than hundred years in many laboratories worldwide. In 1980, Ken Foster developed the first consistent theory about the functionality of algal eyes. He also analyzed published action ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Euk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLU (plant Gene)
Protochlorophyllide,KEGG compound database entr/ref> or monovinyl protochlorophyllide, is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of chlorophyll ''a''. It lacks the phytol side-chain of chlorophyll and the reduced pyrrole in ring D. Protochlorophyllide is highly fluorescent; mutants that accumulate it glow red if irradiated with blue light.Meskauskiene R, Nater M, Goslings D, Kessler F, op den Camp R, Apel K. FLU: a negative regulator of chlorophyll biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001; 98(22):12826-3pdf In angiosperms, the later steps which convert protochlorophyllide to chlorophyll are light-dependent, and such plants are pale ( chlorotic) if grown in the darkness. Gymnosperms, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria have another, light-independent enzyme and grow green in the darkness as well. Conversion to chlorophyll The enzyme that converts protochlorophyllide to chlorophyllide ''a'', the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas Elegans
''Chlamydomonas elegans'' is a species of freshwater green algae The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga .... References External links ''Chlamydomonas elegans'' at AlgaeBase Chlamydomonadaceae Plants described in 1915 {{Chlorophyceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



