|
Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 81
Site 81 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome is a launch site used, along with Site 200, by Proton rockets. It consists of two launch pads, areas 23 and 24. Area 24 is used for Proton-K and Proton-M launches, while Area 23 is inactive. Several planetary probes have been launched from Site 81. Area 23 was used to launch Mars 3, Mars 4, Mars 6 and Venera 11, whilst Area 24 was used by Mars 2, Mars 5, Mars 7, Venera 9, Venera 10 and Venera 12. Several Luna probes were also launched from both areas. The Zarya and Zvezda modules of the International Space Station, as well as Salyut 2, 3 and 5, and the Spektr and Priroda modules of Mir, were launched from Area 23. Area 24 was used to launch Salyut 1, 4 and 6. On 2 July 2013, a Proton-M/ DM-03 launched from Site 81/24 carrying three GLONASS GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
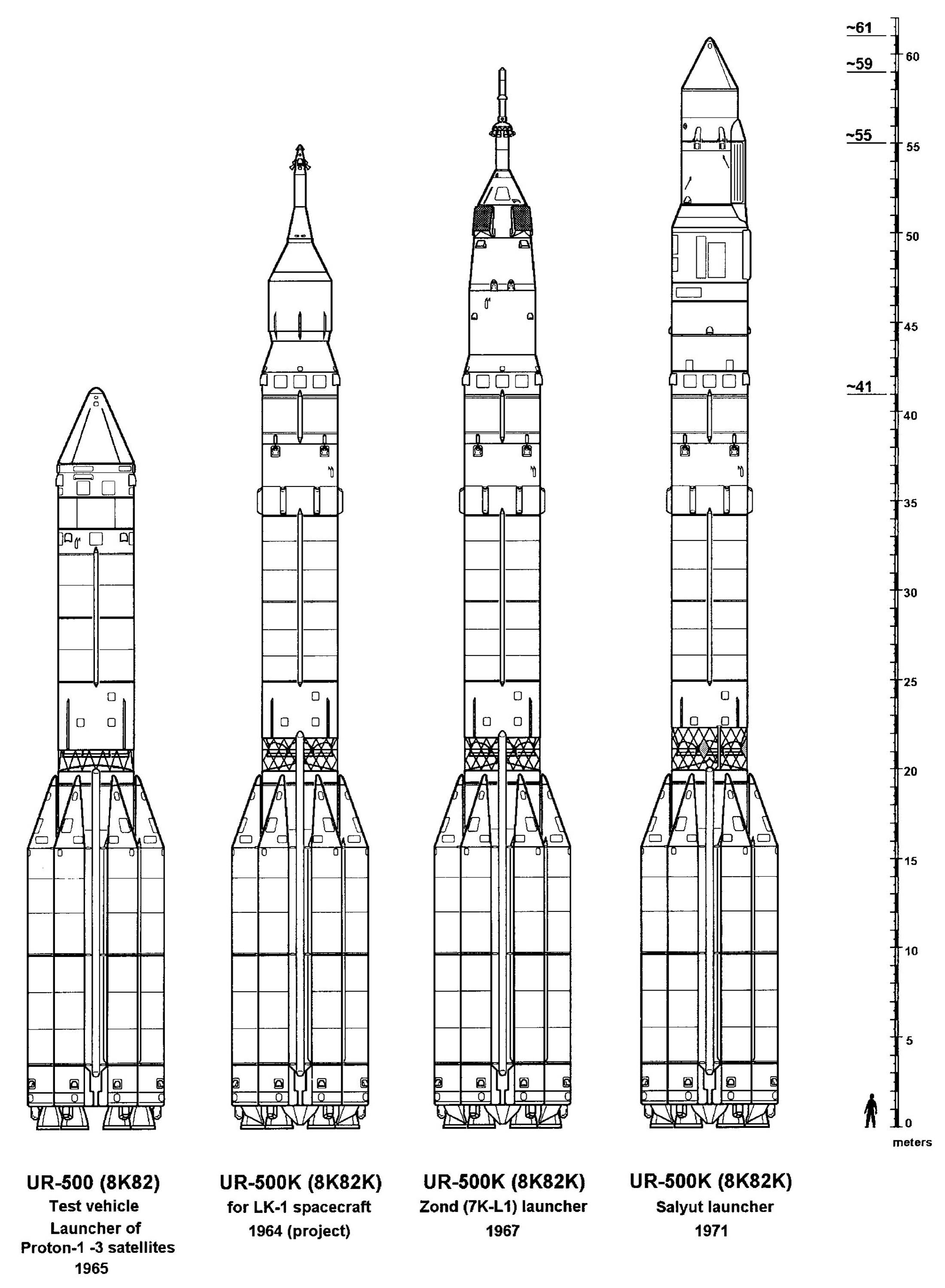
Proton-K
The Proton-K, also designated Proton 8K82K after its GRAU index or SL-12 after its model number, 8K82K, was a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 and 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The maiden flight on 10 March 1967 carried a Soyuz 7K-L1 as part of the Zond program. During the so-called Moon Race these Proton/Soyuz/Zond flights consisted of several uncrewed test flights of Soyuz spacecraft to highly elliptical or circumlunar orbits with the unrealized aim of landing Soviet cosmonauts on the Moon. It was retired from service in favour of the modernised Proton-M, making its 310th and final launch on 30 March 2012. Vehicle description The baseline Proton-K was a three-stage rocket. Thirty were launched in this configuration, with payloads including all of the Soviet Union's ''Salyut'' space stations, all Mir modules with the exception of the Docking Module, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars 3
Mars 3 was a robotic space probe of the Soviet Mars program, launched May 28, 1971, nine days after its twin spacecraft Mars 2. The probes were identical robotic spacecraft launched by Proton-K rockets with a Blok D upper stage, each consisting of an orbiter and an attached lander. After the Mars 2 lander crashed on the Martian surface, the Mars 3 lander became the first spacecraft to attain a soft landing on Mars, on December 2, 1971. It failed 110 seconds after landing, having transmitted only a gray image with no details. The Mars 2 orbiter and Mars 3 orbiter continued to circle Mars and transmit images back to Earth for another eight months. Overview * Launch Date/Time: ** Mars 3: May 28, 1971 at 15:26:30 UTC * Launch mass (including fuel): ** Combined: ** Orbiter: ** Lander: * On-orbit dry mass: * Dimensions: tall, across ( across with solar panels deployed) Orbiter The primary purpose of the 4M-V orbiter was to study the topography of the Martian surface; analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut 3
Salyut 3 (russian: Салют-3; en, Salute 3; also known as OPS-2 or Almaz 2Portree (1995).) was a Soviet space station launched on 25 June 1974. It was the second Almaz military space station, and the first such station to be launched successfully. It was included in the Salyut program to disguise its true military nature.Hall and Shayer (2003). Due to the military nature of the station, the Soviet Union was reluctant to release information about its design, and about the missions relating to the station.Zimmerman (2003). It attained an altitude of 219 to 270 km on launchBond (2002). and NASA reported its final orbital altitude was 268 to 272 km. Only one of the three intended crews successfully boarded and manned the station, brought by Soyuz 14; Soyuz 15 attempted to bring a second crew but failed to dock. Although little official information has been released about the station, several sources report that it contained multiple Earth-observation cameras, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut 2
Salyut 2 (OPS-1) (russian: Салют-2 meaning ''Salute 2'') was a Soviet space station which was launched in 1973 as part of the Salyut programme. It was the first Almaz military space station to fly. Within two weeks of its launch, the station had lost attitude control and depressurized, leaving it unusable. Its orbit decayed and it re-entered the atmosphere on 28 May 1973, without any crews having visited it. Spacecraft Salyut 2 was an Almaz military space station. It was designated part of the Salyut programme in order to conceal the existence of the two separate space station programmes. Salyut 2 was long with a diameter of , and had an internal habitable volume of . At launch it had a mass of . A single aft-mounted docking port was intended for use by Soyuz spacecraft carrying cosmonauts to work aboard the station. Two solar arrays mounted at the aft end of the station near the docking port provided power to the station, generating a total of 3,120 watts of elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarya (ISS Module)
''Zarya'' (russian: Заря, , Dawn), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the russian: "Функционально-грузовой блок", , ''Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok'' or ''ФГБ''), is the first module of the International Space Station to have been launched.NASA, International Space StationZarya(accessed 19 Apr. 2014) The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, it is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The ''Zarya'' is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian ''Salyut'' program. The name ''Zarya'' ("Dawn") was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States. Construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna Programme
The Luna programme (from the Russian word "Luna" meaning "Moon"), occasionally called ''Lunik'' by western media, was a series of robotic spacecraft missions sent to the Moon by the Soviet Union between 1959 and 1976. Fifteen were successful, each designed as either an orbiter or lander, and accomplished many firsts in space exploration. They also performed many experiments, studying the Moon's chemical composition, gravity, temperature, and radiation. Twenty-four spacecraft were formally given the Luna designation, although more were launched. Those that failed to reach orbit were not publicly acknowledged at the time, and not assigned a Luna number. Those that failed in low Earth orbit were usually given Cosmos designations. The estimated cost of the Luna programme in 1964 was US$6–10 billion. Mission types The name ''Luna'' was used to designate a variety of spacecraft designs, to achieve several types of missions: Impactors Impactor spacecraft are designed to hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 12
The Venera 12 (russian: Венера-12 meaning Venus 12) was an uncrewed Soviet space mission designed to explore the planet Venus. Venera 12 was launched on 14 September 1978 at 02:25:13 UTC. After separating from its flight platform on 19 December 1978, the Venera 12 lander entered the Venus atmosphere two days later at 11.2 km/s. During its descent, the lander employed aerodynamic braking followed by parachute braking, ending with atmospheric braking. After a nearly one-hour descent, a soft landing was made at 06:30 Moscow time (0330 UT) on 21 December. Touchdown speed was 7–8 m/s; landing coordinates are . Continuing for about 110 minutes after touchdown, the lander transmitted data to the flight platform for about 110 minutes until the flight platform, which remained in a heliocentric orbit, moved out of range. Venera 11 and 12 carried identical instruments. Flight platform The Venera 12 flight platform carried solar wind detectors, ionosphere electron instru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 10
Venera 10 (russian: Венера-10 meaning ''Venus 10''), or 4V-1 No. 661, was a Soviet uncrewed space mission to Venus. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. It was launched on June 14, 1975, 03:00:31 UTC and had a mass of 5033 kg (11096 lb). Orbiter When the mission launched, the Soviet Union only disclosed that the mission's objective was to explore Venus and the surrounding space. Western sources speculated that the spacecraft contained a lander. The orbiter entered Venus orbit on October 23, 1975. Its mission was to serve as a communications relay for the lander and to explore cloud layers and atmospheric parameters with several instruments and experiments: * 1.6–2.8 μm IR Spectrometer * 8–28 μm IR Radiometer * 352 nm UV Photometer * 2 Photopolarimeters (335–800 nm) * 300–800 nm Spectrometer * Lyman-α H/D Spectrometer * Bistatic radar mapping * CM, DM radio occultations * Triaxial Magnetometer * 345–380 nm UV Camera * 355� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 9
Venera 9 (russian: Венера-9, lit=Venus-9), manufacturer's designation: 4V-1 No. 660, was a Soviet uncrewed space mission to Venus. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. It was launched on June 8, 1975, at 02:38:00 UTC and had a mass of . The orbiter was the first spacecraft to orbit Venus, while the lander was the first to return images from the surface of another planet. Orbiter The orbiter entered Venus orbit on October 20, 1975. Its mission was to act as a communications relay for the lander and to explore cloud layers and atmospheric parameters with several instruments and experiments. It performed 17 survey missions from October 26, 1975, to December 25, 1975. The orbiter consisted of a cylinder with two solar panel wings and a high gain parabolic antenna attached to the curved surface. A bell-shaped unit holding propulsion systems was attached to the bottom of the cylinder, and mounted on top was a sphere which held the lander. Orbiter design The instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars 7
Mars 7 (), also known as 3MP No.51P was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1973 to explore Mars. A 3MP bus spacecraft which comprised the final mission of the Mars programme, it consisted of a lander and a coast stage with instruments to study Mars as it flew past. Due to a malfunction, the lander failed to perform a maneuver necessary to enter the Martian atmosphere, missing the planet and remaining in heliocentric orbit along with the coast stage. Spacecraft Mars 7 spacecraft carried an array of instruments to study Mars. The lander was equipped with a thermometer and barometer to determine the surface conditions, an accelerometer and radio altimeter for descent, and instruments to analyse the surface material including a mass spectrometer. The coast stage, or bus, carried a magnetometer, plasma traps, cosmic ray and micrometeoroid detectors, stereo antennae, and an instrument to study proton and electron fluxes from the Sun. Built by Lavochkin, Mars 7 was the second of two 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars 5
Mars 5 (), also known as 3MS No.53S was a Soviet spacecraft launched to explore Mars. A 3MS spacecraft launched as part of the Mars programme, it successfully entered orbit around Mars in 1974. However, it failed a few weeks later. Spacecraft The Mars 5 spacecraft carried an array of instruments to study Mars. In addition to cameras, it was equipped with a radio telescope, an IR radiometer, multiple photometers, polarimeters, a magnetometer, plasma traps, an electrostatic analyser, a gamma-ray spectrometer, and a radio probe. The Three cameras were a 52mm Vega, a 350mm Zulfar and a panoramic camera. Built by Lavochkin, Mars 5 was the second of two 3MS spacecraft launched to Mars in 1973, following Mars 4. A 3MS was also launched during the 1971 launch window as Kosmos 419. However, due to a launch failure, it failed to depart Earth orbit. In addition to the orbiters, two 3MP lander missions, Mars 6 and Mars 7, were launched during the 1973 window. Launch Mars 5 was launche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars 2
The Mars 2 was an uncrewed space probe of the Mars program, a series of uncrewed Mars landers and orbiters launched by the Soviet Union beginning 19 May 1971. The Mars 2 and Mars 3 missions consisted of identical spacecraft, each with an orbiter and an attached lander. The orbiter is identical to the Venera 9 bus. The type of bus/orbiter is the 4MV. They were launched by a Proton-K heavy launch vehicle with a Blok D upper stage. The lander of Mars 2 became the first human-made object to reach the surface of Mars, although the landing system failed and the lander was lost. Overview * Launch Date/Time: ** Mars 2: 19 May 1971 at 16:22:44 UTC * Launch mass (including fuel): ** Combined: ** Orbiter: ** Lander: * On-orbit dry mass: * Dimensions: tall, across ( across with solar panels deployed) Launch On 19 May 1971, the Proton-K heavy launch vehicle launched the probe from Baikonur Cosmodrome. After the first stage separated the second stage was ignited. The third stage en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


