|
Buried Treasure
Buried treasure is a literary trope commonly associated with depictions of pirates, criminals, and Old West outlaws. According to popular conception, these people often buried their stolen fortunes in remote places, intending to return to them later (often with the use of a pirates treasure map). Pirates Pirates burying treasure was rare. The only pirate known to have actually buried treasure was William Kidd, who is believed to have buried at least some of his wealth on Gardiners Island near Long Island before sailing into New York City. Kidd had originally been commissioned as a privateer for England, but his behavior had strayed into outright piracy, and he hoped that his treasure could serve as a bargaining chip in negotiations to avoid punishment. His bid was unsuccessful, however, and Kidd was hanged as a pirate. In English fiction there are three well-known stories that helped to popularize the myth of buried pirate treasure: '' Wolfert Webber'' (1824) by Washington Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyle Pirates Burying2
Pyle ( cy, Y Pîl) is a village and community (and electoral ward) in Bridgend county borough, Wales. This large village is served by the A48 road, and lies less than one mile from Junction 37 of the M4 motorway, and is therefore only a half-hour journey from the capital city of Wales, Cardiff. The nearest town is the seaside resort of Porthcawl. Within the Community, to the northeast of Pyle, is the adjoining settlement of Kenfig Hill, North Cornelly also adjoins Pyle and the built-up area had a population of 13,701 in 2011. Etymology The English name "Pyle" is derived from the Welsh '' Pîl'', meaning a tidal inlet of the sea, this localised toponym is found along the coast of South Wales, from Pembrokeshire and into Somerset. In this instance it may refer to the mouth of the River Kenfig, which is tidal for its first mile from the sea. A commonly stated, but erroneous derivation from the English word "pile" (a stake) is highly unlikely, with the only settlement in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
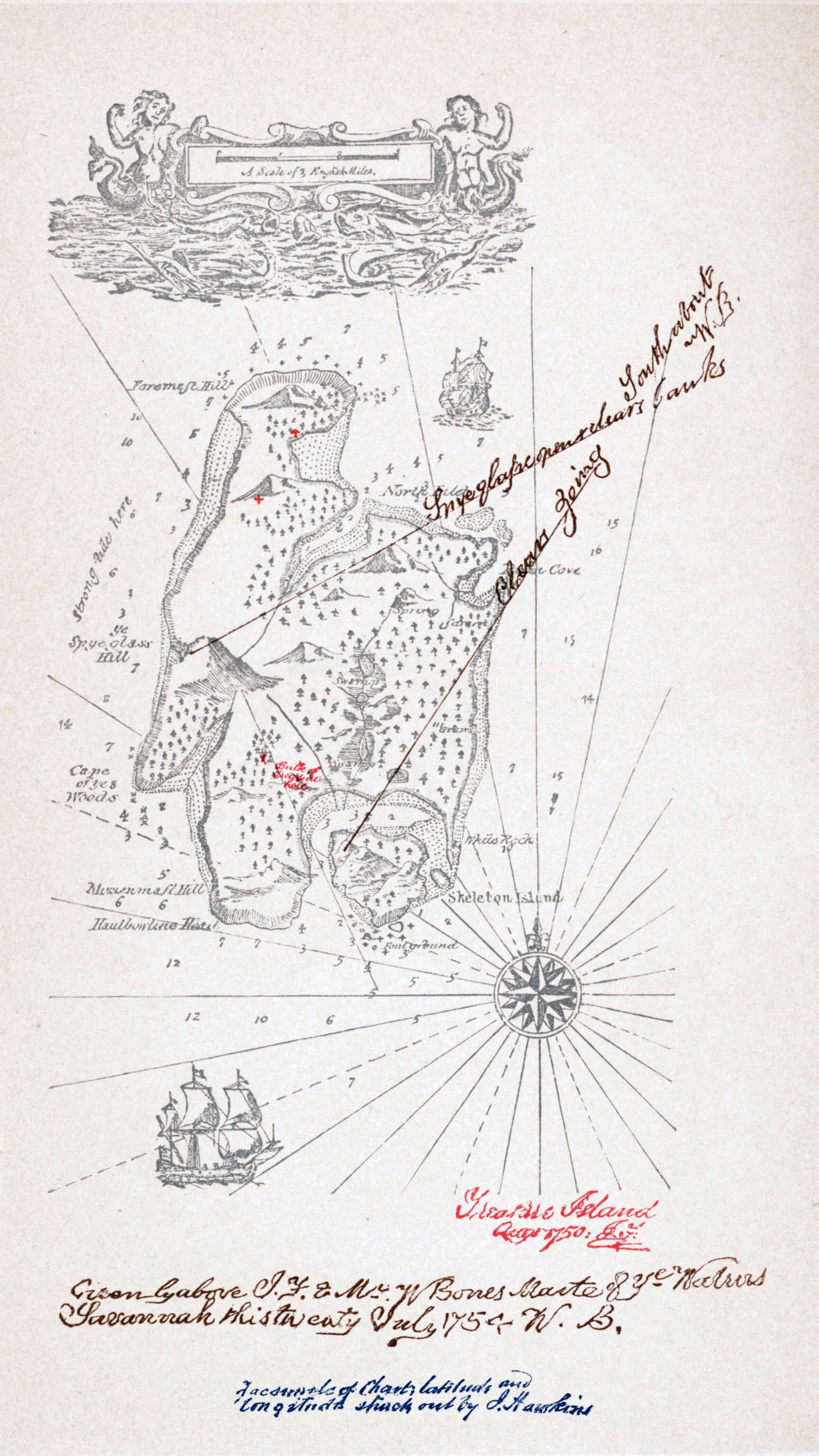
Treasure Island
''Treasure Island'' (originally titled ''The Sea Cook: A Story for Boys''Hammond, J. R. 1984. "Treasure Island." In ''A Robert Louis Stevenson Companion'', Palgrave Macmillan Literary Companions. London: Palgrave Macmillan. .) is an adventure novel by Scottish author Robert Louis Stevenson, telling a story of " buccaneers and buried gold". It is considered a coming-of-age story and is noted for its atmosphere, characters, and action. The novel was originally serialised from 1881 to 1882 in the children's magazine '' Young Folks'', under the title ''Treasure Island or the Mutiny of the Hispaniola'', credited to the pseudonym "Captain George North". It was first published as a book on 14 November 1883 by Cassell & Co. It has since become one of the most often dramatized and adapted of all novels, in numerous media. Since its publication, ''Treasure Island'' has had significant influence on depictions of pirates in popular culture, including elements such as deserted tropical i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khazar
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what for its duration was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the early medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (c. 650–965) the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus. Khazaria long served as a buffer state between the Byzantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Busento
The Busento ( la, Bucentius) is a left tributary of the Crati river, which flows about in Calabria, southern Italy, from the Apennines to the Ionian Sea. The Busento joins the Crati in the center of Cosenza. The legend of Alaric and his burial in Busento inspired the poem by August von Platen-Hallermünde ''Das Grab im Busento'' with a romantic representation of the King's death and burial. Legend The river's fame is due to a historic event in 410, when Alaric, first king of the Goths, died during a siege of the town. According to the legend, his body was buried under the river bed, the stream being temporarily diverted from its course by complex hydraulic engineering while the grave was dug and restored again to its original bed after the funeral. The work was performed by Roman slaves who were killed after the work by Alaric's soldiers so that the exact location of the burial site would remain secret forever. The king's grave and its fabulous treasure have never been found. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaric I
Alaric I (; got, 𐌰𐌻𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, , "ruler of all"; c. 370 – 410 AD) was the first king of the Visigoths, from 395 to 410. He rose to leadership of the Goths who came to occupy Moesia—territory acquired a couple of decades earlier by a combined force of Goths and Alans after the Battle of Adrianople. Alaric began his career under the Gothic soldier Gainas and later joined the Roman army. Once an ally of Rome under the Roman emperor Theodosius, Alaric helped defeat the Franks and other allies of a would-be Roman usurper. Despite losing many thousands of his men, he received little recognition from Rome and left the Roman army disappointed. After the death of Theodosius and the disintegration of the Roman armies in 395, he is described as king of the Visigoths. As the leader of the only effective field force remaining in the Balkans, he sought Roman legitimacy, never quite achieving a position acceptable to himself or to the Roman authorities. He operate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigoth
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is known as the Migration Period. The Visigoths emerged from earlier Gothic groups, including a large group of Thervingi, who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and the Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under their first leader, Alaric I, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sacked Rome in August 410. Afterwards, they began settling down, first in southern Gaul and eventually in Hispania, where they founded the Visigothic Kingdom and maintained a presence from the 5th to the 8th centuries AD. The Visigoths first settled in southern Gaul as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') and the other on the Goths (''Getica''). The latter, along with Isidore of Seville's '' Historia Gothorum'', is one of only two extant ancient works dealing with the early history of the Goths. Other writers, such as Procopius, wrote works on the later history of the Goths. ''Getica'' has been the object of much critical review. Jordanes wrote in Late Latin rather than the classical Ciceronian Latin. According to his own introduction, he had only three days to review what Cassiodorus had written and so he must also have relied on his own knowledge. Life Jordanes writes about himself almost in passing: Paria was Jordanes's paternal grandfather. Jordanes writes that he was secretary to Candac, , an otherwise unknown leader of the Alans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decebalus Treasure
The Decebalus Treasure is written by Cassius Dio concerning events said to have happened in the Roman world during the 2nd century AD. The story During the Second Dacian War many Dacian nobles surrendered or were caught. One of them, Bicilis, disclosed the location of the treasure, buried in a river's bed. "The treasures of Decebalus were also discovered, though hidden beneath the river Sargetia, which ran past his palace. With the help of some captives Decebalus had diverted the course of the river, made an excavation in its bed, and into the cavity had thrown a large amount of silver and gold and other objects of great value that could stand a certain amount of moisture; then he had heaped stones over them and piled on earth, afterwards bringing the river back into his course. He also had caused the same captives to deposit his robes and other articles of a like nature in caves, and after accomplishing this had made away with them to prevent them from disclosing anything. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sargetia
The Strei ( hu, Sztrigy) is a left tributary of the river Mureș in Transylvania, Romania. The upper reach of the river, upstream of the village of Baru, is also known as ''Râul Petros''. It flows through the town Călan and the villages Petros, Baru, Livadia, Pui, Galați, Băiești, Ohaba de sub Piatră, Ciopeia, Subcetate, Covragiu, Bretea Română, Bretea Streiului, Ruși, Strei, Streisângeorgiu, Batiz, Băcia and Simeria Veche. It discharges into the Mureș near Simeria. e-calauza.ro Its length is and its basin size is . Tributaries The following rivers are tributaries to the river Strei (from source to mouth): *Left: Sasu, Jigureasa, Jiguroșița,[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invasion in the reign of Domitian, securing a period of independence during which Decebalus consolidated his rule. When Trajan came to power, his armies invaded Dacia to weaken its threat to the Roman border territories of Moesia. Decebalus was defeated in 102 AD. He remained in power as a client king, but continued to assert his independence, leading to a final and overwhelming Roman invasion north of the Danube in 105 AD. Trajan reduced the Dacian capital Sarmizegetusa to ruins in 106 AD, absorbing some of Dacia into the Empire. Decebalus died by suicide to avoid capture. Early life After the death of Great King Burebista, Dacia split into four, then five smaller kingdoms. Nothing is known about Decebalus' youth or background. Decebalus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to the present-day countries of Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine. A Dacian Kingdom of variable size existed between 82 BC until the Roman conquest in AD 106, reaching its height under King Burebista. As a result of the two wars with Emperor Trajan, the population was dispersed and the central city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans, but was rebuilt by the latter to serve as the capital of the Roman province of Dacia. The Free Dacians, living the territory of modern-day Northern Romania disappeared with the start of the Migration Period. Nomenclature The Dacians are first mentioned in the writings of the Ancient Greeks, in Herodotus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the subsequent founding of Rome (753 BC), the formation of the Republic (509 BC), and the creation of the Empire (27 BC), up until 229 AD. Written in Ancient Greek over 22 years, Dio's work covers approximately 1,000 years of history. Many of his 80 books have survived intact, or as fragments, providing modern scholars with a detailed perspective on Roman history. Biography Lucius Cassius Dio was the son of Cassius Apronianus, a Roman senator and member of the gens Cassia, who was born and raised at Nicaea in Bithynia. Byzantine tradition maintains that Dio's mother was the daughter or sister of the Greek orator and philosopher, Dio Chrysostom; however, this relationship has been disputed. Although Dio was a Roman citizen, he wrote in Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


