|
Campanians
{{Short description, Ancient Italic tribe The Campanians (also Campani) were an ancient Italic tribe, part of the Osci nation, speaking an Oscan language. Descending from the Apennines, the proto-Osci settled in the areas of present-day Campania at the beginning of the 1st millennium BC, or even before. They established themselves there over a previous Italic population of possible Latino-Faliscan origin. The Opici, Ausones and Aurunci were later linguistically and culturally Oscanized. From the 7th to the 5th century BC, Greek colonists submitted or expelled them from the area, but starting from the mid of the 5th century BC, the Osci reconquered many cities on the coasts of present-day Province of Caserta, Naples and Low Latium as also most of the inland.Diodorus Siculus, XII.31. Amongst those reconquered cities there were Cumae (taken from the Greeks) and Capua (from the Etruscans). From the Greeks and the Etruscans the Osci learnt of the institution of the ''Polis'', soo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samnite Wars
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe. * The first of these wars was the result of Rome's intervention to rescue the Campanian city of Capua from a Samnite attack. * The second one was the result of Rome's intervention in the politics of the city of Naples and developed into a contest over the control of central and southern Italy. * Similarly the third war also involved a struggle for control of this part of Italy. The wars extended over half a century, and also drew in the peoples to the east, north, and west of Samnium (land of the Samnites) as well as those of central Italy north of Rome (the Etruscans, Umbri, and Picentes) and the Senone Gauls, but at different times and levels of involvement. Background By the time of the First Samnite War (343 BC), the southwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osci
The Osci (also called Oscans, Opici, Opsci, Obsci, Opicans) were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the language of the Samnites was called Oscan, the Samnites were never referred to as Osci, nor were the Osci called Samnites. Traditions of the Opici fall into the legendary period of Italian history, roughly from the beginning of the first millennium BC until the foundation of the Roman Republic. No consensus can be reached concerning their location and language. By the end of this period, the Oscan language had evolved and was spoken by a number of sovereign tribal states. By far the most important of these in terms of military prowess and wealth was the Samnites, who rivalled Rome for about 50 years in the second half of the 4th century BC, sometimes being allies, and sometimes at war with the city, until they were finally subdued with considera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy. An Oscan-speaking people, who may have originated as an offshoot of the Sabines, they formed a confederation consisting of four tribes: the Hirpini, Caudini, Caraceni, and Pentri. Although allied together against the Gauls in 354 BC, they later became enemies of the Romans and fought them in a series of three wars. Despite an overwhelming victory at the Battle of the Caudine Forks (321 BC), the Samnites were subjugated in 290 BC. Although severely weakened, the Samnites would still side against the Romans, first in the Pyrrhic War and then with Hannibal in the Second Punic War. They also fought in the Social War and later in Sulla's civil war as allies of the Roman consuls Papirius Carbo and Gaius Marius against Sulla, who defeated them and their leader Pontius Telesinus at the Battle of the Colline Gate (82 BC). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Italic Peoples
This list of ancient Italic peoples includes names of Indo-European peoples speaking Italic languages or otherwise considered Italic in sources from the late early 1st millennium BC to the early 1st millennium AD. Ancestors *Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers) ** Proto-Italics (Proto-Italic speakers) Latino-Faliscans * Falisci ** Capenates (in Capena and Ager Capenas, Capena land) **Falerii (in Falerii and Ager Faliscus) ** Sardinia Falisci (in and around Peronia, northeastern Sardinia) *Aborigines (mythology) (Casci Latini) - Latium Sicels **Prisci Latini (Old Latins) (according to tradition and legend they were formed by the merger of Aborigines and Latium Sicels) *** Latini (Latins (Italic tribe)) **** Abolani **** Aesulani **** Acienses **** Albans ( Albani) ( Populi Albenses) (in Alba Longa Land, between the modern-day Lake Albano and Monte Cavo) **** Antemnates (in Antemnae) (sometimes regarded as Sabines) **** Bolani / Bovillani **** Bubetani * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Peoples Of Italy
This list of ancient peoples living in Italy summarises groupings existing before and during the Roman expansion and conquest of Italy. Many of the names are either scholarly inventions or exonyms assigned by the ancient writers of works in ancient Greek and Latin. In regard to the specific names of particular ancient Italian tribes and peoples, the time-window in which historians know the historical ascribed names of ancient Italian peoples mostly falls into the range of about 750 BC (at the legendary foundation of Rome) to about 200 BC (in the middle Roman Republic), the time range in which most of the written documentation first exists of such names and prior to the nearly complete assimilation of Italian peoples into Roman culture. Nearly all of these peoples and tribes spoke Indo-European languages: Italics, Celts, Ancient Greeks, and tribes likely occupying various intermediate positions between these language groups. On the other hand, some Italian peoples (such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
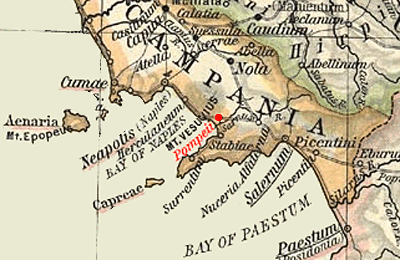
Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-72 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €108 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €18,600 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2018) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.845 · 19th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITF , website ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ausones
"Ausones" (; ), the original Greek form for the Latin "Aurunci", was a name applied by Greek writers to describe various Italic peoples inhabiting the southern and central regions of Italy. The term was used, specifically, to denote the particular tribe which Livy called the Aurunci, but later it was applied to all Italians, and Ausonia became a poetic term, in Greek and Latin, for Italy itself. Usage The usage, by ancient writers, in regard to national appellations is very vague and fluctuating, perhaps in no instance more so than in the case of the Ausones or Ausonians. As synonymous with "Aurunci" Originally "Aurunci" was the appellation given by the Romans to the people called "Ausones" by the Greeks: indeed, the two names are merely different forms of the same, as the letter "r" was a common variation for "s" in Latin (Aurunci = Auronici = Auruni = Ausuni). The identity of the two is distinctly asserted by Servius, and clearly implied by Cassius Dio, where he says tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurunci
The Aurunci were an Italic tribe that lived in southern Italy from around the 1st millennium BC. They were eventually defeated by Rome and subsumed into the Roman Republic during the second half of the 4th century BC. Identity Aurunci is the name given by Roman writers to an ancient race or nation of Italy. It appears that "Aurunci" was the appellation the Romans gave to the people called "Ausones" by the Greeks. One form might be derived from the other by rhotacism (corruption of sound "s" in "r") (Ausoni > Auroni > Auronici > Aurunci). The identity of the two is distinctly asserted by Servius, and clearly implied by Cassius Dio, where he says that the name of Ausonia was properly applied only to the land of the Auruncans, between the Volscians and the Campanians. In like manner, Festus makes the mythical hero Auson the founder of the city of Aurunea. Servius terms the Aurunci one of the most ancient nations of Italy. They appear to have been much more powerful and widely s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osco Diffusione
The National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC) ( fa, شرکت ملی مناطق نفتخیز جنوب ایران, ''Shirkat-e Mily-e Minatâq-e Nuftxiz-e Jinvâb-e Iran'') is a government-owned corporation under the direction of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran, and operates as a subsidiary of National Iranian Oil Company. NISOC is incorporated 1971 in Masjed Soleyman, Khouzestan as Oil Service Company of Iran (OSCO). Currently NISOC is Iran's biggest oil producer, and produce 3 million barrels of oil per day. the company is active in a land area more than 400,000 km2 with headquarters in Ahvaz. NISOC is producing about 83% of all crude oil and 17% of natural gas produced in Iran and ranks as the Iran's biggest oil company. National Iranian South Oilfields Company, through its subsidiaries, produces crude oil, gas, and liquefied gases. The company's reserves portfolio include Ahvaz Field (the world's 3rd largest oil field) and in charge of onshore giant oilfields in Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain. History Ancient era The name of Capua comes from the Etruscan ''Capeva''. The meaning is 'City of Marshes'. Its foundation is attributed by Cato the Elder to the Etruscans, and the date given as about 260 years before it was "taken" by Rome. If this is true it refers not to its capture in the Second Punic War (211 BC) but to its submission to Rome in 338 BC, placing the date of foundation at about 600 BC, while Etruscan power was at its highest. In the area several settlements of the Villanovian civilization were present in prehistoric times, and these were probably enlarged by the Oscans and subsequently by the Etruscans. Etruscan supremacy in Campania came to an end with the Samnite invasion in the latter half of the 5th century BC. About 424 BC it was captured by the Samnites and in 343 BC b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regio I Latium Et Campania
Regio (pl. ''regiones'') is the Latin word for ‘region’ and the Italian word for ‘royal’ It may refer to: *Regiopolis, a concept for urban centers in between metropolitan areas. Ancient toponymy * Regiones of Augustan Italy, the departments in which Roman Emperor Augustus divided Italy. *14 regions of the Augustan Rome, in ancient Rome as a name for quartiers of the city of Rome *14 regions of Medieval Rome, resulting from the redivision of the Rome after the revolution of 1143 *Regio, in ancient Constantinople as a name for the 14 quarters of the city of Constantinople, defined in analogy with those of Rome * Regio Aromatica, name for the Horn of Africa *''Regiones'', administrative subdivisions of the kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England Astronomy * Regio (astronomy), which, in planetary geology, is a large area of a planet or moon that is strongly differentiated in colour or albedo **A regio of Venus: *** Alpha Regio *** Asteria Regio *** Beta Regio *** Ovda Regio **A regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ager Campanus
Ancient Campania (often also identified as Campania Felix or ager Campanus) originally indicated the territory of the ancient city of Capua in the Roman period, and later also the plains of the various neighboring municipalities. It was a very large territory when compared with the other Italic cities of the Roman and pre-Roman period. It extended from the slopes of Mount Massico (to the north) up to the Phlegraean Fields and the Vesuvian area to the south. Initially it also included the '' ager Falernus'', then it was heavily downsized by Rome due to the alliance of the city of Capua with Hannibal. The main inhabited centers of this historical region were (from north to south) Capua, Atella, Liternum, Cumae, Baiae, Puteoli, Acerrae, Nola, Neapolis, Caprae, Oplontis, Pompei Pompei (; nap, Pumpeje, ) or Pompeii (, as in the name of the ancient city) is a city and commune in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Italy, home of the ancient Roman ruins of Pompeii that are part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |