|
Catatonia
Catatonia is a complex neuropsychiatric behavioral syndrome that is characterized by abnormal movements, immobility, abnormal behaviors, and withdrawal. The onset of catatonia can be acute or subtle and symptoms can wax, wane, or change during episodes. There are several subtypes of catatonia: akinetic catatonia, excited catatonia, malignant catatonia, delirious mania, and self-injurious behaviors in autism. Although catatonia has historically been related to schizophrenia (catatonic schizophrenia), catatonia is most often seen in mood disorders. It is now known that catatonic symptoms are nonspecific and may be observed in other mental, neurological, and medical conditions. Catatonia is not a stand-alone diagnosis (although some experts disagree), and the term is used to describe a feature of the underlying disorder. Recognizing and treating catatonia is very important as failure to do so can lead to poor outcomes and can be potentially fatal. Treatment with benzodiazepines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autistic Catatonia
Autistic catatonia or catatonic breakdown is a type of disorder that affects roughly 10 percent of all adults with autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disabilities. Most are not severely affected but a few exhibit stupor and severe excitement, which is the most extreme form of the disorder. Full expression of excitement could be a sign of comorbid bipolar disorder but more research is needed. More than 40 symptoms have been identified to be a result of the disorder, but some of the symptoms overlap with those of autism spectrum disorder, making diagnosing difficult even for a seasoned professional. In a few cases stupor and hyperactivity can continue for weeks or even months. During the excitement phase individuals show combativeness and can have delusions and hallucinations and can also pose a danger to themselves or others and can make marked destruction of property. In the later stages of medium and even more in the severe (and, if left untreated, lethal) state they will al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waxy Flexibility
Waxy flexibility is a psychomotor symptom of catatonia as associated with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or other mental disorders which leads to a decreased response to stimuli and a tendency to remain in an immobile posture. Attempts to reposition the patient are met by "slight, even resistance", and after being repositioned, the patient will typically remain in the new position. Waxy flexibility rarely occurs in cases of delirium. The presence of waxy flexibility along with at least two other catatonic symptoms such as stupor or negativism are enough to warrant a diagnosis of catatonia. If one were to move the arm of someone with waxy flexibility, the patient would keep that arm where it had been positioned until moved again, as if positioning malleable wax. Further alteration of an individual's posture is similar to bending a candle. Although waxy flexibility has historically been linked to schizophrenia, there are also other disorders which it may be associated with, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verbigeration
This glossary covers terms found in the psychiatric literature; the word origins are primarily Greek, but there are also Latin, French, German, and English terms. Many of these terms refer to expressions dating from the early days of psychiatry in Europe. A abreaction Abreaction is a process of vividly reliving repressed memories and emotions related to a past event.Hales E and Yudofsky JA, eds, The American Psychiatric Press Textbook of Psychiatry, Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc., 2003 Sigmund Freud used hypnosis to rid his patients of pathological memories through abreaction. abulia Aboulia or Abulia, in neurology, refers to a lack of will or initiative. The individual is unable to act or make decisions independently. The condition may range from subtle to overwhelming in severity. achromatopsia Achromatopsia is a term referring to or acquired agnosia for color. This term includes color blindness. Achromatopsia is a condition characterized by a partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
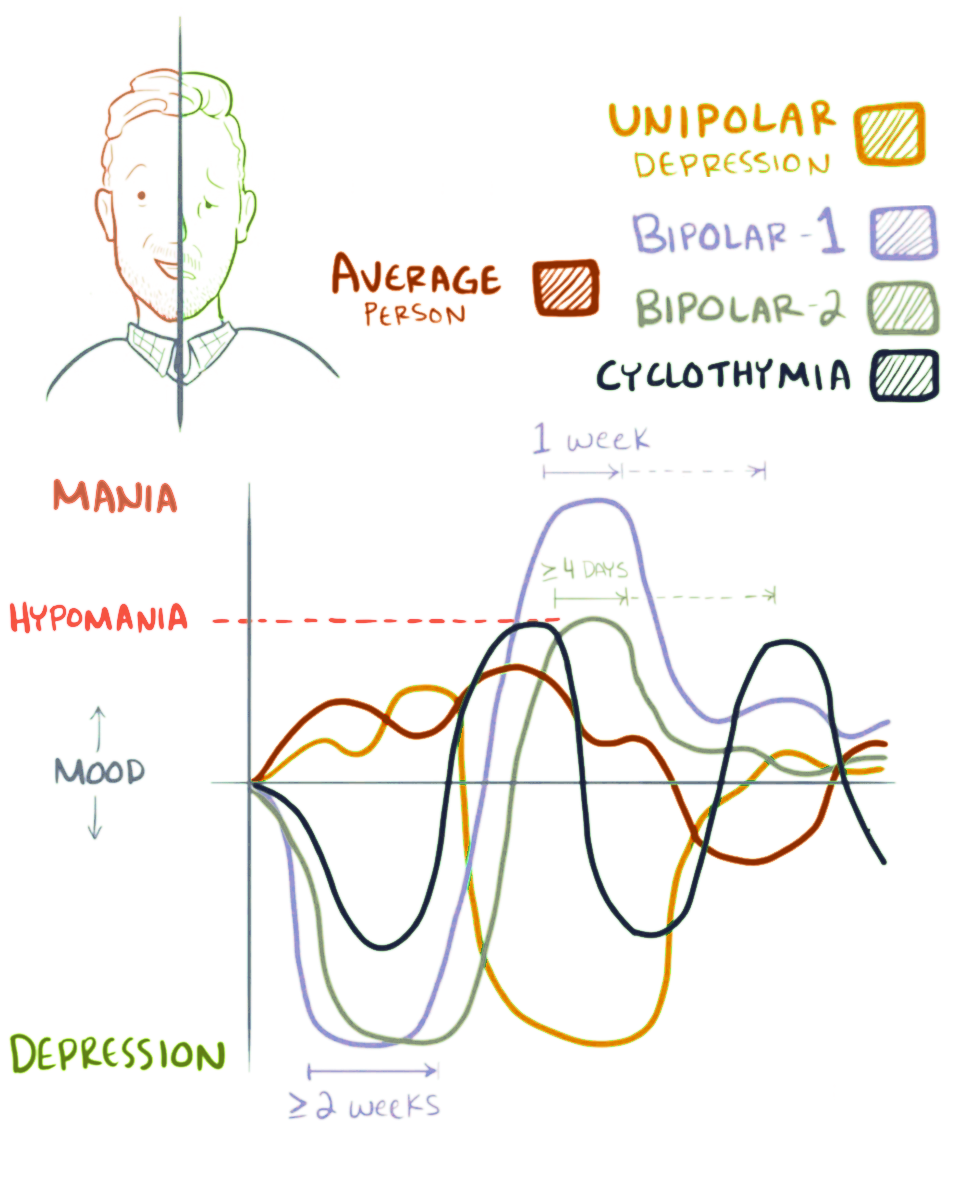
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mood Disorder
A mood disorder, also known as an affective disorder, is any of a group of conditions of mental and behavioral disorder where a disturbance in the person's mood is the main underlying feature. The classification is in the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Mood disorders fall into seven groups, including; abnormally elevated mood, such as mania or hypomania; depressed mood, of which the best-known and most researched is major depressive disorder (MDD) (alternatively known as clinical depression, unipolar depression, or major depression); and moods which cycle between mania and depression, known as bipolar disorder (BD) (formerly known as manic depression). There are several sub-types of depressive disorders or psychiatric syndromes featuring less severe symptoms such as dysthymic disorder (similar to MDD, but longer lasting and more persistent, though often milder) and cyclothymic disorder (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echopraxia
Echopraxia (also known as echokinesis) is the involuntary repetition or imitation of another person's actions. Similar to echolalia, the involuntary repetition of sounds and language, it is one of the echophenomena ("automatic imitative actions without explicit awareness"). It has long been recognized as a core feature of Tourette syndrome, and is considered a complex tic, but it also occurs in autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia and catatonia, aphasia, and disorders involving the startle reflex such as latah. Echopraxia has also been observed in individuals with epilepsy, dementia and autoimmune disorders; the causes of and the link between echopraxia and these disorders is undetermined. The etymology of the term is from Ancient Greek: " ἠχώ (ēkhō) from ἠχή (ēkhē "sound") and " πρᾶξις (praksis, "action, activity, practice)". Characteristics Echopraxia is the involuntary mirroring of an observed action. Imitated actions can range from simple motor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatric treatment where a generalized seizure (without muscular convulsions) is electrically induced to manage refractory mental disorders.Rudorfer, MV, Henry, ME, Sackeim, HA (2003)"Electroconvulsive therapy". In A Tasman, J Kay, JA Lieberman (eds) ''Psychiatry, Second Edition''. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 1865–1901. Typically, 70 to 120 volts are applied externally to the patient's head, resulting in approximately 800 milliamperes of direct current passing between the electrodes, for a duration of 100 milliseconds to 6 seconds, either from temple to temple (bilateral ECT) or from front to back of one side of the head (unilateral ECT). However, only about 1% of the electrical current crosses the bony skull into the brain because skull impedance is about 100 times higher than skin impedance. The ECT procedure was first conducted in 1938 by Italian psychiatrist Ugo Cerletti and rapidly replaced less safe and effective forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a rare but life-threatening reaction that can occur in response to neuroleptic or antipsychotic medication. Symptoms include high fever, confusion, rigid muscles, variable blood pressure, sweating, and fast heart rate. Complications may include rhabdomyolysis, high blood potassium, kidney failure, or seizures. Any medications within the family of neuroleptics can cause the condition, though typical antipsychotics appear to have a higher risk than atypicals, specifically first generation antipsychotics like haloperidol. Onset is often within a few weeks of starting the medication but can occur at any time. Risk factors include dehydration, agitation, and catatonia. Rapidly decreasing the use of levodopa or other dopamine agonists, such as pramipexole, may also trigger the condition. The underlying mechanism involves blockage of dopamine receptors. Diagnosis is based on symptoms. Management includes stopping the triggering medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalepsy
Catalepsy (from Ancient Greek , , "seizing, grasping") is a nervous condition characterized by muscular rigidity and fixity of posture regardless of external stimuli, as well as decreased sensitivity to pain. Signs and symptoms Symptoms include a rigid body, rigid limbs, limbs staying in same position when moved (waxy flexibility), no response, loss of muscle control, and slowing down of bodily functions, such as breathing. Causes Catalepsy is a symptom of certain nervous disorders or conditions such as Parkinson's disease and epilepsy. It is also a characteristic symptom of cocaine withdrawal, as well as one of the features of catatonia. It can be caused by schizophrenia treatment with anti-psychotics, such as haloperidol, and by the anesthetic ketamine. Protein kinase A has been suggested as a mediator of cataleptic behavior. Unsuggested waxy catalepsy, sometimes accompanied by spontaneous anesthesia, is seen as an indicator of hypnotic trance. Suggested or induced r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboulia
In neurology, abulia, or aboulia (from grc, βουλή, meaning "will"),Bailly, A. (2000). Dictionnaire Grec Français, Éditions Hachette. refers to a lack of will or initiative and can be seen as a ''disorder of diminished motivation'' (''DDM''). Abulia falls in the middle of the spectrum of diminished motivation, with apathy being less extreme and akinetic mutism being more extreme than abulia.Marin, R. S., & Wilkosz, P. A. (2005)Disorders of diminished motivation. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 20(4), 377-388. The condition was originally considered to be a disorder of the will,Berrios G.E. and Gili M. (1995) Abulia and impulsiveness revisited. ''Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica'' 92: 161-167 and aboulic individuals are unable to act or make decisions independently; and their condition may range in severity from subtle to overwhelming. In the case of akinetic mutism, many patients describe that as soon as they "will" or attempt a movement, a "counter-will" or "resistance" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizoaffective Disorder
Schizoaffective disorder (SZA, SZD or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and an unstable mood. This diagnosis is made when the person has symptoms of both schizophrenia (usually psychosis) and a mood disorder: either bipolar disorder or depression. The main criterion for a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder is the presence of psychotic symptoms for at least two weeks without any mood symptoms present. Schizoaffective disorder can often be misdiagnosed when the correct diagnosis may be psychotic depression, bipolar I disorder, schizophreniform disorder, or schizophrenia. It is imperative for providers to accurately diagnose patients, as treatment and prognosis differ greatly for most of these diagnoses. There are three forms of schizoaffective disorder: bipolar (or manic) type (marked by symptoms of schizophrenia and mania), depressive type (marked by symptoms of schizophrenia and depression), and mixed type (marked by symptoms of schizop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Functions
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence (e.g., reasoning and problem-solving). Executive functions gradually develop and change across the lifespan of an individual and can be improved at any time over the course of a person's life. Similarly, these cognitive processes can be adversely affected by a variety of events which affect an individual. Both neuropsychological tests (e.g., the St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |