|
BRCK
The Bulgarian Revolutionary Central Committee ( bg, Български революционен централен комитет, ''Balgarski revolyutsionen tsentralen komitet'') or BRCC was a Bulgarian revolutionary organisation founded in 1869 among the Bulgarian emigrant circles in Romania. The decisive influence for the establishment of the committee was exerted by the ''Svoboda'' ("Freedom") newspaper which Lyuben Karavelov began to publish in the autumn of 1869. Some of the other revolutionaries who took active part in the formation and work of the BRCK were Panayot Hitov, Vasil Levski and Dimitar Tsenovich. Karavelov was elected chairman of the BRCK in the spring of 1870. He also prepared the first programme of the organisation (promulgated in Geneva on 1 August 1870), which envisaged the liberation of Bulgaria through a nationwide revolution and the establishment of a democratic republic. By the end of 1871, both Karavelov and Vasil Levski, the leader of the other Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
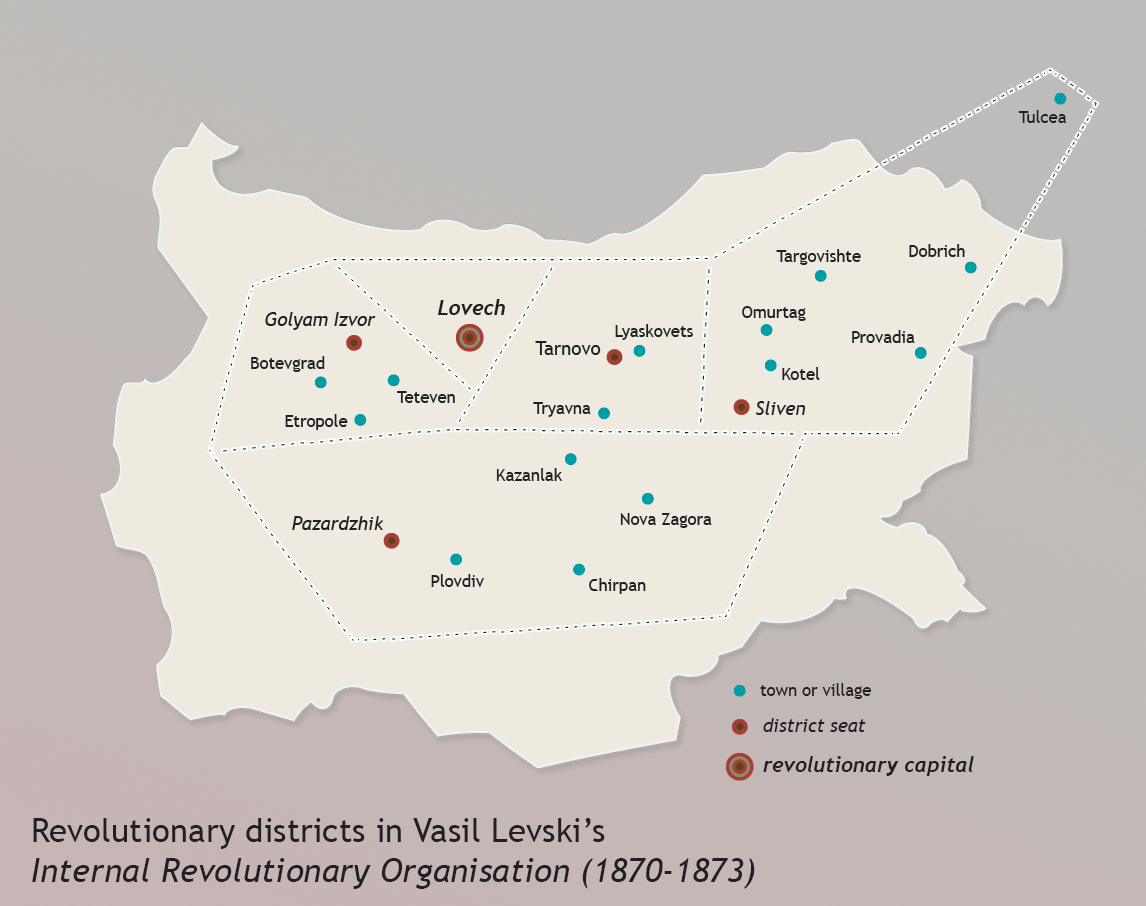
Internal Revolutionary Organisation
The Internal Revolutionary Organisation ( bg, Вътрешна революционна организация) or IRO was a Bulgarian revolutionary organisation founded and built up by Bulgarian revolutionary Vasil Levski in the period between 1869 and 1871. The organisation represented a network of regional revolutionary committees which were governed by a Central Committee in the town of Lovech. The foundation of IRO reflected Levski's ideas that the centre of revolutionary activity be transferred from the Bulgarian emigrant circles in Romania to Bulgaria proper. In 1871, Levski prepared the Charter of the organisation in the spirit of his own political views: liberation of Bulgaria from the Ottomans through a nationwide revolution and establishment of the country as a democratic republic with guarantees for the equality of all of its citizens regardless of their ethnicity or religion. By the end of 1872, both Levski and Lyuben Karavelov, the chairman of the Bulgarian Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute Brtsk Cover
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, and regulations issued by government agencies. Publication and organization In virtually all countries, newly enacted statutes are published and distributed so that everyone can look up the statutory law. This can be done in the form of a government gazette which may include other kinds of legal notices released by the government, or in the form of a series of books whose content is limited to legislative acts. In either form, statutes are traditionally published in chronological order based on date of enactment. A universal problem encountered by lawmakers throughout human history is how to organize published statutes. Such publications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1869 Establishments In Romania
Events January–March * January 3 – Abdur Rahman Khan is defeated at Tinah Khan, and exiled from Afghanistan. * January 5 – Scotland's oldest professional football team, Kilmarnock F.C., is founded. * January 20 – Elizabeth Cady Stanton is the first woman to testify before the United States Congress. * January 21 – The P.E.O. Sisterhood, a philanthropic educational organization for women, is founded at Iowa Wesleyan College in Mount Pleasant, Iowa. * January 27 – The Republic of Ezo is proclaimed on the northern Japanese island of Ezo (which will be renamed Hokkaidō on September 20) by remaining adherents to the Tokugawa shogunate. * February 5 – Prospectors in Moliagul, Victoria, Australia, discover the largest alluvial gold nugget ever found, known as the "Welcome Stranger". * February 20 – Ranavalona II, the Merina Queen of Madagascar, is baptized. * February 25 – The Iron and Steel Institute is formed in L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizations Established In 1869
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. The word is derived from the Greek word ''organon'', which means tool or instrument, musical instrument, and organ. Types There are a variety of legal types of organizations, including corporations, governments, non-governmental organizations, political organizations, international organizations, armed forces, charities, not-for-profit corporations, partnerships, cooperatives, and educational institutions, etc. A hybrid organization is a body that operates in both the public sector and the private sector simultaneously, fulfilling public duties and developing commercial market activities. A voluntary association is an organization consisting of volunteers. Such organizations may be able to operate without legal formalities, depending on jurisdiction, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Revolutionary Organisations
Bulgarian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria * Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group * Bulgarian language, a Slavic language * Bulgarian alphabet * A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria * Bulgarian culture * Bulgarian cuisine, a representative of the cuisine of Southeastern Europe See also * * List of Bulgarians, include * Bulgarian name, names of Bulgarians * Bulgarian umbrella, an umbrella with a hidden pneumatic mechanism * Bulgar (other) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (other) The term Bulgarian-Serbian War or Serbian-Bulgarian War may refer to: * Bulgarian-Serbian War (839-842) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (853) * Bulgarian-Serbian wars (917-924) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (1330) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (1885) * Bulgarian-Serbi ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonian Secret Revolutionary Committee
The Macedonian Secret Revolutionary Committee (MSRC) ( bg, Македонски Таен Революционен Комитет (МТРК) Macedonian: Македонски Таен Револуционерен Комитет(МТРК)) was founded in in Plovdiv. It was developed later in Geneva in a secret, anarchistic, brotherhood called "Geneva group". The Bulgarian anarchist movement grew in the 1890s, and the territory of Principality of Bulgaria became a staging-point for anarchist activities against the Ottomans. Its activists were the students Michail Gerdjikov, Petar Mandjukov, Petar Sokolov, Slavi Merdjanov, Dimitar Ganchev, Konstantin Antonov and others. In 1893 they started in Plovdiv revolutionary activity as founders of the MSRC, which was proclaimed there in 1895. At the end of 1897 part of the group moved to Switzerland (Lozana and Geneva), where it made close connections with the revolutionary immigration and founded in 1898 the so-called ''Geneva group' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
April Uprising
The April Uprising ( bg, Априлско въстание, Aprilsko vastanie) was an insurrection organised by the Bulgarians in the Ottoman Empire from April to May 1876. The regular Ottoman Army and irregular bashi-bazouk units brutally suppressed the rebels, resulting in a public outcry in Europe, with many famous intellectuals condemning the atrocities—labelled the Bulgarian Horrors or Bulgarian atrocities—by the Ottomans and supporting the oppressed Bulgarian population. This outrage was key for the re-establishment of Bulgaria in 1878. The 1876 uprising involved only those parts of the Ottoman territories populated predominantly by Bulgarians. The emergence of Bulgarian national sentiments was closely related to the re-establishment of the independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church in 1870. Background In Europe, in the 18th century, the classic non-national states were the ''multi-ethnic empires'' such as the Ottoman Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire, whose pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giurgiu
Giurgiu (; bg, Гюргево) is a city in southern Romania. The seat of Giurgiu County, it lies in the historical region of Muntenia. It is situated amongst mud-flats and marshes on the left bank of the Danube facing the Bulgarian city of Ruse on the opposite bank. Three small islands face the city, and a larger one shelters its port, Smarda. The rich grain-growing land to the north is traversed by a railway to Bucharest, the first line opened in Romania, which was built in 1869 and afterwards extended to Smarda. Giurgiu exports timber, grain, salt and petroleum, and imports coal, iron, and textiles. The Giurgiu-Ruse Friendship Bridge, in the shared Bulgarian-Romanian section of the Danube, crosses the river in the outskirts of the city. History The area around Giurgiu was densely populated at the time of the Dacians (1st century BC) as archeological evidence shows, and Burebista's capital was in this area (it is thought to be in Popeşti on the Argeş River). Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stara Zagora
Stara Zagora ( bg, Стара Загора, ) is the sixth-largest city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of the homonymous Stara Zagora Province. Name The name comes from the Slavic root ''star'' ("old") and the name of the medieval region of Zagore ("beyond the alkanmountains" in Slavic) The original name was Beroe, which was changed to Ulpia Augusta Traiana by the Romans. From the 6th century the city was called Vereja and, from 784, Irenopolis ( Greek: Ειρηνούπολις) in honour of the Byzantine empress Irene of Athens. In the Middle Ages it was called Boruj by the Bulgarians and later, Železnik. The Turks called it Eski Hisar (old fort) and Eski Zagra, from which its current name derives, assigned in 1871. History The original Thracian settlement dates from the 5-4th century BC when it was called Beroe or Beroia. The city was founded by Philip II of Macedon in 342 BC. Under the Roman Empire, the city was renamed ''Ulpia Augusta Traiana'' in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hristo Botev
Hristo Botev ( bg, Христо Ботев, ), born Hristo Botyov Petkov (Христо Ботьов Петков; – ), was a Bulgarian revolutionary and poet. Botev is considered by Bulgarians to be a symbolic historical figure and national hero. His poetry is a prime example of the literature of the Bulgarian National Revival, though he is considered to be ahead of his contemporaries in his political, philosophical, and aesthetic views. Biography Early years Botev was born in Kalofer (some historians suggested that he was born in Karlovo and after several days was brought to Kalofer). His father, Botyo Petkov (1815–1869), was a teacher and one of the most significant figures of the late period of the Bulgarian National Revival towards the end of the Ottoman occupation. He had a strong influence on his son during the latter's youth. In 1863, after completing his elementary education in Kalofer, Botev was sent by his father to a high school in Odessa.Trencsényi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimitar Obshti
Dimitar Obshti ( bg, Димитър Общи) was a 19th-century Bulgarian revolutionary, who fought for the liberation of Bulgaria, Serbia and Crete from the Ottoman Empire, as well as for the ''Risorgimento'' of Italy. Biography Obshti was born around 1835 in Gjakova, Sanjak of Peć, Ottoman Empire. He joined the first Bulgarian Legion organised in exile, in Serbia's capital Belgrade, in 1862. There he received military training and met Vasil Levski who became his lifetime comrade in arms. They fought together against the invading Ottomans in Serbia. In April 1868 the Serbian authorities disbanded the Bulgarian legion and expelled its participants from the country. Obshti subsequently joined the forces of the Italian revolutionary Giuseppe Garibaldi and later took part in the 1866–1869 Cretan uprising. In 1869 he became one of the founders of the Bulgarian Revolutionary Central Committee (BRCC) in Bucharest, Romania. In June 1871 Obshti was sent to Ottoman Bulgaria to se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |