|
Bay Of Whales
The Bay of Whales was a natural ice harbour, or iceport, indenting the front of the Ross Ice Shelf just north of Roosevelt Island, Antarctica. It is the southernmost point of open ocean not only of the Ross Sea, but worldwide. The Ross Sea extends much further south – as far as the Gould Coast, some from the South Pole – but most of that area is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf rather than open sea. Discovery and naming Ernest Shackleton named the feature on January 24, 1908, during the Nimrod Expedition, because of the large number of whales seen near this location. History During his quest for the South Pole, Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen established a temporary base, which he named Framheim, at the Bay of Whales. The base was used between January 1911February 1912, and was named after Amundsen's ship '' Fram''. The Bay of Whales has also served as a logistical support base for several other important Antarctic expeditions, including: * 1928–1930: Richard E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
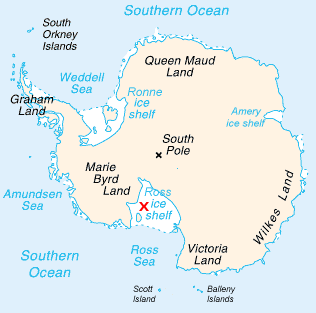
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Janu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Framheim
Framheim was the name of explorer Roald Amundsen's base at the Bay of Whales on the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica during his successful quest for the South Pole. It was used between January 1911 and February 1912. Cabin and tents The hut was constructed in sections by a master carpenter, Jørgen Stubberud and erected at Amundsen's home in Norway, then dismantled for shipment to Antarctica on the '' Fram''. Framheim literally means "home of the Fram". During its construction in Norway, Amundsen maintained that the hut was for "observation", which would fit in nicely with his supposed intent to head to the North Pole. To the more than casual student of exploration, it was obvious that the hut was intended as living quarters. Amundsen was headed to the South Pole. The cabin was an early example of a pre-fabricated structure, and employed a custom dining table which could retract to the ceiling for cleaning beneath. It measured eight by four meters, and the walls were made up of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Pier
An ice pier or ice wharf is a man-made structure used to assist the unloading of ships in Antarctica. It is constructed by pumping seawater into a contained area and allowing the water to freeze. By repeating this procedure several times, additional layers are built up. The final structure is many metres in thickness, and strong enough to support container trucks. Operation Deep Freeze personnel constructed the first floating ice pier at Antarctica’s southernmost sea port at McMurdo Station in 1973."Unique ice pier provides harbor for ships," Antarctic Sun. January 8, 2006; McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Ice piers have been in use each season since, at McMurdo's natural [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island is known as an ''insular shelf''. The continental margin, between the continental shelf and the abyssal plain, comprises a steep continental slope, surrounded by the flatter continental rise, in which sediment from the continent above cascades down the slope and accumulates as a pile of sediment at the base of the slope. Extending as far as 500 km (310 mi) from the slope, it consists of thick sediments deposited by turbidity currents from the shelf and slope. The continental rise's gradient is intermediate between the gradients of the slope and the shelf. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the name continental shelf was given a legal definition as the stretch of the seabed adjacent to the shores of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Dependency
The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a circular sector, sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160th meridian east, 160° east to 150th meridian west, 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60th parallel south, 60° south. It is claimed by New Zealand, a claim accepted only by the other six countries with territorial claims in Antarctica. Under the 1961 Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, of which all territorial claimants are signatories, including New Zealand, all claims are held in abeyance. Article IV states: "No acts or activities taking place while the present Treaty is in force shall constitute a basis for asserting, supporting or denying a claim to territorial sovereignty in Antarctica or create any rights of sovereignty in Antarctica". The Dependency takes its name from James Clark Ross, Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered the Ross Sea, and includes part of Victoria Land, and most of the Ross Ice Shelf. Ross Island, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceberg B-9
Iceberg B-9 was an iceberg that calved from Antarctica in 1987. It measured long and wide; it had a total area of , and is one of the longest icebergs ever recorded. This calving took place immediately east of the future calving site of Iceberg B-15; it carried away Little America V which had been closed in December 1959. Starting in October 1987, Iceberg B-9 drifted for 22 months, covering on its journey. Initially, B-9 moved northwest for seven months, before being drawn southward by a subsurface current that eventually led to its colliding with the Ross Ice Shelf in August 1988. It then made a radius gyre before resuming its northwest drift. It moved at an average speed of per day over the continental shelf, as measured by NOAA-10 and DMSP satellite positions, and by the ARGOS data buoy positions. In early August 1989, B-9 broke into three large pieces north of Cape Adare. These pieces were designated as B-9A, , B-9B, , and B-9C, . B-9A drifted east and was located about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Shelf
An ice shelf is a large floating platform of ice that forms where a glacier or ice sheet flows down to a coastline and onto the ocean surface. Ice shelves are only found in Antarctica, Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic. The boundary between the floating ice shelf and the anchor ice (resting on bedrock) that feeds it is the grounding line. The thickness of ice shelves can range from about to . In contrast, sea ice is formed on water, is much thinner (typically less than ), and forms throughout the Arctic Ocean. It is also found in the Southern Ocean around the continent of Antarctica. The movement of ice shelves is principally driven by gravity-induced pressure from the grounded ice. That flow continually moves ice from the grounding line to the seaward front of the shelf. In steady state, about half of Antarctica's ice shelf mass is lost to basal melt and half is lost to calving, but the relative importance of each process varies significantly between ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Calving
Ice calving, also known as glacier calving or iceberg calving, is the breaking of ice chunks from the edge of a glacier.Essentials of Geology, 3rd edition, Stephen Marshak It is a form of ice ablation or ice disruption. It is the sudden release and breaking away of a mass of ice from a glacier, iceberg, ice front, ice shelf, or crevasse. The ice that breaks away can be classified as an iceberg, but may also be a growler, bergy bit, or a crevasse wall breakaway.Glossary of Glacier Terms Ellin Beltz, 2006. Retrieved July 2009. Calving of glaciers is often accompanied by a loud cracking or booming sound before blocks of ice up to high break loose and crash into the water. The entry of the ice into the water causes large, and often hazardous waves. The waves formed in locations like |
USCGC Southwind (WAGB-280)
USCGC ''Southwind'' (WAGB-280) was a that served in the United States Coast Guard as USCGC ''Southwind'' (WAG-280), the Soviet Navy as the ''Admiral Makarov'', the United States Navy as USS ''Atka'' (AGB-3) and again in the U.S. Coast Guard as USCGC ''Southwind'' (WAGB-280). Construction ''Southwind'' was the third of the of icebreakers operated by the United States Coast Guard. Her keel was laid on 20 July 1942 at the Western Pipe and Steel Company shipyards in San Pedro, California, she was christened by Mrs. Ona Jones and launched on 8 March 1943, and commissioned on 15 July 1944. Her hull was of unprecedented strength and structural integrity, with a relatively short length in proportion to the great power developed, a cut away forefoot, rounded bottom, and fore, aft and side heeling tanks. Diesel electric machinery was chosen for its controllability and resistance to damage. ''Southwind'', along with the other Wind-class icebreakers, was heavily armed for an icebrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Service Expedition
The United States Antarctic Service Expedition (1939–1941), often referred to as Byrd’s Third Antarctic Expedition, was an expedition jointly sponsored by the United States Navy, State Department, Department of the Interior and The Treasury. Although a U.S.-government sponsored expedition, additional support came from donations and gifts by private citizens, corporations and institutions. Description of expedition Background, orders and goals Rear Admiral Richard Evelyn Byrd donated many of the supplies that he had gathered for his own expedition, the largest item being the ''Bear of Oakland'', commissioned as the USS ''Bear'' (AG-29) on 11 September 1939. A second ship, the USMS ''North Star'', a 1434-ton wooden ice ship built for the Bureau of Indian Affairs, was supplied by the Department of the Interior. A total of 125 men departed from the United States in the two ships of the United States Antarctic Service Expedition. Most of the men who made up the expedition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard E
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", "Rick", " Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |