|
Border Reivers
Border reivers were raiders along the Anglo-Scottish border from the late 13th century to the beginning of the 17th century. They included both Scottish and English people, and they raided the entire border country without regard to their victims' nationality. Their heyday was in the last hundred years of their existence, during the time of the House of Stuart in the Kingdom of Scotland and the House of Tudor in the Kingdom of England. Background Scotland and England were frequently at war during the late Middle Ages. During these wars, the livelihood of the people on the Borders was devastated by the contending armies. Even when the countries were not formally at war, tension remained high, and royal authority in either or both kingdoms was often weak, particularly in remote locations. The difficulty and uncertainties of basic human survival meant that communities and/or people kindred to each other would seek security through group strength and cunning. They would attem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reivers Raid On Gilnockie Tower
Border reivers were raiders along the Anglo-Scottish border from the late 13th century to the beginning of the 17th century. They included both Scottish and English people, and they raided the entire border country without regard to their victims' nationality. Their heyday was in the last hundred years of their existence, during the time of the House of Stuart in the Kingdom of Scotland and the House of Tudor in the Kingdom of England. Background Scotland and England were frequently at war during the late Middle Ages. During these wars, the livelihood of the people on the Borders was devastated by the contending armies. Even when the countries were not formally at war, tension remained high, and royal authority in either or both kingdoms was often weak, particularly in remote locations. The difficulty and uncertainties of basic human survival meant that communities and/or people kindred to each other would seek security through group strength and cunning. They would attempt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Language
Scots ( endonym: ''Scots''; gd, Albais, ) is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland (where the local dialect is known as Ulster Scots). Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, Northern Isles and northern Ulster, it is sometimes called Lowland Scots or Broad Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Goidelic Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides and Galloway after the 16th century. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged independently from the same source: Early Middle English (1150–1300). Scots is recognised as an indigenous language of Scotland, a regional or minority language of Europe, as well as a vulnerable language by UNESCO. In the 2011 Scottish Census, over 1.5 million people in Scotland reported being able to speak Scots. As there are no universally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublet (clothing)
A doublet (/ˈdʌblɪt/; derived from the Ital. ''giubbetta'') is a man's snug-fitting jacket that is shaped and fitted to the man's body. The garment was worn in Spain, and spread to the rest of Western Europe, from the late Middle Ages up to the mid-17th century. The doublet was hip length or waist length and worn over the shirt or drawers. Until the end of the 15th century, the doublet was usually worn under another layer of clothing such as a gown, mantle, overtunic or jerkin when in public. Originally it was a mere stitched and quilted lining ("doubling"), worn under a hauberk or cuirass to prevent bruising and chafing. Doublets were sometimes opened to the waistline in a deep V. The edges might be left free or laced across the shirt front. If there was space left it might be filled with a stomacher. By the 1520s, the edges of the doublet more frequently met at the center front. Then, like many other originally practical items in the history of men's wear, from the late 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
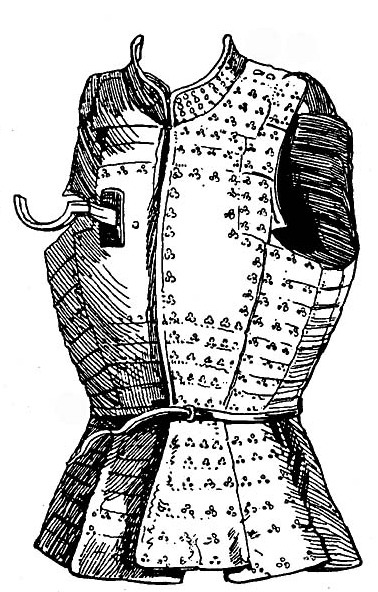
Jack Of Plate
A jack of plate is a type of armour made up of small iron plates sewn between layers of felt and canvas. They were commonly referred to simply as a "jack" (although this could also refer to any outer garment). This type of armour was used by common Medieval European soldiers as well as by the rebel peasants known as Jacquerie. The present day equivalent is perhaps a bullet-proof vest. The jack is similar to the brigandine. The main difference is in the method of construction: a brigandine is riveted whereas a jack is sewn. Jacks of plate were created by stitching as many as 1000 small overlapping squares of iron between two canvases. The garments weighed about , which made them much more acceptable to the wearer than solid breastplates. They also offered a tactical advantage: they allowed soldiers to rest the butts of weapons firmly against their shoulders, which wasn't feasible with smooth-surfaced plate armours. Unlike plate they made no attempt to be bulletproof. Jacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigandine
A brigandine is a form of body armour from the Middle Ages. It is a garment typically made of heavy cloth, canvas, or leather, lined internally with small oblong steel plates riveted to the fabric, sometimes with a second layer of fabric on the inside. Origins Protective clothing and armour have been used by armies from earliest recorded history; the King James Version of the Bible (Jeremiah 46:4) translates the Hebrew סריון ''ÇiRYON'' or שריון ''SiRYoN'' "coat of mail" as "brigandine". Medieval brigandines were essentially a refinement of the earlier coat of plates, which developed in the late 12th century, typically of simpler construction with larger metal plates. This armour of Asian origin reached Europe after the Mongol invasion in 1240 that destroyed the Kievan Rus' and severely damaged the Kingdom of Hungary in 1241. The new armour became very popular first in Eastern Europe, especially in Hungary, towards the end of the 13th century and was adopted in west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumbrian Tartan
Border tartan, sometimes known as Borders tartan, Northumbrian tartan, Northumberland tartan, shepherds' plaid, Border drab, or Border check, is a design used in woven fabrics historically associated with the Anglo-Scottish Border, particularly with the Scottish Borders and Northumberland. Possibly the most identifiable Border tartan garment of the region is the Maud (plaid), maud, made popular from the 1820s by fashionable Border Scots such as Walter Scott, Sir Walter Scott, James Hogg, Henry Scott Riddell and Robbie Burns, Robert Burns. The modern Border tartan is a crossweave of small dark and light checks, much plainer than the better-known Tartan, Scottish tartans. Traditionally, the yarn for the light squares was simply untreated sheep's wool and the darker yarn was the same wool dyed with simple vegetable dyes, such as alder bark or water flag, or the untreated wool of a black sheep. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hobelar
Hobelars were a type of light cavalry, or mounted infantry, used in Western Europe during the Middle Ages for skirmishing. They originated in 13th century Ireland, and generally rode hobbies, a type of light and agile horse. Origins According to James Lydon, "There can be little doubt that the hobelar as a type of soldier originated in Ireland ... between the fully armoured knight on the 'equus coopertus' and the lightly armoured archer on the 'equus discoopertus' there was an intermediate stage. This intermediary ... was provided by the hobelar." He further states that hobelars were highly mobile, and excelled in scouting, reconnaissance and patrols ... eminently suited to the terrain in which military operations had to be conducted in Ireland. However superior the Norman knight might be upon the field of battle, the bogs and woods of Ireland gave little opportunity for the mail-clad charge. Thus there evolved in Ireland, as a habitual part of every Anglo-Norman force, a type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galloway Pony
The Galloway pony is an extinct horse breed, once native to Scotland and northern England. It was said to have "good looks, a wide, deep chest and a tendency to pace rather than trot." In the 18th century Galloways were bred in Swaledale, to haul lead ore. The breed was mentioned by Shakespeare as "Galloway nags" in Henry IV, Part 2. "Thrust him down stairs! know we not Galloway nags?" Pistol - Henry IV, Part 2 by William Shakespeare A survey in 1814 stated: The province of Galloway formerly possessed a breed of horses peculiar to itself, which were in high estimation for the saddle, being, though of a small size, exceedingly hardy and active. They were larger than the ponies of Wales, and the north of Scotland, and rose from twelve to fourteen hands in height. The soils of Galloway, in their unimproved state, are evidently adapted for rearing such a breed of horses; and in the moors and mountainous part of the country, a few of the native breed are still to be found. � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have been undertaken over time by its subdivisions, which have also been subject to History of local government in Yorkshire, periodic reform. Throughout these changes, Yorkshire has continued to be recognised as a geographic territory and cultural region. The name is familiar and well understood across the United Kingdom and is in common use in the media and the Yorkshire Regiment, military, and also features in the titles of current areas of civil administration such as North Yorkshire, South Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and the East Riding of Yorkshire. Within the borders of the historic county of Yorkshire are large stretches of countryside, including the Yorkshire Dales, North York Moors and Peak District nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county in 1974 History Before the county During Roman times the area was part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |